fix: a star in docs
This commit is contained in:
4
.gitignore
vendored
4
.gitignore
vendored
@@ -1,2 +1,4 @@
|
||||
multiagent1/
|
||||
__pycache__/
|
||||
logic1/
|
||||
__pycache__/
|
||||
.gitignore
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -63,4 +63,8 @@ conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/f
|
||||
|
||||
### MultiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
相关文件和介绍在 [multiagent](https://github.com/ACMClassCourse-2023/PPCA-AIPacMan-2024/tree/main/multiagent) 文件夹下。
|
||||
相关文件和介绍在 [multiagent](https://github.com/ACMClassCourse-2023/PPCA-AIPacMan-2024/tree/main/multiagent) 文件夹下。
|
||||
|
||||
### Logic
|
||||
|
||||
相关文件和介绍在 [logic](https://github.com/ACMClassCourse-2023/PPCA-AIPacMan-2024/tree/main/logic) 文件夹下。
|
||||
96
logic/README.md
Normal file
96
logic/README.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
~~coming soon~~
|
||||
|
||||
#### 介绍
|
||||
|
||||
在这个项目中,你将编写简单的 Python 函数,生成描述 Pacman 物理状态(记为 **pacphysics**)的逻辑句子。然后,你将使用 SAT 求解器 pycosat,解决与 规划(生成动作序列以到达目标位置并吃掉所有点)、定位(根据本地传感器模型在地图中找到自己)、建图(从零开始构建地图)以及 SLAM(同时定位与建图)相关的逻辑推理任务。
|
||||
|
||||
你需要补全的代码文件有:
|
||||
|
||||
- logicPlan.py
|
||||
|
||||
你可以阅读并参考来帮助你实现代码的文件有:
|
||||
|
||||
- logic.py
|
||||
- logicAgents.py:以逻辑规划形式定义了Pacman在本项目中将遇到的两个具体问题。
|
||||
- game.py:Pacman世界的内部模拟器代码。你可能需要查看的是其中的Grid类。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以忽略其他支持文件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### The Expr Class
|
||||
|
||||
在本项目的第一部分,你将使用 `logic.py` 中定义的 `Expr` 类来构建命题逻辑句子。一个 `Expr` 对象被实现为一棵树,每个节点是逻辑运算符 $(\vee, \wedge, \neg, \to, \leftrightarrow )$ ,叶子节点是文字(A, B, C, D)。以下是一个句子及其表示的示例:
|
||||
$$
|
||||
(A \wedge B) \leftrightarrow (\neg C \vee D)
|
||||
$$
|
||||
|
||||
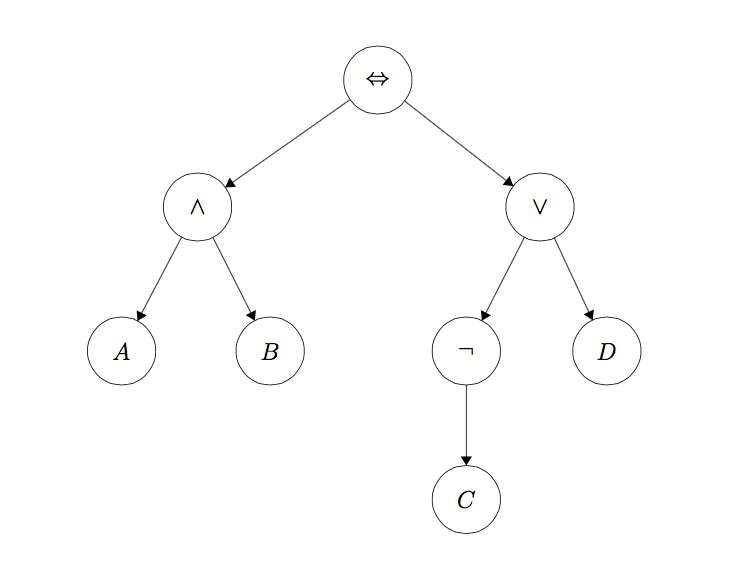
|
||||
|
||||
要实例化名为 'A' 的符号,请像这样调用构造函数:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
A = Expr('A')
|
||||
```
|
||||
该 `Expr` 类允许你使用 Python 运算符来构建这些表达式。以下是可用的 Python 运算符及其含义:
|
||||
|
||||
- `~A`: $\neg A$
|
||||
- `A & B`: $A \wedge B$
|
||||
- `A | B`: $A \vee B$
|
||||
- `A >> B`: $A \to B$
|
||||
- `A % B`: $A \leftrightarrow B$
|
||||
|
||||
因此要构建表达式 $A \wedge B$,你可以这样做:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
A = Expr('A')
|
||||
B = Expr('B')
|
||||
A_and_B = A & B
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(请注意,该示例中赋值运算符左边 `A` 只是一个 Python 变量名,即 `symbol1 = Expr('A')` 也可以正常工作。)
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 conjoin 和 disjoin:**
|
||||
|
||||
在可能的情况下,必须使用 `conjoin` 和 `disjoin` 操作符。`conjoin` 创建一个链式的 `&`(逻辑与)表达式,`disjoin` 创建一个链式的 `|`(逻辑或)表达式。假设你想检查条件 A、B、C、D 和 E 是否全部为真。简单的实现方法是写 `condition = A & B & C & D & E`,但这实际上会转换为 `((((A & B) & C) & D) & E)`,这会创建一个非常嵌套的逻辑树(见下图中的(1)),调试起来非常困难。相反,`conjoin` 可以创建一个扁平的树(见下图中的(2))。
|
||||
|
||||
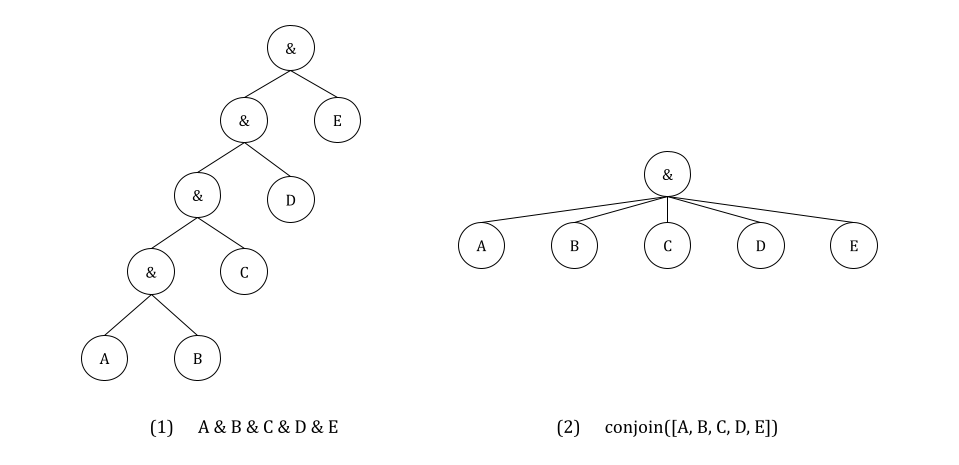
|
||||
|
||||
#### 命题符号命名(重要!)
|
||||
在项目的后续部分,请使用以下变量命名规则:
|
||||
|
||||
- 引入变量时,必须以大写字母开头(包括 `Expr`)。
|
||||
- 变量名中只能出现以下字符:`A-Z`、`a-z`、`0-9`、`_`、`^`、`[`、`]`。
|
||||
- 逻辑连接字符 (`&`, `|`) 不得出现在变量名中。例如,`Expr('A & B')` 是非法的,因为它试图创建一个名为 `'A & B'` 的常量符号。应使用 `Expr('A') & Expr('B')` 来创建逻辑表达式。
|
||||
|
||||
**Pacphysics 符号**
|
||||
|
||||
- `PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y, time=t)`:表示 Pacman 是否在时间 `t` 处于 (x,y),写作 `P[x,y]_t`。
|
||||
- `PropSymbolExpr(wall_str, x, y)`:表示 `(x,y)` 处是否有墙,写作 `WALL[x,y]`。
|
||||
- `PropSymbolExpr(action, time=t)`:表示 Pacman 是否在时间 `t` 采取 `action` 动作,其中 `action` 是 `DIRECTIONS` 的元素,例如 North_t`。
|
||||
- 一般情况下,`PropSymbolExpr(str, a1, a2, a3, a4, time=a5)` 创建表达式 `str[a1,a2,a3,a4]_a5`,其中 `str` 是一个字符串。
|
||||
|
||||
`logic.py` 文件中有关于 `Expr` 类的更多详细文档。
|
||||
|
||||
#### SAT 求解器
|
||||
|
||||
一个SAT(可满足性)求解器接受编码世界规则的逻辑表达式,并返回一个满足该表达式的模型(逻辑符号的真值分配),如果存在这样的模型。为了高效地从表达式中找到可能的模型,我们利用 [pycosat](https://pypi.org/project/pycosat/) 模块,这是 [picoSAT](https://fmv.jku.at/picosat/) 库的Python包装器。
|
||||
|
||||
运行`conda install pycosat` 安装。
|
||||
|
||||
**测试pycosat安装**:
|
||||
|
||||
在 `logic` 目录下运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
python pycosat_test.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这应该输出:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[1, -2, -3, -4, 5]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在设置过程中遇到问题,请告知我们。这对于完成项目至关重要,我们不希望你在安装过程中浪费时间。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Q1: Logic Warm-up
|
||||
|
||||
1
logic/VERSION
Normal file
1
logic/VERSION
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
v1.2
|
||||
644
logic/agents.py
Normal file
644
logic/agents.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,644 @@
|
||||
# agents.py
|
||||
# ---------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""Implement Agents and Environments (Chapters 1-2).
|
||||
|
||||
Code originally from https://code.google.com/p/aima-python/
|
||||
|
||||
The class hierarchies are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
Thing ## A physical object that can exist in an environment
|
||||
Agent
|
||||
Wumpus
|
||||
Dirt
|
||||
Wall
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
Environment ## An environment holds objects, runs simulations
|
||||
XYEnvironment
|
||||
VacuumEnvironment
|
||||
WumpusEnvironment
|
||||
|
||||
An agent program is a callable instance, taking percepts and choosing actions
|
||||
SimpleReflexAgentProgram
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
EnvGUI ## A window with a graphical representation of the Environment
|
||||
|
||||
EnvToolbar ## contains buttons for controlling EnvGUI
|
||||
|
||||
EnvCanvas ## Canvas to display the environment of an EnvGUI
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# TO DO:
|
||||
# Implement grabbing correctly.
|
||||
# When an object is grabbed, does it still have a location?
|
||||
# What if it is released?
|
||||
# What if the grabbed or the grabber is deleted?
|
||||
# What if the grabber moves?
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Speed control in GUI does not have any effect -- fix it.
|
||||
|
||||
from logic_utils import *
|
||||
import random, copy
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Thing(object):
|
||||
"""This represents any physical object that can appear in an Environment.
|
||||
You subclass Thing to get the things you want. Each thing can have a
|
||||
.__name__ slot (used for output only)."""
|
||||
def __repr__(self):
|
||||
return '<%s>' % getattr(self, '__name__', self.__class__.__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
def is_alive(self):
|
||||
"Things that are 'alive' should return true."
|
||||
return hasattr(self, 'alive') and self.alive
|
||||
|
||||
def show_state(self):
|
||||
"Display the agent's internal state. Subclasses should override."
|
||||
print("I don't know how to show_state.")
|
||||
|
||||
def display(self, canvas, x, y, width, height):
|
||||
# Do we need this?
|
||||
"Display an image of this Thing on the canvas."
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
class Agent(Thing):
|
||||
"""An Agent is a subclass of Thing with one required slot,
|
||||
.program, which should hold a function that takes one argument, the
|
||||
percept, and returns an action. (What counts as a percept or action
|
||||
will depend on the specific environment in which the agent exists.)
|
||||
Note that 'program' is a slot, not a method. If it were a method,
|
||||
then the program could 'cheat' and look at aspects of the agent.
|
||||
It's not supposed to do that: the program can only look at the
|
||||
percepts. An agent program that needs a model of the world (and of
|
||||
the agent itself) will have to build and maintain its own model.
|
||||
There is an optional slot, .performance, which is a number giving
|
||||
the performance measure of the agent in its environment."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, program=None):
|
||||
self.alive = True
|
||||
self.bump = False
|
||||
if program is None:
|
||||
def program(percept):
|
||||
return raw_input('Percept=%s; action? ' % percept)
|
||||
assert callable(program)
|
||||
self.program = program
|
||||
|
||||
def can_grab(self, thing):
|
||||
"""Returns True if this agent can grab this thing.
|
||||
Override for appropriate subclasses of Agent and Thing."""
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def TraceAgent(agent):
|
||||
"""Wrap the agent's program to print its input and output. This will let
|
||||
you see what the agent is doing in the environment."""
|
||||
old_program = agent.program
|
||||
def new_program(percept):
|
||||
action = old_program(percept)
|
||||
print('%s perceives %s and does %s' % (agent, percept, action))
|
||||
return action
|
||||
agent.program = new_program
|
||||
return agent
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
def TableDrivenAgentProgram(table):
|
||||
"""This agent selects an action based on the percept sequence.
|
||||
It is practical only for tiny domains.
|
||||
To customize it, provide as table a dictionary of all
|
||||
{percept_sequence:action} pairs. [Fig. 2.7]"""
|
||||
percepts = []
|
||||
def program(percept):
|
||||
percepts.append(percept)
|
||||
action = table.get(tuple(percepts))
|
||||
return action
|
||||
return program
|
||||
|
||||
def RandomAgentProgram(actions):
|
||||
"An agent that chooses an action at random, ignoring all percepts."
|
||||
return lambda percept: random.choice(actions)
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
def SimpleReflexAgentProgram(rules, interpret_input):
|
||||
"This agent takes action based solely on the percept. [Fig. 2.10]"
|
||||
def program(percept):
|
||||
state = interpret_input(percept)
|
||||
rule = rule_match(state, rules)
|
||||
action = rule.action
|
||||
return action
|
||||
return program
|
||||
|
||||
def ModelBasedReflexAgentProgram(rules, update_state):
|
||||
"This agent takes action based on the percept and state. [Fig. 2.12]"
|
||||
def program(percept):
|
||||
program.state = update_state(program.state, program.action, percept)
|
||||
rule = rule_match(program.state, rules)
|
||||
action = rule.action
|
||||
return action
|
||||
program.state = program.action = None
|
||||
return program
|
||||
|
||||
def rule_match(state, rules):
|
||||
"Find the first rule that matches state."
|
||||
for rule in rules:
|
||||
if rule.matches(state):
|
||||
return rule
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
loc_A, loc_B = (0, 0), (1, 0) # The two locations for the Vacuum world
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def RandomVacuumAgent():
|
||||
"Randomly choose one of the actions from the vacuum environment."
|
||||
return Agent(RandomAgentProgram(['Right', 'Left', 'Suck', 'NoOp']))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def TableDrivenVacuumAgent():
|
||||
"[Fig. 2.3]"
|
||||
table = {((loc_A, 'Clean'),): 'Right',
|
||||
((loc_A, 'Dirty'),): 'Suck',
|
||||
((loc_B, 'Clean'),): 'Left',
|
||||
((loc_B, 'Dirty'),): 'Suck',
|
||||
((loc_A, 'Clean'), (loc_A, 'Clean')): 'Right',
|
||||
((loc_A, 'Clean'), (loc_A, 'Dirty')): 'Suck',
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
((loc_A, 'Clean'), (loc_A, 'Clean'), (loc_A, 'Clean')): 'Right',
|
||||
((loc_A, 'Clean'), (loc_A, 'Clean'), (loc_A, 'Dirty')): 'Suck',
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Agent(TableDrivenAgentProgram(table))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def ReflexVacuumAgent():
|
||||
"A reflex agent for the two-state vacuum environment. [Fig. 2.8]"
|
||||
def program(percept):
|
||||
(location, status) = percept
|
||||
if status == 'Dirty': return 'Suck'
|
||||
elif location == loc_A: return 'Right'
|
||||
elif location == loc_B: return 'Left'
|
||||
return Agent(program)
|
||||
|
||||
def ModelBasedVacuumAgent():
|
||||
"An agent that keeps track of what locations are clean or dirty."
|
||||
model = {loc_A: None, loc_B: None}
|
||||
def program(percept):
|
||||
"Same as ReflexVacuumAgent, except if everything is clean, do NoOp."
|
||||
(location, status) = percept
|
||||
model[location] = status ## Update the model here
|
||||
if model[loc_A] == model[loc_B] == 'Clean': return 'NoOp'
|
||||
elif status == 'Dirty': return 'Suck'
|
||||
elif location == loc_A: return 'Right'
|
||||
elif location == loc_B: return 'Left'
|
||||
return Agent(program)
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Environment(object):
|
||||
"""Abstract class representing an Environment. 'Real' Environment classes
|
||||
inherit from this. Your Environment will typically need to implement:
|
||||
percept: Define the percept that an agent sees.
|
||||
execute_action: Define the effects of executing an action.
|
||||
Also update the agent.performance slot.
|
||||
The environment keeps a list of .things and .agents (which is a subset
|
||||
of .things). Each agent has a .performance slot, initialized to 0.
|
||||
Each thing has a .location slot, even though some environments may not
|
||||
need this."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.things = []
|
||||
self.agents = []
|
||||
|
||||
def thing_classes(self):
|
||||
return [] ## List of classes that can go into environment
|
||||
|
||||
def percept(self, agent):
|
||||
"Return the percept that the agent sees at this point. (Implement this.)"
|
||||
abstract
|
||||
|
||||
def execute_action(self, agent, action):
|
||||
"Change the world to reflect this action. (Implement this.)"
|
||||
abstract
|
||||
|
||||
def default_location(self, thing):
|
||||
"Default location to place a new thing with unspecified location."
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
def exogenous_change(self):
|
||||
"If there is spontaneous change in the world, override this."
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def is_done(self):
|
||||
"By default, we're done when we can't find a live agent."
|
||||
return not any(agent.is_alive() for agent in self.agents)
|
||||
|
||||
def step(self):
|
||||
"""Run the environment for one time step. If the
|
||||
actions and exogenous changes are independent, this method will
|
||||
do. If there are interactions between them, you'll need to
|
||||
override this method."""
|
||||
if not self.is_done():
|
||||
actions = [agent.program(self.percept(agent))
|
||||
for agent in self.agents]
|
||||
for (agent, action) in zip(self.agents, actions):
|
||||
self.execute_action(agent, action)
|
||||
self.exogenous_change()
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self, steps=1000):
|
||||
"Run the Environment for given number of time steps."
|
||||
for step in range(steps):
|
||||
if self.is_done(): return
|
||||
self.step()
|
||||
|
||||
def list_things_at(self, location, tclass=Thing):
|
||||
"Return all things exactly at a given location."
|
||||
return [thing for thing in self.things
|
||||
if thing.location == location and isinstance(thing, tclass)]
|
||||
|
||||
def some_things_at(self, location, tclass=Thing):
|
||||
"""Return true if at least one of the things at location
|
||||
is an instance of class tclass (or a subclass)."""
|
||||
return self.list_things_at(location, tclass) != []
|
||||
|
||||
def add_thing(self, thing, location=None):
|
||||
"""Add a thing to the environment, setting its location. For
|
||||
convenience, if thing is an agent program we make a new agent
|
||||
for it. (Shouldn't need to override this."""
|
||||
if not isinstance(thing, Thing):
|
||||
thing = Agent(thing)
|
||||
assert thing not in self.things, "Don't add the same thing twice"
|
||||
thing.location = location or self.default_location(thing)
|
||||
self.things.append(thing)
|
||||
if isinstance(thing, Agent):
|
||||
thing.performance = 0
|
||||
self.agents.append(thing)
|
||||
|
||||
def delete_thing(self, thing):
|
||||
"""Remove a thing from the environment."""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.things.remove(thing)
|
||||
except ValueError as e:
|
||||
print(e)
|
||||
print(" in Environment delete_thing")
|
||||
print(" Thing to be removed: %s at %s" % (thing, thing.location))
|
||||
print(" from list: %s" % [(thing, thing.location)
|
||||
for thing in self.things])
|
||||
if thing in self.agents:
|
||||
self.agents.remove(thing)
|
||||
|
||||
class XYEnvironment(Environment):
|
||||
"""This class is for environments on a 2D plane, with locations
|
||||
labelled by (x, y) points, either discrete or continuous.
|
||||
|
||||
Agents perceive things within a radius. Each agent in the
|
||||
environment has a .location slot which should be a location such
|
||||
as (0, 1), and a .holding slot, which should be a list of things
|
||||
that are held."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, width=10, height=10):
|
||||
super(XYEnvironment, self).__init__()
|
||||
update(self, width=width, height=height, observers=[])
|
||||
|
||||
def things_near(self, location, radius=None):
|
||||
"Return all things within radius of location."
|
||||
if radius is None: radius = self.perceptible_distance
|
||||
radius2 = radius * radius
|
||||
return [thing for thing in self.things
|
||||
if distance2(location, thing.location) <= radius2]
|
||||
|
||||
perceptible_distance = 1
|
||||
|
||||
def percept(self, agent):
|
||||
"By default, agent perceives things within a default radius."
|
||||
return [self.thing_percept(thing, agent)
|
||||
for thing in self.things_near(agent.location)]
|
||||
|
||||
def execute_action(self, agent, action):
|
||||
agent.bump = False
|
||||
if action == 'TurnRight':
|
||||
agent.heading = self.turn_heading(agent.heading, -1)
|
||||
elif action == 'TurnLeft':
|
||||
agent.heading = self.turn_heading(agent.heading, +1)
|
||||
elif action == 'Forward':
|
||||
self.move_to(agent, vector_add(agent.heading, agent.location))
|
||||
# elif action == 'Grab':
|
||||
# things = [thing for thing in self.list_things_at(agent.location)
|
||||
# if agent.can_grab(thing)]
|
||||
# if things:
|
||||
# agent.holding.append(things[0])
|
||||
elif action == 'Release':
|
||||
if agent.holding:
|
||||
agent.holding.pop()
|
||||
|
||||
def thing_percept(self, thing, agent): #??? Should go to thing?
|
||||
"Return the percept for this thing."
|
||||
return thing.__class__.__name__
|
||||
|
||||
def default_location(self, thing):
|
||||
return (random.choice(self.width), random.choice(self.height))
|
||||
|
||||
def move_to(self, thing, destination):
|
||||
"Move a thing to a new location."
|
||||
thing.bump = self.some_things_at(destination, Obstacle)
|
||||
if not thing.bump:
|
||||
thing.location = destination
|
||||
for o in self.observers:
|
||||
o.thing_moved(thing)
|
||||
|
||||
def add_thing(self, thing, location=(1, 1)):
|
||||
super(XYEnvironment, self).add_thing(thing, location)
|
||||
thing.holding = []
|
||||
thing.held = None
|
||||
for obs in self.observers:
|
||||
obs.thing_added(thing)
|
||||
|
||||
def delete_thing(self, thing):
|
||||
super(XYEnvironment, self).delete_thing(thing)
|
||||
# Any more to do? Thing holding anything or being held?
|
||||
for obs in self.observers:
|
||||
obs.thing_deleted(thing)
|
||||
|
||||
def add_walls(self):
|
||||
"Put walls around the entire perimeter of the grid."
|
||||
for x in range(self.width):
|
||||
self.add_thing(Wall(), (x, 0))
|
||||
self.add_thing(Wall(), (x, self.height-1))
|
||||
for y in range(self.height):
|
||||
self.add_thing(Wall(), (0, y))
|
||||
self.add_thing(Wall(), (self.width-1, y))
|
||||
|
||||
def add_observer(self, observer):
|
||||
"""Adds an observer to the list of observers.
|
||||
An observer is typically an EnvGUI.
|
||||
|
||||
Each observer is notified of changes in move_to and add_thing,
|
||||
by calling the observer's methods thing_moved(thing)
|
||||
and thing_added(thing, loc)."""
|
||||
self.observers.append(observer)
|
||||
|
||||
def turn_heading(self, heading, inc):
|
||||
"Return the heading to the left (inc=+1) or right (inc=-1) of heading."
|
||||
return turn_heading(heading, inc)
|
||||
|
||||
class Obstacle(Thing):
|
||||
"""Something that can cause a bump, preventing an agent from
|
||||
moving into the same square it's in."""
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
class Wall(Obstacle):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
## Vacuum environment
|
||||
|
||||
class Dirt(Thing):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
class VacuumEnvironment(XYEnvironment):
|
||||
"""The environment of [Ex. 2.12]. Agent perceives dirty or clean,
|
||||
and bump (into obstacle) or not; 2D discrete world of unknown size;
|
||||
performance measure is 100 for each dirt cleaned, and -1 for
|
||||
each turn taken."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, width=10, height=10):
|
||||
super(VacuumEnvironment, self).__init__(width, height)
|
||||
self.add_walls()
|
||||
|
||||
def thing_classes(self):
|
||||
return [Wall, Dirt, ReflexVacuumAgent, RandomVacuumAgent,
|
||||
TableDrivenVacuumAgent, ModelBasedVacuumAgent]
|
||||
|
||||
def percept(self, agent):
|
||||
"""The percept is a tuple of ('Dirty' or 'Clean', 'Bump' or 'None').
|
||||
Unlike the TrivialVacuumEnvironment, location is NOT perceived."""
|
||||
status = if_(self.some_things_at(agent.location, Dirt),
|
||||
'Dirty', 'Clean')
|
||||
bump = if_(agent.bump, 'Bump', 'None')
|
||||
return (status, bump)
|
||||
|
||||
def execute_action(self, agent, action):
|
||||
if action == 'Suck':
|
||||
dirt_list = self.list_things_at(agent.location, Dirt)
|
||||
if dirt_list != []:
|
||||
dirt = dirt_list[0]
|
||||
agent.performance += 100
|
||||
self.delete_thing(dirt)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
super(VacuumEnvironment, self).execute_action(agent, action)
|
||||
|
||||
if action != 'NoOp':
|
||||
agent.performance -= 1
|
||||
|
||||
class TrivialVacuumEnvironment(Environment):
|
||||
"""This environment has two locations, A and B. Each can be Dirty
|
||||
or Clean. The agent perceives its location and the location's
|
||||
status. This serves as an example of how to implement a simple
|
||||
Environment."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super(TrivialVacuumEnvironment, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.status = {loc_A: random.choice(['Clean', 'Dirty']),
|
||||
loc_B: random.choice(['Clean', 'Dirty'])}
|
||||
|
||||
def thing_classes(self):
|
||||
return [Wall, Dirt, ReflexVacuumAgent, RandomVacuumAgent,
|
||||
TableDrivenVacuumAgent, ModelBasedVacuumAgent]
|
||||
|
||||
def percept(self, agent):
|
||||
"Returns the agent's location, and the location status (Dirty/Clean)."
|
||||
return (agent.location, self.status[agent.location])
|
||||
|
||||
def execute_action(self, agent, action):
|
||||
"""Change agent's location and/or location's status; track performance.
|
||||
Score 10 for each dirt cleaned; -1 for each move."""
|
||||
if action == 'Right':
|
||||
agent.location = loc_B
|
||||
agent.performance -= 1
|
||||
elif action == 'Left':
|
||||
agent.location = loc_A
|
||||
agent.performance -= 1
|
||||
elif action == 'Suck':
|
||||
if self.status[agent.location] == 'Dirty':
|
||||
agent.performance += 10
|
||||
self.status[agent.location] = 'Clean'
|
||||
|
||||
def default_location(self, thing):
|
||||
"Agents start in either location at random."
|
||||
return random.choice([loc_A, loc_B])
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
## The Wumpus World
|
||||
|
||||
class Gold(Thing): pass
|
||||
class Pit(Thing): pass
|
||||
class Arrow(Thing): pass
|
||||
class Wumpus(Agent): pass
|
||||
class Explorer(Agent): pass
|
||||
|
||||
class WumpusEnvironment(XYEnvironment):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, width=10, height=10):
|
||||
super(WumpusEnvironment, self).__init__(width, height)
|
||||
self.add_walls()
|
||||
|
||||
def thing_classes(self):
|
||||
return [Wall, Gold, Pit, Arrow, Wumpus, Explorer]
|
||||
|
||||
## Needs a lot of work ...
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
def compare_agents(EnvFactory, AgentFactories, n=10, steps=1000):
|
||||
"""See how well each of several agents do in n instances of an environment.
|
||||
Pass in a factory (constructor) for environments, and several for agents.
|
||||
Create n instances of the environment, and run each agent in copies of
|
||||
each one for steps. Return a list of (agent, average-score) tuples."""
|
||||
envs = [EnvFactory() for i in range(n)]
|
||||
return [(A, test_agent(A, steps, copy.deepcopy(envs)))
|
||||
for A in AgentFactories]
|
||||
|
||||
def test_agent(AgentFactory, steps, envs):
|
||||
"Return the mean score of running an agent in each of the envs, for steps"
|
||||
def score(env):
|
||||
agent = AgentFactory()
|
||||
env.add_thing(agent)
|
||||
env.run(steps)
|
||||
return agent.performance
|
||||
return mean(map(score, envs))
|
||||
|
||||
#_________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
__doc__ += """
|
||||
>>> a = ReflexVacuumAgent()
|
||||
>>> a.program((loc_A, 'Clean'))
|
||||
'Right'
|
||||
>>> a.program((loc_B, 'Clean'))
|
||||
'Left'
|
||||
>>> a.program((loc_A, 'Dirty'))
|
||||
'Suck'
|
||||
>>> a.program((loc_A, 'Dirty'))
|
||||
'Suck'
|
||||
|
||||
>>> e = TrivialVacuumEnvironment()
|
||||
>>> e.add_thing(ModelBasedVacuumAgent())
|
||||
>>> e.run(5)
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments, and some agents, are randomized, so the best we can
|
||||
## give is a range of expected scores. If this test fails, it does
|
||||
## not necessarily mean something is wrong.
|
||||
>>> envs = [TrivialVacuumEnvironment() for i in range(100)]
|
||||
>>> def testv(A): return test_agent(A, 4, copy.deepcopy(envs))
|
||||
>>> 7 < testv(ModelBasedVacuumAgent) < 11
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> 5 < testv(ReflexVacuumAgent) < 9
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> 2 < testv(TableDrivenVacuumAgent) < 6
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> 0.5 < testv(RandomVacuumAgent) < 3
|
||||
True
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# GUI - Graphical User Interface for Environments
|
||||
# If you do not have tkinter installed, either get a new installation of Python
|
||||
# (tkinter is standard in all new releases), or delete the rest of this file
|
||||
# and muddle through without a GUI.
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import tkinter as tk
|
||||
|
||||
class EnvGUI(tk.Tk, object):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, env, title = 'AIMA GUI', cellwidth=50, n=10):
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize window
|
||||
|
||||
super(EnvGUI, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.title(title)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create components
|
||||
|
||||
canvas = EnvCanvas(self, env, cellwidth, n)
|
||||
toolbar = EnvToolbar(self, env, canvas)
|
||||
for w in [canvas, toolbar]:
|
||||
w.pack(side="bottom", fill="x", padx="3", pady="3")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EnvToolbar(tk.Frame, object):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, parent, env, canvas):
|
||||
super(EnvToolbar, self).__init__(parent, relief='raised', bd=2)
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize instance variables
|
||||
|
||||
self.env = env
|
||||
self.canvas = canvas
|
||||
self.running = False
|
||||
self.speed = 1.0
|
||||
|
||||
# Create buttons and other controls
|
||||
|
||||
for txt, cmd in [('Step >', self.env.step),
|
||||
('Run >>', self.run),
|
||||
('Stop [ ]', self.stop),
|
||||
('List things', self.list_things),
|
||||
('List agents', self.list_agents)]:
|
||||
tk.Button(self, text=txt, command=cmd).pack(side='left')
|
||||
|
||||
tk.Label(self, text='Speed').pack(side='left')
|
||||
scale = tk.Scale(self, orient='h',
|
||||
from_=(1.0), to=10.0, resolution=1.0,
|
||||
command=self.set_speed)
|
||||
scale.set(self.speed)
|
||||
scale.pack(side='left')
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
print('run')
|
||||
self.running = True
|
||||
self.background_run()
|
||||
|
||||
def stop(self):
|
||||
print('stop')
|
||||
self.running = False
|
||||
|
||||
def background_run(self):
|
||||
if self.running:
|
||||
self.env.step()
|
||||
# ms = int(1000 * max(float(self.speed), 0.5))
|
||||
#ms = max(int(1000 * float(self.delay)), 1)
|
||||
delay_sec = 1.0 / max(self.speed, 1.0) # avoid division by zero
|
||||
ms = int(1000.0 * delay_sec) # seconds to milliseconds
|
||||
self.after(ms, self.background_run)
|
||||
|
||||
def list_things(self):
|
||||
print("Things in the environment:")
|
||||
for thing in self.env.things:
|
||||
print("%s at %s" % (thing, thing.location))
|
||||
|
||||
def list_agents(self):
|
||||
print("Agents in the environment:")
|
||||
for agt in self.env.agents:
|
||||
print("%s at %s" % (agt, agt.location))
|
||||
|
||||
def set_speed(self, speed):
|
||||
self.speed = float(speed)
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
434
logic/autograder.py
Normal file
434
logic/autograder.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,434 @@
|
||||
# autograder.py
|
||||
# -------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# imports from python standard library
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import grading
|
||||
import importlib.util
|
||||
import optparse
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import projectParams
|
||||
import random
|
||||
random.seed(0)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from pacman import GameState
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# register arguments and set default values
|
||||
def readCommand(argv):
|
||||
parser = optparse.OptionParser(description='Run public tests on student code')
|
||||
parser.set_defaults(generateSolutions=False, edxOutput=False, gsOutput=False, muteOutput=False, printTestCase=False, noGraphics=False)
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
parser.set_defaults(generatePublicTests=False)
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
parser.add_option('--test-directory',
|
||||
dest='testRoot',
|
||||
default='test_cases',
|
||||
help='Root test directory which contains subdirectories corresponding to each question')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--student-code',
|
||||
dest='studentCode',
|
||||
default=projectParams.STUDENT_CODE_DEFAULT,
|
||||
help='comma separated list of student code files')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--code-directory',
|
||||
dest='codeRoot',
|
||||
default="",
|
||||
help='Root directory containing the student and testClass code')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--test-case-code',
|
||||
dest='testCaseCode',
|
||||
default=projectParams.PROJECT_TEST_CLASSES,
|
||||
help='class containing testClass classes for this project')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--generate-solutions',
|
||||
dest='generateSolutions',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Write solutions generated to .solution file')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--edx-output',
|
||||
dest='edxOutput',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Generate edX output files')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--gradescope-output',
|
||||
dest='gsOutput',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Generate GradeScope output files')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--mute',
|
||||
dest='muteOutput',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Mute output from executing tests')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--print-tests', '-p',
|
||||
dest='printTestCase',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Print each test case before running them.')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--test', '-t',
|
||||
dest='runTest',
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help='Run one particular test. Relative to test root.')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--question', '-q',
|
||||
dest='gradeQuestion',
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help='Grade one particular question.')
|
||||
parser.add_option('--no-graphics',
|
||||
dest='noGraphics',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='No graphics display for pacman games.')
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
parser.add_option('--generate-public-tests',
|
||||
dest='generatePublicTests',
|
||||
action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Generate ./test_cases/* from ./private_test_cases/*')
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
(options, args) = parser.parse_args(argv)
|
||||
return options
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# confirm we should author solution files
|
||||
def confirmGenerate():
|
||||
print('WARNING: this action will overwrite any solution files.')
|
||||
print('Are you sure you want to proceed? (yes/no)')
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
ans = sys.stdin.readline().strip()
|
||||
if ans == 'yes':
|
||||
break
|
||||
elif ans == 'no':
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('please answer either "yes" or "no"')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: Fix this so that it tracebacks work correctly
|
||||
# Looking at source of the traceback module, presuming it works
|
||||
# the same as the intepreters, it uses co_filename. This is,
|
||||
# however, a readonly attribute.
|
||||
def setModuleName(module, filename):
|
||||
functionType = type(confirmGenerate)
|
||||
classType = type(optparse.Option)
|
||||
|
||||
for i in dir(module):
|
||||
o = getattr(module, i)
|
||||
if hasattr(o, '__file__'):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
if type(o) == functionType:
|
||||
setattr(o, '__file__', filename)
|
||||
elif type(o) == classType:
|
||||
setattr(o, '__file__', filename)
|
||||
# TODO: assign member __file__'s?
|
||||
#print(i, type(o))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#from cStringIO import StringIO
|
||||
|
||||
# def loadModuleString(moduleSource):
|
||||
# # Below broken, imp doesn't believe its being passed a file:
|
||||
# # ValueError: load_module arg#2 should be a file or None
|
||||
# #
|
||||
# #f = StringIO(moduleCodeDict[k])
|
||||
# #tmp = imp.load_module(k, f, k, (".py", "r", imp.PY_SOURCE))
|
||||
# tmp = imp.new_module(k)
|
||||
# exec(moduleCodeDict[k], tmp.__dict__)
|
||||
# setModuleName(tmp, k)
|
||||
# return tmp
|
||||
|
||||
import py_compile
|
||||
|
||||
def loadModuleFile(moduleName, filePath):
|
||||
# https://docs.python.org/3/library/importlib.html#importing-a-source-file-directly
|
||||
spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location(moduleName, filePath)
|
||||
module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)
|
||||
spec.loader.exec_module(module)
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def readFile(path, root=""):
|
||||
"Read file from disk at specified path and return as string"
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(root, path), 'r') as handle:
|
||||
return handle.read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#######################################################################
|
||||
# Error Hint Map
|
||||
#######################################################################
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: use these
|
||||
ERROR_HINT_MAP = {
|
||||
'q1': {
|
||||
"<type 'exceptions.IndexError'>": """
|
||||
We noticed that your project threw an IndexError on q1.
|
||||
While many things may cause this, it may have been from
|
||||
assuming a certain number of successors from a state space
|
||||
or assuming a certain number of actions available from a given
|
||||
state. Try making your code more general (no hardcoded indices)
|
||||
and submit again!
|
||||
"""
|
||||
},
|
||||
'q3': {
|
||||
"<type 'exceptions.AttributeError'>": """
|
||||
We noticed that your project threw an AttributeError on q3.
|
||||
While many things may cause this, it may have been from assuming
|
||||
a certain size or structure to the state space. For example, if you have
|
||||
a line of code assuming that the state is (x, y) and we run your code
|
||||
on a state space with (x, y, z), this error could be thrown. Try
|
||||
making your code more general and submit again!
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
import pprint
|
||||
|
||||
def splitStrings(d):
|
||||
d2 = dict(d)
|
||||
for k in d:
|
||||
if k[0:2] == "__":
|
||||
del d2[k]
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if d2[k].find("\n") >= 0:
|
||||
d2[k] = d2[k].split("\n")
|
||||
return d2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def printTest(testDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
pp = pprint.PrettyPrinter(indent=4)
|
||||
print("Test case:")
|
||||
for line in testDict["__raw_lines__"]:
|
||||
print(" |", line)
|
||||
print("Solution:")
|
||||
for line in solutionDict["__raw_lines__"]:
|
||||
print(" |", line)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def runTest(testName, moduleDict, printTestCase=False, display=None):
|
||||
import testParser
|
||||
import testClasses
|
||||
for module in moduleDict:
|
||||
setattr(sys.modules[__name__], module, moduleDict[module])
|
||||
|
||||
testDict = testParser.TestParser(testName + ".test").parse()
|
||||
solutionDict = testParser.TestParser(testName + ".solution").parse()
|
||||
test_out_file = os.path.join('%s.test_output' % testName)
|
||||
testDict['test_out_file'] = test_out_file
|
||||
testClass = getattr(projectTestClasses, testDict['class'])
|
||||
|
||||
questionClass = getattr(testClasses, 'Question')
|
||||
question = questionClass({'max_points': 0}, display)
|
||||
testCase = testClass(question, testDict)
|
||||
|
||||
if printTestCase:
|
||||
printTest(testDict, solutionDict)
|
||||
|
||||
# This is a fragile hack to create a stub grades object
|
||||
grades = grading.Grades(projectParams.PROJECT_NAME, [(None, 0)])
|
||||
testCase.execute(grades, moduleDict, solutionDict)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# returns all the tests you need to run in order to run question
|
||||
def getDepends(testParser, testRoot, question):
|
||||
allDeps = [question]
|
||||
questionDict = testParser.TestParser(os.path.join(testRoot, question, 'CONFIG')).parse()
|
||||
if 'depends' in questionDict:
|
||||
depends = questionDict['depends'].split()
|
||||
for d in depends:
|
||||
# run dependencies first
|
||||
allDeps = getDepends(testParser, testRoot, d) + allDeps
|
||||
return allDeps
|
||||
|
||||
# get list of questions to grade
|
||||
def getTestSubdirs(testParser, testRoot, questionToGrade):
|
||||
# THIS IS WHERE QUESTIONS ARE SPECIFIED
|
||||
problemDict = testParser.TestParser(os.path.join(testRoot, 'CONFIG')).parse()
|
||||
if questionToGrade != None:
|
||||
questions = getDepends(testParser, testRoot, questionToGrade)
|
||||
if len(questions) > 1:
|
||||
print('Note: due to dependencies, the following tests will be run: %s' % ' '.join(questions))
|
||||
return questions
|
||||
if 'order' in problemDict:
|
||||
return problemDict['order'].split()
|
||||
return sorted(os.listdir(testRoot))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# evaluate student code
|
||||
def evaluate(generateSolutions, testRoot, moduleDict, exceptionMap=ERROR_HINT_MAP,
|
||||
edxOutput=False, muteOutput=False, gsOutput=False,
|
||||
printTestCase=False, questionToGrade=None, display=None):
|
||||
# imports of testbench code. note that the testClasses import must follow
|
||||
# the import of student code due to dependencies
|
||||
import testParser
|
||||
import testClasses
|
||||
for module in moduleDict:
|
||||
setattr(sys.modules[__name__], module, moduleDict[module])
|
||||
|
||||
questions = []
|
||||
questionDicts = {}
|
||||
# HERE IS WHERE QUESTIONS ARE CREATED
|
||||
test_subdirs = getTestSubdirs(testParser, testRoot, questionToGrade)
|
||||
for q in test_subdirs:
|
||||
subdir_path = os.path.join(testRoot, q)
|
||||
if not os.path.isdir(subdir_path) or q[0] == '.':
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
# create a question object
|
||||
questionDict = testParser.TestParser(os.path.join(subdir_path, 'CONFIG')).parse()
|
||||
questionClass = getattr(testClasses, questionDict['class'])
|
||||
question = questionClass(questionDict, display)
|
||||
questionDicts[q] = questionDict
|
||||
|
||||
# load test cases into question
|
||||
tests = [t for t in os.listdir(
|
||||
subdir_path) if re.match(r'[^#~.].*\.test\Z', t)]
|
||||
tests = [re.match(r'(.*)\.test\Z', t).group(1) for t in tests]
|
||||
for t in sorted(tests):
|
||||
test_file = os.path.join(subdir_path, '%s.test' % t)
|
||||
solution_file = os.path.join(subdir_path, '%s.solution' % t)
|
||||
test_out_file = os.path.join(subdir_path, '%s.test_output' % t)
|
||||
testDict = testParser.TestParser(test_file).parse()
|
||||
if testDict.get("disabled", "false").lower() == "true":
|
||||
continue
|
||||
testDict['test_out_file'] = test_out_file
|
||||
testClass = getattr(projectTestClasses, testDict['class'])
|
||||
testCase = testClass(question, testDict)
|
||||
|
||||
def makefun(testCase, solution_file):
|
||||
if generateSolutions:
|
||||
# write solution file to disk
|
||||
return lambda grades: testCase.writeSolution(moduleDict, solution_file)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# read in solution dictionary and pass as an argument
|
||||
testDict = testParser.TestParser(test_file).parse()
|
||||
solutionDict = testParser.TestParser(solution_file).parse()
|
||||
if printTestCase:
|
||||
return lambda grades: printTest(testDict, solutionDict) or testCase.execute(grades, moduleDict, solutionDict)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return lambda grades: testCase.execute(grades, moduleDict, solutionDict)
|
||||
question.addTestCase(testCase, makefun(testCase, solution_file))
|
||||
|
||||
# Note extra function is necessary for scoping reasons
|
||||
def makefun(question):
|
||||
return lambda grades: question.execute(grades)
|
||||
setattr(sys.modules[__name__], q, makefun(question))
|
||||
questions.append((q, question.getMaxPoints()))
|
||||
|
||||
grades = grading.Grades(projectParams.PROJECT_NAME, questions,
|
||||
gsOutput=gsOutput, edxOutput=edxOutput, muteOutput=muteOutput)
|
||||
if questionToGrade == None:
|
||||
for q in questionDicts:
|
||||
for prereq in questionDicts[q].get('depends', '').split():
|
||||
grades.addPrereq(q, prereq)
|
||||
|
||||
grades.grade(sys.modules[__name__], bonusPic=projectParams.BONUS_PIC)
|
||||
return grades.points
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def getDisplay(graphicsByDefault, options=None):
|
||||
graphics = graphicsByDefault
|
||||
if options is not None and options.noGraphics:
|
||||
graphics = False
|
||||
if graphics:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import graphicsDisplay
|
||||
return graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics(1, frameTime=.05)
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
import textDisplay
|
||||
return textDisplay.NullGraphics()
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
|
||||
def copy(srcDir, destDir, filename):
|
||||
srcFilename = os.path.join(srcDir, filename)
|
||||
destFilename = os.path.join(destDir, filename)
|
||||
print("Copying {} -> {}".format(srcFilename, destFilename))
|
||||
shutil.copy(srcFilename, destFilename)
|
||||
# with open(os.path.join(srcDir, filename), 'r') as f1:
|
||||
# with open(os.path.join(destDir, filename), 'w') as f2:
|
||||
# f2.write(f1.read())
|
||||
|
||||
def generatePublicTests(moduleDict, privateRoot='private_test_cases', publicRoot='test_cases'):
|
||||
import testParser
|
||||
import testClasses
|
||||
for module in moduleDict:
|
||||
setattr(sys.modules[__name__], module, moduleDict[module])
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(publicRoot): os.mkdir(publicRoot)
|
||||
copy(privateRoot, publicRoot, 'CONFIG')
|
||||
for q in sorted(os.listdir(privateRoot)):
|
||||
private_subdir_path = os.path.join(privateRoot, q)
|
||||
public_subdir_path = os.path.join(publicRoot, q)
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(public_subdir_path): os.mkdir(public_subdir_path)
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.isdir(private_subdir_path) or q[0] == '.':
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
copy(private_subdir_path, public_subdir_path, 'CONFIG')
|
||||
|
||||
# create a question object
|
||||
questionDict = testParser.TestParser(os.path.join(public_subdir_path, 'CONFIG')).parse()
|
||||
questionClass = getattr(testClasses, questionDict['class'])
|
||||
question = questionClass(questionDict, getDisplay(False))
|
||||
|
||||
tests = list(filter(lambda t: re.match(r'[^#~.].*\.test\Z', t), os.listdir(private_subdir_path)))
|
||||
tests = list(map(lambda t: re.match(r'(.*)\.test\Z', t).group(1), tests))
|
||||
for t in sorted(tests):
|
||||
test_file = os.path.join(private_subdir_path, '%s.test' % t)
|
||||
public_test_file = os.path.join(public_subdir_path, '%s.test' % t)
|
||||
test_out_file = os.path.join(public_subdir_path, '%s.test_output' % t)
|
||||
print("Creating public test case {} from {}".format(public_test_file, test_file))
|
||||
|
||||
testDict = testParser.TestParser(test_file).parse()
|
||||
if testDict.get("disabled", "false").lower() == "true":
|
||||
continue
|
||||
testDict['test_out_file'] = test_out_file
|
||||
testClass = getattr(projectTestClasses, testDict['class'])
|
||||
testCase = testClass(question, testDict)
|
||||
|
||||
testCase.createPublicVersion()
|
||||
testCase.emitPublicVersion(public_test_file)
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
options = readCommand(sys.argv)
|
||||
if options.generateSolutions:
|
||||
confirmGenerate()
|
||||
codePaths = options.studentCode.split(',')
|
||||
# moduleCodeDict = {}
|
||||
# for cp in codePaths:
|
||||
# moduleName = re.match(r'.*?([^/]*)\.py', cp).group(1)
|
||||
# moduleCodeDict[moduleName] = readFile(cp, root=options.codeRoot)
|
||||
# moduleCodeDict['projectTestClasses'] = readFile(options.testCaseCode, root=options.codeRoot)
|
||||
# moduleDict = loadModuleDict(moduleCodeDict)
|
||||
|
||||
moduleDict = {}
|
||||
for cp in codePaths:
|
||||
moduleName = re.match(r'.*?([^/]*)\.py', cp).group(1)
|
||||
moduleDict[moduleName] = loadModuleFile(moduleName, os.path.join(options.codeRoot, cp))
|
||||
|
||||
moduleName = re.match(r'.*?([^/]*)\.py', options.testCaseCode).group(1)
|
||||
moduleDict['projectTestClasses'] = loadModuleFile(moduleName, os.path.join(options.codeRoot, options.testCaseCode))
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
if options.generatePublicTests:
|
||||
generatePublicTests(moduleDict)
|
||||
sys.exit()
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
if options.runTest != None:
|
||||
runTest(options.runTest, moduleDict, printTestCase=options.printTestCase, display=getDisplay(True, options))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
evaluate(options.generateSolutions, options.testRoot, moduleDict,
|
||||
gsOutput=options.gsOutput,
|
||||
edxOutput=options.edxOutput, muteOutput=options.muteOutput, printTestCase=options.printTestCase,
|
||||
questionToGrade=options.gradeQuestion, display=getDisplay(options.gradeQuestion != None, options))
|
||||
42
logic/doctests.py
Normal file
42
logic/doctests.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
# doctests.py
|
||||
# -----------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""Run all doctests from modules on the command line. Use -v for verbose.
|
||||
|
||||
Example usages:
|
||||
|
||||
python doctests.py *.py
|
||||
python doctests.py -v *.py
|
||||
|
||||
You can add more module-level tests with
|
||||
__doc__ += "..."
|
||||
You can add stochastic tests with
|
||||
__doc__ += random_tests("...")
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
import sys, glob, doctest
|
||||
args = [arg for arg in sys.argv[1:] if arg != '-v']
|
||||
if not args: args = ['*.py']
|
||||
modules = [__import__(name.replace('.py',''))
|
||||
for arg in args for name in glob.glob(arg)]
|
||||
|
||||
print("Testing %d modules..." % len(modules))
|
||||
for module in modules:
|
||||
doctest.testmod(module, report=1, optionflags=doctest.REPORT_UDIFF)
|
||||
summary = doctest.master.summarize() if modules else (0, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
print()
|
||||
print()
|
||||
print('%d failed out of %d tests' % summary)
|
||||
791
logic/game.py
Normal file
791
logic/game.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,791 @@
|
||||
# game.py
|
||||
# -------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from util import *
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import traceback
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
#######################
|
||||
# Parts worth reading #
|
||||
#######################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Agent:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
An agent must define a getAction method, but may also define the
|
||||
following methods which will be called if they exist:
|
||||
|
||||
def registerInitialState(self, state): # inspects the starting state
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, index=0):
|
||||
self.index = index
|
||||
self.live_checking = False
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
The Agent will receive a GameState (from either {pacman, capture, sonar}.py) and
|
||||
must return an action from Directions.{North, South, East, West, Stop}
|
||||
"""
|
||||
raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Directions:
|
||||
NORTH = 'North'
|
||||
SOUTH = 'South'
|
||||
EAST = 'East'
|
||||
WEST = 'West'
|
||||
STOP = 'Stop'
|
||||
|
||||
LEFT = {NORTH: WEST,
|
||||
SOUTH: EAST,
|
||||
EAST: NORTH,
|
||||
WEST: SOUTH,
|
||||
STOP: STOP}
|
||||
|
||||
RIGHT = dict([(y, x) for x, y in list(LEFT.items())])
|
||||
|
||||
REVERSE = {NORTH: SOUTH,
|
||||
SOUTH: NORTH,
|
||||
EAST: WEST,
|
||||
WEST: EAST,
|
||||
STOP: STOP}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Configuration:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A Configuration holds the (x,y) coordinate of a character, along with its
|
||||
traveling direction.
|
||||
|
||||
The convention for positions, like a graph, is that (0,0) is the lower left corner, x increases
|
||||
horizontally and y increases vertically. Therefore, north is the direction of increasing y, or (0,1).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, pos, direction):
|
||||
self.pos = pos
|
||||
self.direction = direction
|
||||
|
||||
def getPosition(self):
|
||||
return (self.pos)
|
||||
|
||||
def getDirection(self):
|
||||
return self.direction
|
||||
|
||||
def isInteger(self):
|
||||
x, y = self.pos
|
||||
return x == int(x) and y == int(y)
|
||||
|
||||
def __eq__(self, other):
|
||||
if other == None:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return (self.pos == other.pos and self.direction == other.direction)
|
||||
|
||||
def __hash__(self):
|
||||
x = hash(self.pos)
|
||||
y = hash(self.direction)
|
||||
return hash(x + 13 * y)
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
return "(x,y)="+str(self.pos)+", "+str(self.direction)
|
||||
|
||||
def generateSuccessor(self, vector):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generates a new configuration reached by translating the current
|
||||
configuration by the action vector. This is a low-level call and does
|
||||
not attempt to respect the legality of the movement.
|
||||
|
||||
Actions are movement vectors.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
x, y = self.pos
|
||||
dx, dy = vector
|
||||
direction = Actions.vectorToDirection(vector)
|
||||
if direction == Directions.STOP:
|
||||
direction = self.direction # There is no stop direction
|
||||
return Configuration((x + dx, y+dy), direction)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AgentState:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
AgentStates hold the state of an agent (configuration, speed, scared, etc).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, startConfiguration, isPacman):
|
||||
self.start = startConfiguration
|
||||
self.configuration = startConfiguration
|
||||
self.isPacman = isPacman
|
||||
self.scaredTimer = 0
|
||||
# state below potentially used for contest only
|
||||
self.numCarrying = 0
|
||||
self.numReturned = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
if self.isPacman:
|
||||
return "Pacman: " + str(self.configuration)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return "Ghost: " + str(self.configuration)
|
||||
|
||||
def __eq__(self, other):
|
||||
if other == None:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return self.configuration == other.configuration and self.scaredTimer == other.scaredTimer
|
||||
|
||||
def __hash__(self):
|
||||
return hash(hash(self.configuration) + 13 * hash(self.scaredTimer))
|
||||
|
||||
def copy(self):
|
||||
state = AgentState(self.start, self.isPacman)
|
||||
state.configuration = self.configuration
|
||||
state.scaredTimer = self.scaredTimer
|
||||
state.numCarrying = self.numCarrying
|
||||
state.numReturned = self.numReturned
|
||||
return state
|
||||
|
||||
def getPosition(self):
|
||||
if self.configuration == None:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
return self.configuration.getPosition()
|
||||
|
||||
def getDirection(self):
|
||||
return self.configuration.getDirection()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Grid:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A 2-dimensional array of objects backed by a list of lists. Data is accessed
|
||||
via grid[x][y] where (x,y) are positions on a Pacman map with x horizontal,
|
||||
y vertical and the origin (0,0) in the bottom left corner.
|
||||
|
||||
The __str__ method constructs an output that is oriented like a pacman board.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, width, height, initialValue=False, bitRepresentation=None):
|
||||
if initialValue not in [False, True]:
|
||||
raise Exception('Grids can only contain booleans')
|
||||
self.CELLS_PER_INT = 30
|
||||
|
||||
self.width = width
|
||||
self.height = height
|
||||
self.data = [[initialValue for y in range(height)] for x in range(width)]
|
||||
if bitRepresentation:
|
||||
self._unpackBits(bitRepresentation)
|
||||
|
||||
def __getitem__(self, i):
|
||||
return self.data[i]
|
||||
|
||||
def __setitem__(self, key, item):
|
||||
self.data[key] = item
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
out = [[str(self.data[x][y])[0] for x in range(self.width)] for y in range(self.height)]
|
||||
out.reverse()
|
||||
return '\n'.join([''.join(x) for x in out])
|
||||
|
||||
def __eq__(self, other):
|
||||
if other == None:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return self.data == other.data
|
||||
|
||||
def __hash__(self):
|
||||
# return hash(str(self))
|
||||
base = 1
|
||||
h = 0
|
||||
for l in self.data:
|
||||
for i in l:
|
||||
if i:
|
||||
h += base
|
||||
base *= 2
|
||||
return hash(h)
|
||||
|
||||
def copy(self):
|
||||
g = Grid(self.width, self.height)
|
||||
g.data = [x[:] for x in self.data]
|
||||
return g
|
||||
|
||||
def deepCopy(self):
|
||||
return self.copy()
|
||||
|
||||
def shallowCopy(self):
|
||||
g = Grid(self.width, self.height)
|
||||
g.data = self.data
|
||||
return g
|
||||
|
||||
def count(self, item=True):
|
||||
return sum([x.count(item) for x in self.data])
|
||||
|
||||
def asList(self, key=True):
|
||||
list = []
|
||||
for x in range(self.width):
|
||||
for y in range(self.height):
|
||||
if self[x][y] == key:
|
||||
list.append((x, y))
|
||||
return list
|
||||
|
||||
def makeOuterWalls(self):
|
||||
for x in range(self.width):
|
||||
for y in range(self.height):
|
||||
self.data[x][y] = self.data[x][y] or (
|
||||
(x == 0 or x == self.width - 1)
|
||||
or (y == 0 or y == self.height - 1)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def outer_wall_coords(self):
|
||||
outer_wall_coords_list = []
|
||||
for x in range(self.width):
|
||||
for y in range(self.height):
|
||||
if ((x == 0 or x == self.width - 1)
|
||||
or (y == 0 or y == self.height - 1)):
|
||||
outer_wall_coords_list.append((x, y))
|
||||
return outer_wall_coords_list
|
||||
|
||||
def packBits(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns an efficient int list representation
|
||||
|
||||
(width, height, bitPackedInts...)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
bits = [self.width, self.height]
|
||||
currentInt = 0
|
||||
for i in range(self.height * self.width):
|
||||
bit = self.CELLS_PER_INT - (i % self.CELLS_PER_INT) - 1
|
||||
x, y = self._cellIndexToPosition(i)
|
||||
if self[x][y]:
|
||||
currentInt += 2 ** bit
|
||||
if (i + 1) % self.CELLS_PER_INT == 0:
|
||||
bits.append(currentInt)
|
||||
currentInt = 0
|
||||
bits.append(currentInt)
|
||||
return tuple(bits)
|
||||
|
||||
def _cellIndexToPosition(self, index):
|
||||
x = index // self.height
|
||||
y = index % self.height
|
||||
return x, y
|
||||
|
||||
def _unpackBits(self, bits):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Fills in data from a bit-level representation
|
||||
"""
|
||||
cell = 0
|
||||
for packed in bits:
|
||||
for bit in self._unpackInt(packed, self.CELLS_PER_INT):
|
||||
if cell == self.width * self.height:
|
||||
break
|
||||
x, y = self._cellIndexToPosition(cell)
|
||||
self[x][y] = bit
|
||||
cell += 1
|
||||
|
||||
def _unpackInt(self, packed, size):
|
||||
bools = []
|
||||
if packed < 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError("must be a positive integer")
|
||||
for i in range(size):
|
||||
n = 2 ** (self.CELLS_PER_INT - i - 1)
|
||||
if packed >= n:
|
||||
bools.append(True)
|
||||
packed -= n
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bools.append(False)
|
||||
return bools
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reconstituteGrid(bitRep):
|
||||
if type(bitRep) is not type((1, 2)):
|
||||
return bitRep
|
||||
width, height = bitRep[:2]
|
||||
return Grid(width, height, bitRepresentation=bitRep[2:])
|
||||
|
||||
####################################
|
||||
# Parts you shouldn't have to read #
|
||||
####################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Actions:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A collection of static methods for manipulating move actions.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Directions
|
||||
_directions = {Directions.NORTH: (0, 1),
|
||||
Directions.SOUTH: (0, -1),
|
||||
Directions.EAST: (1, 0),
|
||||
Directions.WEST: (-1, 0),
|
||||
Directions.STOP: (0, 0)}
|
||||
|
||||
_directionsAsList = _directions.items()
|
||||
|
||||
TOLERANCE = .001
|
||||
|
||||
def reverseDirection(action):
|
||||
if action == Directions.NORTH:
|
||||
return Directions.SOUTH
|
||||
if action == Directions.SOUTH:
|
||||
return Directions.NORTH
|
||||
if action == Directions.EAST:
|
||||
return Directions.WEST
|
||||
if action == Directions.WEST:
|
||||
return Directions.EAST
|
||||
return action
|
||||
reverseDirection = staticmethod(reverseDirection)
|
||||
|
||||
def vectorToDirection(vector):
|
||||
dx, dy = vector
|
||||
if dy > 0:
|
||||
return Directions.NORTH
|
||||
if dy < 0:
|
||||
return Directions.SOUTH
|
||||
if dx < 0:
|
||||
return Directions.WEST
|
||||
if dx > 0:
|
||||
return Directions.EAST
|
||||
return Directions.STOP
|
||||
vectorToDirection = staticmethod(vectorToDirection)
|
||||
|
||||
def directionToVector(direction, speed=1.0):
|
||||
dx, dy = Actions._directions[direction]
|
||||
return (dx * speed, dy * speed)
|
||||
directionToVector = staticmethod(directionToVector)
|
||||
|
||||
def getPossibleActions(config, walls):
|
||||
possible = []
|
||||
x, y = config.pos
|
||||
x_int, y_int = int(x + 0.5), int(y + 0.5)
|
||||
|
||||
# In between grid points, all agents must continue straight
|
||||
if (abs(x - x_int) + abs(y - y_int) > Actions.TOLERANCE):
|
||||
return [config.getDirection()]
|
||||
|
||||
for dir, vec in Actions._directionsAsList:
|
||||
dx, dy = vec
|
||||
next_y = y_int + dy
|
||||
next_x = x_int + dx
|
||||
if not walls[next_x][next_y]:
|
||||
possible.append(dir)
|
||||
|
||||
return possible
|
||||
|
||||
getPossibleActions = staticmethod(getPossibleActions)
|
||||
|
||||
def getLegalNeighbors(position, walls):
|
||||
x, y = position
|
||||
x_int, y_int = int(x + 0.5), int(y + 0.5)
|
||||
neighbors = []
|
||||
for dir, vec in Actions._directionsAsList:
|
||||
dx, dy = vec
|
||||
next_x = x_int + dx
|
||||
if next_x < 0 or next_x == walls.width:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
next_y = y_int + dy
|
||||
if next_y < 0 or next_y == walls.height:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if not walls[next_x][next_y]:
|
||||
neighbors.append((next_x, next_y))
|
||||
return neighbors
|
||||
getLegalNeighbors = staticmethod(getLegalNeighbors)
|
||||
|
||||
def getSuccessor(position, action):
|
||||
dx, dy = Actions.directionToVector(action)
|
||||
x, y = position
|
||||
return (x + dx, y + dy)
|
||||
getSuccessor = staticmethod(getSuccessor)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GameStateData:
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, prevState=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generates a new data packet by copying information from its predecessor.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if prevState != None:
|
||||
self.food = prevState.food.shallowCopy()
|
||||
self.capsules = prevState.capsules[:]
|
||||
self.agentStates = self.copyAgentStates(prevState.agentStates)
|
||||
self.layout = prevState.layout
|
||||
self._eaten = prevState._eaten
|
||||
self.score = prevState.score
|
||||
|
||||
self._foodEaten = None
|
||||
self._foodAdded = None
|
||||
self._capsuleEaten = None
|
||||
self._agentMoved = None
|
||||
self._lose = False
|
||||
self._win = False
|
||||
self.scoreChange = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def deepCopy(self):
|
||||
state = GameStateData(self)
|
||||
state.food = self.food.deepCopy()
|
||||
state.layout = self.layout.deepCopy()
|
||||
state._agentMoved = self._agentMoved
|
||||
state._foodEaten = self._foodEaten
|
||||
state._foodAdded = self._foodAdded
|
||||
state._capsuleEaten = self._capsuleEaten
|
||||
return state
|
||||
|
||||
def copyAgentStates(self, agentStates):
|
||||
copiedStates = []
|
||||
for agentState in agentStates:
|
||||
copiedStates.append(agentState.copy())
|
||||
return copiedStates
|
||||
|
||||
def __eq__(self, other):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Allows two states to be compared.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if other == None:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
# TODO Check for type of other
|
||||
if not self.agentStates == other.agentStates:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
if not self.food == other.food:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
if not self.capsules == other.capsules:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
if not self.score == other.score:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def __hash__(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Allows states to be keys of dictionaries.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for i, state in enumerate(self.agentStates):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
int(hash(state))
|
||||
except TypeError as e:
|
||||
print(e)
|
||||
# hash(state)
|
||||
return int((hash(tuple(self.agentStates)) + 13*hash(self.food) + 113 * hash(tuple(self.capsules)) + 7 * hash(self.score)) % 1048575)
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
width, height = self.layout.width, self.layout.height
|
||||
map = Grid(width, height)
|
||||
if type(self.food) == type((1, 2)):
|
||||
self.food = reconstituteGrid(self.food)
|
||||
for x in range(width):
|
||||
for y in range(height):
|
||||
food, walls = self.food, self.layout.walls
|
||||
map[x][y] = self._foodWallStr(food[x][y], walls[x][y])
|
||||
|
||||
for agentState in self.agentStates:
|
||||
if agentState == None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if agentState.configuration == None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
x, y = [int(i) for i in nearestPoint(agentState.configuration.pos)]
|
||||
agent_dir = agentState.configuration.direction
|
||||
if agentState.isPacman:
|
||||
map[x][y] = self._pacStr(agent_dir)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
map[x][y] = self._ghostStr(agent_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
for x, y in self.capsules:
|
||||
map[x][y] = 'o'
|
||||
|
||||
return str(map) + ("\nScore: %d\n" % self.score)
|
||||
|
||||
def _foodWallStr(self, hasFood, hasWall):
|
||||
if hasFood:
|
||||
return '.'
|
||||
elif hasWall:
|
||||
return '%'
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return ' '
|
||||
|
||||
def _pacStr(self, dir):
|
||||
if dir == Directions.NORTH:
|
||||
return 'v'
|
||||
if dir == Directions.SOUTH:
|
||||
return '^'
|
||||
if dir == Directions.WEST:
|
||||
return '>'
|
||||
return '<'
|
||||
|
||||
def _ghostStr(self, dir):
|
||||
return 'G'
|
||||
if dir == Directions.NORTH:
|
||||
return 'M'
|
||||
if dir == Directions.SOUTH:
|
||||
return 'W'
|
||||
if dir == Directions.WEST:
|
||||
return '3'
|
||||
return 'E'
|
||||
|
||||
def initialize(self, layout, numGhostAgents):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Creates an initial game state from a layout array (see layout.py).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.food = layout.food.copy()
|
||||
#self.capsules = []
|
||||
self.capsules = layout.capsules[:]
|
||||
self.layout = layout
|
||||
self.score = 0
|
||||
self.scoreChange = 0
|
||||
|
||||
self.agentStates = []
|
||||
numGhosts = 0
|
||||
|
||||
## Randomize which ghosts appear
|
||||
#agentPositions = layout.agentPositions
|
||||
#random.shuffle(agentPositions)
|
||||
|
||||
for isPacman, pos in layout.agentPositions:
|
||||
if not isPacman:
|
||||
if numGhosts == numGhostAgents:
|
||||
continue # Max ghosts reached already
|
||||
else:
|
||||
numGhosts += 1
|
||||
self.agentStates.append(AgentState(
|
||||
Configuration(pos, Directions.STOP), isPacman))
|
||||
self._eaten = [False for a in self.agentStates]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import boinc
|
||||
_BOINC_ENABLED = True
|
||||
except:
|
||||
_BOINC_ENABLED = False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Game:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
The Game manages the control flow, soliciting actions from agents.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, agents, display, rules, startingIndex=0, muteAgents=False, catchExceptions=False):
|
||||
self.agentCrashed = False
|
||||
self.agents = agents
|
||||
self.display = display
|
||||
self.rules = rules
|
||||
self.startingIndex = startingIndex
|
||||
self.gameOver = False
|
||||
self.muteAgents = muteAgents
|
||||
self.catchExceptions = catchExceptions
|
||||
self.moveHistory = []
|
||||
self.totalAgentTimes = [0 for agent in agents]
|
||||
self.totalAgentTimeWarnings = [0 for agent in agents]
|
||||
self.agentTimeout = False
|
||||
import io
|
||||
self.agentOutput = [io.StringIO() for agent in agents]
|
||||
|
||||
def getProgress(self):
|
||||
if self.gameOver:
|
||||
return 1.0
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return self.rules.getProgress(self)
|
||||
|
||||
def _agentCrash(self, agentIndex, quiet=False):
|
||||
"Helper method for handling agent crashes"
|
||||
if not quiet:
|
||||
traceback.print_exc()
|
||||
self.gameOver = True
|
||||
self.agentCrashed = True
|
||||
self.rules.agentCrash(self, agentIndex)
|
||||
|
||||
OLD_STDOUT = None
|
||||
OLD_STDERR = None
|
||||
|
||||
def mute(self, agentIndex):
|
||||
if not self.muteAgents:
|
||||
return
|
||||
global OLD_STDOUT, OLD_STDERR
|
||||
import io
|
||||
OLD_STDOUT = sys.stdout
|
||||
OLD_STDERR = sys.stderr
|
||||
sys.stdout = self.agentOutput[agentIndex]
|
||||
sys.stderr = self.agentOutput[agentIndex]
|
||||
|
||||
def unmute(self):
|
||||
if not self.muteAgents:
|
||||
return
|
||||
global OLD_STDOUT, OLD_STDERR
|
||||
# Revert stdout/stderr to originals
|
||||
sys.stdout = OLD_STDOUT
|
||||
sys.stderr = OLD_STDERR
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Main control loop for game play.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.display.initialize(self.state.data)
|
||||
self.numMoves = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# self.display.initialize(self.state.makeObservation(1).data)
|
||||
# inform learning agents of the game start
|
||||
for i in range(len(self.agents)):
|
||||
agent = self.agents[i]
|
||||
if not agent:
|
||||
self.mute(i)
|
||||
# this is a null agent, meaning it failed to load
|
||||
# the other team wins
|
||||
print("Agent %d failed to load" % i, file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
self._agentCrash(i, quiet=True)
|
||||
return
|
||||
if ("registerInitialState" in dir(agent)):
|
||||
self.mute(i)
|
||||
if self.catchExceptions:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
timed_func = TimeoutFunction(agent.registerInitialState, int(self.rules.getMaxStartupTime(i)))
|
||||
try:
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
timed_func(self.state.deepCopy())
|
||||
time_taken = time.time() - start_time
|
||||
self.totalAgentTimes[i] += time_taken
|
||||
except TimeoutFunctionException:
|
||||
print("Agent %d ran out of time on startup!" % i, file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
self.agentTimeout = True
|
||||
self._agentCrash(i, quiet=True)
|
||||
return
|
||||
except Exception as data:
|
||||
self._agentCrash(i, quiet=False)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
return
|
||||
else:
|
||||
agent.registerInitialState(self.state.deepCopy())
|
||||
# TODO: could this exceed the total time
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
|
||||
agentIndex = self.startingIndex
|
||||
numAgents = len(self.agents)
|
||||
|
||||
while not self.gameOver:
|
||||
# Fetch the next agent
|
||||
agent = self.agents[agentIndex]
|
||||
move_time = 0
|
||||
skip_action = False
|
||||
# Generate an observation of the state
|
||||
if 'observationFunction' in dir(agent):
|
||||
self.mute(agentIndex)
|
||||
if self.catchExceptions:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
timed_func = TimeoutFunction(agent.observationFunction, int(self.rules.getMoveTimeout(agentIndex)))
|
||||
try:
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
observation = timed_func(self.state.deepCopy())
|
||||
except TimeoutFunctionException:
|
||||
skip_action = True
|
||||
move_time += time.time() - start_time
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
except Exception as data:
|
||||
self._agentCrash(agentIndex, quiet=False)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
return
|
||||
else:
|
||||
observation = agent.observationFunction(self.state.deepCopy())
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
observation = self.state.deepCopy()
|
||||
|
||||
# Solicit an action
|
||||
action = None
|
||||
self.mute(agentIndex)
|
||||
if self.catchExceptions:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
#timed_func = TimeoutFunction(agent.getAction, int(self.rules.getMoveTimeout(agentIndex)) - int(move_time))
|
||||
timed_func = TimeoutFunction(agent.getAction, 1800)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
if skip_action:
|
||||
raise TimeoutFunctionException()
|
||||
action = timed_func(observation)
|
||||
if agent.live_checking:
|
||||
yield action[1]
|
||||
action = action[0]
|
||||
except TimeoutFunctionException:
|
||||
print("Agent %d timed out on a single move!" % agentIndex, file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
self.agentTimeout = True
|
||||
self._agentCrash(agentIndex, quiet=True)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
move_time += time.time() - start_time
|
||||
|
||||
if move_time > self.rules.getMoveWarningTime(agentIndex):
|
||||
self.totalAgentTimeWarnings[agentIndex] += 1
|
||||
print("Agent %d took too long to make a move! This is warning %d" % (agentIndex, self.totalAgentTimeWarnings[agentIndex]), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
if self.totalAgentTimeWarnings[agentIndex] > self.rules.getMaxTimeWarnings(agentIndex):
|
||||
print("Agent %d exceeded the maximum number of warnings: %d" % (agentIndex, self.totalAgentTimeWarnings[agentIndex]), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
self.agentTimeout = True
|
||||
self._agentCrash(agentIndex, quiet=True)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
self.totalAgentTimes[agentIndex] += move_time
|
||||
#print("Agent: %d, time: %f, total: %f" % (agentIndex, move_time, self.totalAgentTimes[agentIndex]))
|
||||
if self.totalAgentTimes[agentIndex] > self.rules.getMaxTotalTime(agentIndex):
|
||||
print("Agent %d ran out of time! (time: %1.2f)" % (agentIndex, self.totalAgentTimes[agentIndex]), file=sys.stderr)
|
||||
self.agentTimeout = True
|
||||
self._agentCrash(agentIndex, quiet=True)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
return
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
except Exception as data:
|
||||
self._agentCrash(agentIndex)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
return
|
||||
else:
|
||||
action = agent.getAction(observation)
|
||||
|
||||
# Hack for layouts without food
|
||||
if action == "EndGame":
|
||||
print("Ending game")
|
||||
break
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
|
||||
# Execute the action
|
||||
self.moveHistory.append((agentIndex, action))
|
||||
if self.catchExceptions:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.state = self.state.generateSuccessor( agentIndex, action )
|
||||
except Exception as data:
|
||||
self.mute(agentIndex)
|
||||
self._agentCrash(agentIndex)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
return
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.state = self.state.generateSuccessor(agentIndex, action)
|
||||
|
||||
# Change the display
|
||||
self.display.update(self.state.data)
|
||||
###idx = agentIndex - agentIndex % 2 + 1
|
||||
###self.display.update( self.state.makeObservation(idx).data )
|
||||
|
||||
# Allow for game specific conditions (winning, losing, etc.)
|
||||
self.rules.process(self.state, self)
|
||||
# Track progress
|
||||
if agentIndex == numAgents + 1:
|
||||
self.numMoves += 1
|
||||
# Next agent
|
||||
agentIndex = (agentIndex + 1) % numAgents
|
||||
|
||||
if _BOINC_ENABLED:
|
||||
boinc.set_fraction_done(self.getProgress())
|
||||
|
||||
# inform a learning agent of the game result
|
||||
for agentIndex, agent in enumerate(self.agents):
|
||||
if "final" in dir(agent):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.mute(agentIndex)
|
||||
agent.final(self.state)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
except Exception as data:
|
||||
if not self.catchExceptions:
|
||||
raise
|
||||
self._agentCrash(agentIndex)
|
||||
self.unmute()
|
||||
return
|
||||
self.display.finish()
|
||||
yield
|
||||
90
logic/ghostAgents.py
Normal file
90
logic/ghostAgents.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
# ghostAgents.py
|
||||
# --------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from game import Agent
|
||||
from game import Actions
|
||||
from game import Directions
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from util import manhattanDistance
|
||||
import util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GhostAgent(Agent):
|
||||
def __init__(self, index):
|
||||
self.index = index
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
dist = self.getDistribution(state)
|
||||
if len(dist) == 0:
|
||||
return Directions.STOP
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return util.chooseFromDistribution(dist)
|
||||
|
||||
def getDistribution(self, state):
|
||||
"Returns a Counter encoding a distribution over actions from the provided state."
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class RandomGhost(GhostAgent):
|
||||
"A ghost that chooses a legal action uniformly at random."
|
||||
|
||||
def getDistribution(self, state):
|
||||
dist = util.Counter()
|
||||
for a in state.getLegalActions(self.index):
|
||||
dist[a] = 1.0
|
||||
dist.normalize()
|
||||
return dist
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DirectionalGhost(GhostAgent):
|
||||
"A ghost that prefers to rush Pacman, or flee when scared."
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, index, prob_attack=0.8, prob_scaredFlee=0.8):
|
||||
self.index = index
|
||||
self.prob_attack = prob_attack
|
||||
self.prob_scaredFlee = prob_scaredFlee
|
||||
|
||||
def getDistribution(self, state):
|
||||
# Read variables from state
|
||||
ghostState = state.getGhostState(self.index)
|
||||
legalActions = state.getLegalActions(self.index)
|
||||
pos = state.getGhostPosition(self.index)
|
||||
isScared = ghostState.scaredTimer > 0
|
||||
|
||||
speed = 1
|
||||
if isScared:
|
||||
speed = 0.5
|
||||
|
||||
actionVectors = [Actions.directionToVector( a, speed ) for a in legalActions]
|
||||
newPositions = [(pos[0]+a[0], pos[1]+a[1]) for a in actionVectors]
|
||||
pacmanPosition = state.getPacmanPosition()
|
||||
|
||||
# Select best actions given the state
|
||||
distancesToPacman = [manhattanDistance( pos, pacmanPosition ) for pos in newPositions]
|
||||
if isScared:
|
||||
bestScore = max(distancesToPacman)
|
||||
bestProb = self.prob_scaredFlee
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bestScore = min(distancesToPacman)
|
||||
bestProb = self.prob_attack
|
||||
bestActions = [action for action, distance in zip( legalActions, distancesToPacman ) if distance == bestScore]
|
||||
|
||||
# Construct distribution
|
||||
dist = util.Counter()
|
||||
for a in bestActions:
|
||||
dist[a] = bestProb / len(bestActions)
|
||||
for a in legalActions:
|
||||
dist[a] += (1-bestProb) / len(legalActions)
|
||||
dist.normalize()
|
||||
return dist
|
||||
323
logic/grading.py
Normal file
323
logic/grading.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,323 @@
|
||||
# grading.py
|
||||
# ----------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"Common code for autograders"
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import html
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import traceback
|
||||
import pdb
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||
import util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Grades:
|
||||
"A data structure for project grades, along with formatting code to display them"
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, projectName, questionsAndMaxesList,
|
||||
gsOutput=False, edxOutput=False, muteOutput=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Defines the grading scheme for a project
|
||||
projectName: project name
|
||||
questionsAndMaxesDict: a list of (question name, max points per question)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.questions = [el[0] for el in questionsAndMaxesList]
|
||||
self.maxes = dict(questionsAndMaxesList)
|
||||
self.points = Counter()
|
||||
self.messages = dict([(q, []) for q in self.questions])
|
||||
self.project = projectName
|
||||
self.start = time.localtime()[1:6]
|
||||
self.sane = True # Sanity checks
|
||||
self.currentQuestion = None # Which question we're grading
|
||||
self.edxOutput = edxOutput
|
||||
self.gsOutput = gsOutput # GradeScope output
|
||||
self.mute = muteOutput
|
||||
self.prereqs = defaultdict(set)
|
||||
|
||||
# print 'Autograder transcript for %s' % self.project
|
||||
print('Starting on %d-%d at %d:%02d:%02d' % self.start)
|
||||
|
||||
def addPrereq(self, question, prereq):
|
||||
self.prereqs[question].add(prereq)
|
||||
|
||||
def grade(self, gradingModule, exceptionMap={}, bonusPic=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Grades each question
|
||||
gradingModule: the module with all the grading functions (pass in with sys.modules[__name__])
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
completedQuestions = set([])
|
||||
for q in self.questions:
|
||||
print('\nQuestion %s' % q)
|
||||
print('=' * (9 + len(q)))
|
||||
print()
|
||||
self.currentQuestion = q
|
||||
|
||||
incompleted = self.prereqs[q].difference(completedQuestions)
|
||||
if len(incompleted) > 0:
|
||||
prereq = incompleted.pop()
|
||||
print( \
|
||||
"""*** NOTE: Make sure to complete Question %s before working on Question %s,
|
||||
*** because Question %s builds upon your answer for Question %s.
|
||||
""" % (prereq, q, q, prereq))
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
if self.mute: util.mutePrint()
|
||||
try:
|
||||
util.TimeoutFunction(getattr(gradingModule, q), 1800)(self) # Call the question's function
|
||||
# TimeoutFunction(getattr(gradingModule, q),1200)(self) # Call the question's function
|
||||
except Exception as inst: # originally, Exception, inst
|
||||
self.addExceptionMessage(q, inst, traceback)
|
||||
self.addErrorHints(exceptionMap, inst, q[1])
|
||||
except:
|
||||
self.fail('FAIL: Terminated with a string exception.')
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
if self.mute: util.unmutePrint()
|
||||
|
||||
if self.points[q] >= self.maxes[q]:
|
||||
completedQuestions.add(q)
|
||||
|
||||
print('\n### Question %s: %d/%d ###\n' % (q, self.points[q], self.maxes[q]))
|
||||
|
||||
print('\nFinished at %d:%02d:%02d' % time.localtime()[3:6])
|
||||
print("\nProvisional grades\n==================")
|
||||
|
||||
for q in self.questions:
|
||||
print('Question %s: %d/%d' % (q, self.points[q], self.maxes[q]))
|
||||
print('------------------')
|
||||
print('Total: %d/%d' % (self.points.totalCount(), sum(self.maxes.values())))
|
||||
if bonusPic and self.points.totalCount() == 25:
|
||||
print("""
|
||||
|
||||
ALL HAIL GRANDPAC.
|
||||
LONG LIVE THE GHOSTBUSTING KING.
|
||||
|
||||
--- ---- ---
|
||||
| \ / + \ / |
|
||||
| + \--/ \--/ + |
|
||||
| + + |
|
||||
| + + + |
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
\ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
\ / @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
V \ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
\ / @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
V @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
/\ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
/ \ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
/\ / @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
/ \ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
/ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@
|
||||
|
||||
""")
|
||||
print("""
|
||||
Your grades are NOT yet registered. To register your grades, make sure
|
||||
to follow your instructor's guidelines to receive credit on your project.
|
||||
""")
|
||||
|
||||
if self.edxOutput:
|
||||
self.produceOutput()
|
||||
if self.gsOutput:
|
||||
self.produceGradeScopeOutput()
|
||||
|
||||
def addExceptionMessage(self, q, inst, traceback):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Method to format the exception message, this is more complicated because
|
||||
we need to html.escape the traceback but wrap the exception in a <pre> tag
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.fail('FAIL: Exception raised: %s' % inst)
|
||||
self.addMessage('')
|
||||
for line in traceback.format_exc().split('\n'):
|
||||
self.addMessage(line)
|
||||
|
||||
def addErrorHints(self, exceptionMap, errorInstance, questionNum):
|
||||
typeOf = str(type(errorInstance))
|
||||
questionName = 'q' + questionNum
|
||||
errorHint = ''
|
||||
|
||||
# question specific error hints
|
||||
if exceptionMap.get(questionName):
|
||||
questionMap = exceptionMap.get(questionName)
|
||||
if (questionMap.get(typeOf)):
|
||||
errorHint = questionMap.get(typeOf)
|
||||
# fall back to general error messages if a question specific
|
||||
# one does not exist
|
||||
if (exceptionMap.get(typeOf)):
|
||||
errorHint = exceptionMap.get(typeOf)
|
||||
|
||||
# dont include the HTML if we have no error hint
|
||||
if not errorHint:
|
||||
return ''
|
||||
|
||||
for line in errorHint.split('\n'):
|
||||
self.addMessage(line)
|
||||
|
||||
def produceGradeScopeOutput(self):
|
||||
out_dct = {}
|
||||
|
||||
# total of entire submission
|
||||
total_possible = sum(self.maxes.values())
|
||||
total_score = sum(self.points.values())
|
||||
out_dct['score'] = total_score
|
||||
out_dct['max_score'] = total_possible
|
||||
out_dct['output'] = "Total score (%d / %d)" % (total_score, total_possible)
|
||||
|
||||
# individual tests
|
||||
tests_out = []
|
||||
for name in self.questions:
|
||||
test_out = {}
|
||||
# test name
|
||||
test_out['name'] = name
|
||||
# test score
|
||||
test_out['score'] = self.points[name]
|
||||
test_out['max_score'] = self.maxes[name]
|
||||
# others
|
||||
is_correct = self.points[name] >= self.maxes[name]
|
||||
test_out['output'] = " Question {num} ({points}/{max}) {correct}".format(
|
||||
num=(name[1] if len(name) == 2 else name),
|
||||
points=test_out['score'],
|
||||
max=test_out['max_score'],
|
||||
correct=('X' if not is_correct else ''),
|
||||
)
|
||||
test_out['tags'] = []
|
||||
tests_out.append(test_out)
|
||||
out_dct['tests'] = tests_out
|
||||
|
||||
# file output
|
||||
with open('gradescope_response.json', 'w') as outfile:
|
||||
json.dump(out_dct, outfile)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
def produceOutput(self):
|
||||
edxOutput = open('edx_response.html', 'w')
|
||||
edxOutput.write("<div>")
|
||||
|
||||
# first sum
|
||||
total_possible = sum(self.maxes.values())
|
||||
total_score = sum(self.points.values())
|
||||
checkOrX = '<span class="incorrect"/>'
|
||||
if (total_score >= total_possible):
|
||||
checkOrX = '<span class="correct"/>'
|
||||
header = """
|
||||
<h3>
|
||||
Total score ({total_score} / {total_possible})
|
||||
</h3>
|
||||
""".format(total_score=total_score,
|
||||
total_possible=total_possible,
|
||||
checkOrX=checkOrX
|
||||
)
|
||||
edxOutput.write(header)
|
||||
|
||||
for q in self.questions:
|
||||
if len(q) == 2:
|
||||
name = q[1]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
name = q
|
||||
checkOrX = '<span class="incorrect"/>'
|
||||
if (self.points[q] >= self.maxes[q]):
|
||||
checkOrX = '<span class="correct"/>'
|
||||
# messages = '\n<br/>\n'.join(self.messages[q])
|
||||
messages = "<pre>%s</pre>" % '\n'.join(self.messages[q])
|
||||
output = """
|
||||
<div class="test">
|
||||
<section>
|
||||
<div class="shortform">
|
||||
Question {q} ({points}/{max}) {checkOrX}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="longform">
|
||||
{messages}
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</section>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
""".format(q=name,
|
||||
max=self.maxes[q],
|
||||
messages=messages,
|
||||
checkOrX=checkOrX,
|
||||
points=self.points[q]
|
||||
)
|
||||
# print "*** output for Question %s " % q[1]
|
||||
# print output
|
||||
edxOutput.write(output)
|
||||
edxOutput.write("</div>")
|
||||
edxOutput.close()
|
||||
edxOutput = open('edx_grade', 'w')
|
||||
edxOutput.write(str(self.points.totalCount()))
|
||||
edxOutput.close()
|
||||
|
||||
def fail(self, message, raw=False):
|
||||
"Sets sanity check bit to false and outputs a message"
|
||||
self.sane = False
|
||||
self.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
self.addMessage(message, raw)
|
||||
|
||||
def assignZeroCredit(self):
|
||||
self.points[self.currentQuestion] = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def addPoints(self, amt):
|
||||
self.points[self.currentQuestion] += amt
|
||||
|
||||
def deductPoints(self, amt):
|
||||
self.points[self.currentQuestion] -= amt
|
||||
|
||||
def assignFullCredit(self, message="", raw=False):
|
||||
self.points[self.currentQuestion] = self.maxes[self.currentQuestion]
|
||||
if message != "":
|
||||
self.addMessage(message, raw)
|
||||
|
||||
def addMessage(self, message, raw=False):
|
||||
if not raw:
|
||||
# We assume raw messages, formatted for HTML, are printed separately
|
||||
if self.mute: util.unmutePrint()
|
||||
print('*** ' + message)
|
||||
if self.mute: util.mutePrint()
|
||||
message = html.escape(message)
|
||||
self.messages[self.currentQuestion].append(message)
|
||||
|
||||
def addMessageToEmail(self, message):
|
||||
print("WARNING**** addMessageToEmail is deprecated %s" % message)
|
||||
for line in message.split('\n'):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# print '%%% ' + line + ' %%%'
|
||||
# self.messages[self.currentQuestion].append(line)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Counter(dict):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Dict with default 0
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __getitem__(self, idx):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return dict.__getitem__(self, idx)
|
||||
except KeyError:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
def totalCount(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the sum of counts for all keys.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return sum(self.values())
|
||||
|
||||
792
logic/graphicsDisplay.py
Normal file
792
logic/graphicsDisplay.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,792 @@
|
||||
# graphicsDisplay.py
|
||||
# ------------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from graphicsUtils import *
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from game import Directions
|
||||
|
||||
###########################
|
||||
# GRAPHICS DISPLAY CODE #
|
||||
###########################
|
||||
|
||||
# Most code by Dan Klein and John Denero written or rewritten for cs188, UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# Some code from a Pacman implementation by LiveWires, and used / modified with permission.
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_GRID_SIZE = 30.0
|
||||
INFO_PANE_HEIGHT = 35
|
||||
BACKGROUND_COLOR = formatColor(0, 0, 0)
|
||||
WALL_COLOR = formatColor(0.0/255.0, 51.0/255.0, 255.0/255.0)
|
||||
INFO_PANE_COLOR = formatColor(.4, .4, 0)
|
||||
SCORE_COLOR = formatColor(.9, .9, .9)
|
||||
PACMAN_OUTLINE_WIDTH = 2
|
||||
PACMAN_CAPTURE_OUTLINE_WIDTH = 4
|
||||
|
||||
GHOST_COLORS = []
|
||||
GHOST_COLORS.append(formatColor(.9, 0, 0)) # Red
|
||||
GHOST_COLORS.append(formatColor(0, .3, .9)) # Blue
|
||||
GHOST_COLORS.append(formatColor(.98, .41, .07)) # Orange
|
||||
GHOST_COLORS.append(formatColor(.1, .75, .7)) # Green
|
||||
GHOST_COLORS.append(formatColor(1.0, 0.6, 0.0)) # Yellow
|
||||
GHOST_COLORS.append(formatColor(.4, 0.13, 0.91)) # Purple
|
||||
|
||||
TEAM_COLORS = GHOST_COLORS[:2]
|
||||
|
||||
GHOST_SHAPE = [
|
||||
(0, 0.3),
|
||||
(0.25, 0.75),
|
||||
(0.5, 0.3),
|
||||
(0.75, 0.75),
|
||||
(0.75, -0.5),
|
||||
(0.5, -0.75),
|
||||
(-0.5, -0.75),
|
||||
(-0.75, -0.5),
|
||||
(-0.75, 0.75),
|
||||
(-0.5, 0.3),
|
||||
(-0.25, 0.75)
|
||||
]
|
||||
GHOST_SIZE = 0.65
|
||||
SCARED_COLOR = formatColor(1, 1, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
GHOST_VEC_COLORS = [colorToVector(c) for c in GHOST_COLORS]
|
||||
|
||||
PACMAN_COLOR = formatColor(255.0/255.0, 255.0/255.0, 61.0/255)
|
||||
PALE_PACMAN_COLOR = formatColor(255.0/255.0, 255.0/255.0, 255.0/255)
|
||||
PACMAN_SCALE = 0.5
|
||||
#pacman_speed = 0.25
|
||||
|
||||
# Food
|
||||
FOOD_COLOR = formatColor(1, 1, 1)
|
||||
FOOD_SIZE = 0.1
|
||||
|
||||
# Laser
|
||||
LASER_COLOR = formatColor(1, 0, 0)
|
||||
LASER_SIZE = 0.02
|
||||
|
||||
# Capsule graphics
|
||||
CAPSULE_COLOR = formatColor(1, 1, 1)
|
||||
CAPSULE_SIZE = 0.25
|
||||
|
||||
# Drawing walls
|
||||
WALL_RADIUS = 0.15
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class InfoPane:
|
||||
def __init__(self, layout, gridSize):
|
||||
self.gridSize = gridSize
|
||||
self.width = (layout.width) * gridSize
|
||||
self.base = (layout.height + 1) * gridSize
|
||||
self.height = INFO_PANE_HEIGHT
|
||||
self.fontSize = 24
|
||||
self.textColor = PACMAN_COLOR
|
||||
self.drawPane()
|
||||
|
||||
def toScreen(self, pos, y=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Translates a point relative from the bottom left of the info pane.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if y == None:
|
||||
x, y = pos
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x = pos
|
||||
|
||||
x = self.gridSize + x # Margin
|
||||
y = self.base + y
|
||||
return x, y
|
||||
|
||||
def drawPane(self):
|
||||
self.scoreText = text(self.toScreen(0, 0), self.textColor, "SCORE: 0", "Times", self.fontSize, "bold")
|
||||
|
||||
def initializeGhostDistances(self, distances):
|
||||
self.ghostDistanceText = []
|
||||
|
||||
size = 20
|
||||
if self.width < 240:
|
||||
size = 12
|
||||
if self.width < 160:
|
||||
size = 10
|
||||
|
||||
for i, d in enumerate(distances):
|
||||
t = text(self.toScreen(self.width//2 + self.width//8 * i, 0), GHOST_COLORS[i+1], d, "Times", size, "bold")
|
||||
self.ghostDistanceText.append(t)
|
||||
|
||||
def updateScore(self, score):
|
||||
changeText(self.scoreText, "SCORE: % 4d" % score)
|
||||
|
||||
def setTeam(self, isBlue):
|
||||
text = "RED TEAM"
|
||||
if isBlue:
|
||||
text = "BLUE TEAM"
|
||||
self.teamText = text(self.toScreen(300, 0), self.textColor, text, "Times", self.fontSize, "bold")
|
||||
|
||||
def updateGhostDistances(self, distances):
|
||||
if len(distances) == 0:
|
||||
return
|
||||
if 'ghostDistanceText' not in dir(self):
|
||||
self.initializeGhostDistances(distances)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for i, d in enumerate(distances):
|
||||
changeText(self.ghostDistanceText[i], d)
|
||||
|
||||
def drawGhost(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def drawPacman(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def drawWarning(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def clearIcon(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def updateMessage(self, message):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def clearMessage(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PacmanGraphics:
|
||||
def __init__(self, zoom=1.0, frameTime=0.0, capture=False, render_walls_beforehand=True):
|
||||
self.have_window = 0
|
||||
self.currentGhostImages = {}
|
||||
self.pacmanImage = None
|
||||
self.zoom = zoom
|
||||
self.gridSize = DEFAULT_GRID_SIZE * zoom
|
||||
self.capture = capture
|
||||
self.frameTime = frameTime
|
||||
self.render_walls_beforehand = render_walls_beforehand
|
||||
|
||||
def checkNullDisplay(self):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def initialize(self, state, isBlue=False):
|
||||
self.isBlue = isBlue
|
||||
self.startGraphics(state)
|
||||
|
||||
# self.drawDistributions(state)
|
||||
self.distributionImages = None # Initialized lazily
|
||||
self.drawStaticObjects(state)
|
||||
self.drawAgentObjects(state)
|
||||
|
||||
# Information
|
||||
self.previousState = state
|
||||
|
||||
def startGraphics(self, state):
|
||||
self.layout = state.layout
|
||||
layout = self.layout
|
||||
self.width = layout.width
|
||||
self.height = layout.height
|
||||
self.make_window(self.width, self.height)
|
||||
self.infoPane = InfoPane(layout, self.gridSize)
|
||||
self.currentState = layout
|
||||
|
||||
def drawDistributions(self, state):
|
||||
walls = state.layout.walls
|
||||
dist = []
|
||||
for x in range(walls.width):
|
||||
distx = []
|
||||
dist.append(distx)
|
||||
for y in range(walls.height):
|
||||
(screen_x, screen_y) = self.to_screen((x, y))
|
||||
block = square((screen_x, screen_y),
|
||||
0.5 * self.gridSize,
|
||||
color=BACKGROUND_COLOR,
|
||||
filled=1, behind=2)
|
||||
distx.append(block)
|
||||
self.distributionImages = dist
|
||||
|
||||
def drawStaticObjects(self, state):
|
||||
layout = self.layout
|
||||
if self.render_walls_beforehand:
|
||||
print("rendering walls beforehand")
|
||||
self.drawWalls(layout.walls)
|
||||
self.food = self.drawFood(layout.food)
|
||||
self.capsules = self.drawCapsules(layout.capsules)
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def drawAgentObjects(self, state):
|
||||
self.agentImages = [] # (agentState, image)
|
||||
for index, agent in enumerate(state.agentStates):
|
||||
if agent.isPacman:
|
||||
image = self.drawPacman(agent, index)
|
||||
self.agentImages.append((agent, image))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image = self.drawGhost(agent, index)
|
||||
self.agentImages.append((agent, image))
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def swapImages(self, agentIndex, newState):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Changes an image from a ghost to a pacman or vis versa (for capture)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
prevState, prevImage = self.agentImages[agentIndex]
|
||||
for item in prevImage:
|
||||
remove_from_screen(item)
|
||||
if newState.isPacman:
|
||||
image = self.drawPacman(newState, agentIndex)
|
||||
self.agentImages[agentIndex] = (newState, image)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
image = self.drawGhost(newState, agentIndex)
|
||||
self.agentImages[agentIndex] = (newState, image)
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def update(self, newState):
|
||||
agentIndex = newState._agentMoved
|
||||
agentState = newState.agentStates[agentIndex]
|
||||
|
||||
if self.agentImages[agentIndex][0].isPacman != agentState.isPacman:
|
||||
self.swapImages(agentIndex, agentState)
|
||||
prevState, prevImage = self.agentImages[agentIndex]
|
||||
if agentState.isPacman:
|
||||
self.animatePacman(agentState, prevState, prevImage)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.moveGhost(agentState, agentIndex, prevState, prevImage)
|
||||
self.agentImages[agentIndex] = (agentState, prevImage)
|
||||
|
||||
if newState._foodEaten != None:
|
||||
self.removeFood(newState._foodEaten, self.food)
|
||||
if newState._capsuleEaten != None:
|
||||
self.removeCapsule(newState._capsuleEaten, self.capsules)
|
||||
self.infoPane.updateScore(newState.score)
|
||||
if 'ghostDistances' in dir(newState):
|
||||
self.infoPane.updateGhostDistances(newState.ghostDistances)
|
||||
|
||||
def make_window(self, width, height):
|
||||
grid_width = (width-1) * self.gridSize
|
||||
grid_height = (height-1) * self.gridSize
|
||||
screen_width = 2*self.gridSize + grid_width
|
||||
screen_height = 2*self.gridSize + grid_height + INFO_PANE_HEIGHT
|
||||
|
||||
begin_graphics(screen_width,
|
||||
screen_height,
|
||||
BACKGROUND_COLOR,
|
||||
"Pacman")
|
||||
|
||||
def drawPacman(self, pacman, index):
|
||||
position = self.getPosition(pacman)
|
||||
screen_point = self.to_screen(position)
|
||||
endpoints = self.getEndpoints(self.getDirection(pacman))
|
||||
|
||||
width = PACMAN_OUTLINE_WIDTH
|
||||
outlineColor = PACMAN_COLOR
|
||||
fillColor = PACMAN_COLOR
|
||||
|
||||
if self.capture:
|
||||
outlineColor = TEAM_COLORS[index % 2]
|
||||
fillColor = GHOST_COLORS[index]
|
||||
width = PACMAN_CAPTURE_OUTLINE_WIDTH
|
||||
|
||||
return [circle(screen_point, PACMAN_SCALE * self.gridSize,
|
||||
fillColor=fillColor, outlineColor=outlineColor,
|
||||
endpoints=endpoints,
|
||||
width=width)]
|
||||
|
||||
def getEndpoints(self, direction, position=(0, 0)):
|
||||
x, y = position
|
||||
pos = x - int(x) + y - int(y)
|
||||
width = 30 + 80 * math.sin(math.pi * pos)
|
||||
|
||||
delta = width / 2
|
||||
if (direction == 'West'):
|
||||
endpoints = (180+delta, 180-delta)
|
||||
elif (direction == 'North'):
|
||||
endpoints = (90+delta, 90-delta)
|
||||
elif (direction == 'South'):
|
||||
endpoints = (270+delta, 270-delta)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
endpoints = (0+delta, 0-delta)
|
||||
return endpoints
|
||||
|
||||
def movePacman(self, position, direction, image):
|
||||
screenPosition = self.to_screen(position)
|
||||
endpoints = self.getEndpoints(direction, position)
|
||||
r = PACMAN_SCALE * self.gridSize
|
||||
moveCircle(image[0], screenPosition, r, endpoints)
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def animatePacman(self, pacman, prevPacman, image):
|
||||
if self.frameTime < 0:
|
||||
print('Press any key to step forward, "q" to play')
|
||||
keys = wait_for_keys()
|
||||
if 'q' in keys:
|
||||
self.frameTime = 0.1
|
||||
if self.frameTime > 0.01 or self.frameTime < 0:
|
||||
start = time.time()
|
||||
fx, fy = self.getPosition(prevPacman)
|
||||
px, py = self.getPosition(pacman)
|
||||
frames = 1.0
|
||||
for i in range(1, int(frames) + 1):
|
||||
pos = px*i/frames + fx*(frames-i)/frames, py*i/frames + fy*(frames-i)/frames
|
||||
self.movePacman(pos, self.getDirection(pacman), image)
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
sleep(abs(self.frameTime) / frames)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.movePacman(self.getPosition(pacman), self.getDirection(pacman), image)
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def getGhostColor(self, ghost, ghostIndex):
|
||||
if ghost.scaredTimer > 0:
|
||||
return SCARED_COLOR
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return GHOST_COLORS[ghostIndex % 6]
|
||||
|
||||
def drawGhost(self, ghost, agentIndex):
|
||||
pos = self.getPosition(ghost)
|
||||
dir = self.getDirection(ghost)
|
||||
(screen_x, screen_y) = (self.to_screen(pos))
|
||||
coords = []
|
||||
for (x, y) in GHOST_SHAPE:
|
||||
coords.append((x*self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE + screen_x,
|
||||
y*self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE + screen_y))
|
||||
|
||||
colour = self.getGhostColor(ghost, agentIndex)
|
||||
body = polygon(coords, colour, filled=1)
|
||||
WHITE = formatColor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
|
||||
BLACK = formatColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
|
||||
|
||||
dx = 0
|
||||
dy = 0
|
||||
if dir == 'North':
|
||||
dy = -0.2
|
||||
if dir == 'South':
|
||||
dy = 0.2
|
||||
if dir == 'East':
|
||||
dx = 0.2
|
||||
if dir == 'West':
|
||||
dx = -0.2
|
||||
leftEye = circle((screen_x + self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(-0.3+dx/1.5),
|
||||
screen_y - self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3-dy/1.5)),
|
||||
self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*0.2, WHITE, WHITE)
|
||||
rightEye = circle((screen_x + self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3+dx/1.5),
|
||||
screen_y - self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3-dy/1.5)),
|
||||
self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*0.2, WHITE, WHITE)
|
||||
leftPupil = circle((screen_x + self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(-0.3+dx),
|
||||
screen_y - self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3-dy)),
|
||||
self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*0.08, BLACK, BLACK)
|
||||
rightPupil = circle((screen_x + self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3+dx),
|
||||
screen_y - self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3-dy)),
|
||||
self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*0.08, BLACK, BLACK)
|
||||
ghostImageParts = []
|
||||
ghostImageParts.append(body)
|
||||
ghostImageParts.append(leftEye)
|
||||
ghostImageParts.append(rightEye)
|
||||
ghostImageParts.append(leftPupil)
|
||||
ghostImageParts.append(rightPupil)
|
||||
|
||||
return ghostImageParts
|
||||
|
||||
def moveEyes(self, pos, dir, eyes):
|
||||
(screen_x, screen_y) = (self.to_screen(pos))
|
||||
dx = 0
|
||||
dy = 0
|
||||
if dir == 'North':
|
||||
dy = -0.2
|
||||
if dir == 'South':
|
||||
dy = 0.2
|
||||
if dir == 'East':
|
||||
dx = 0.2
|
||||
if dir == 'West':
|
||||
dx = -0.2
|
||||
moveCircle(eyes[0],(screen_x+self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(-0.3+dx/1.5), screen_y-self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3-dy/1.5)), self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*0.2)
|
||||
moveCircle(eyes[1],(screen_x+self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3+dx/1.5), screen_y-self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3-dy/1.5)), self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*0.2)
|
||||
moveCircle(eyes[2],(screen_x+self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(-0.3+dx), screen_y-self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3-dy)), self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*0.08)
|
||||
moveCircle(eyes[3],(screen_x+self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3+dx), screen_y-self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*(0.3-dy)), self.gridSize*GHOST_SIZE*0.08)
|
||||
|
||||
def moveGhost(self, ghost, ghostIndex, prevGhost, ghostImageParts):
|
||||
old_x, old_y = self.to_screen(self.getPosition(prevGhost))
|
||||
new_x, new_y = self.to_screen(self.getPosition(ghost))
|
||||
delta = new_x - old_x, new_y - old_y
|
||||
|
||||
for ghostImagePart in ghostImageParts:
|
||||
move_by(ghostImagePart, delta)
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
if ghost.scaredTimer > 0:
|
||||
color = SCARED_COLOR
|
||||
else:
|
||||
color = GHOST_COLORS[ghostIndex]
|
||||
edit(ghostImageParts[0], ('fill', color), ('outline', color))
|
||||
self.moveEyes(self.getPosition(ghost), self.getDirection(ghost), ghostImageParts[-4:])
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def getPosition(self, agentState):
|
||||
if agentState.configuration == None:
|
||||
return (-1000, -1000)
|
||||
return agentState.getPosition()
|
||||
|
||||
def getDirection(self, agentState):
|
||||
if agentState.configuration == None:
|
||||
return Directions.STOP
|
||||
return agentState.configuration.getDirection()
|
||||
|
||||
def finish(self):
|
||||
end_graphics()
|
||||
|
||||
def to_screen(self, point):
|
||||
(x, y) = point
|
||||
#y = self.height - y
|
||||
x = (x + 1)*self.gridSize
|
||||
y = (self.height - y)*self.gridSize
|
||||
return (x, y)
|
||||
|
||||
# Fixes some TK issue with off-center circles
|
||||
def to_screen2(self, point):
|
||||
(x, y) = point
|
||||
#y = self.height - y
|
||||
x = (x + 1)*self.gridSize
|
||||
y = (self.height - y)*self.gridSize
|
||||
return (x, y)
|
||||
|
||||
def drawWalls(self, wallMatrix, wallColor=None, obsMatrix=None):
|
||||
if not wallColor:
|
||||
wallColor = WALL_COLOR
|
||||
for xNum, x in enumerate(wallMatrix):
|
||||
if self.capture and (xNum * 2) < wallMatrix.width: wallColor = TEAM_COLORS[0]
|
||||
if self.capture and (xNum * 2) >= wallMatrix.width: wallColor = TEAM_COLORS[1]
|
||||
|
||||
for yNum, cell in enumerate(x):
|
||||
if cell: # There's a wall here
|
||||
pos = (xNum, yNum)
|
||||
if obsMatrix and not obsMatrix[xNum][yNum]:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
screen = self.to_screen(pos)
|
||||
screen2 = self.to_screen2(pos)
|
||||
|
||||
# draw each quadrant of the square based on adjacent walls
|
||||
wIsWall = self.isWall(xNum-1, yNum, wallMatrix)
|
||||
eIsWall = self.isWall(xNum+1, yNum, wallMatrix)
|
||||
nIsWall = self.isWall(xNum, yNum+1, wallMatrix)
|
||||
sIsWall = self.isWall(xNum, yNum-1, wallMatrix)
|
||||
nwIsWall = self.isWall(xNum-1, yNum+1, wallMatrix)
|
||||
swIsWall = self.isWall(xNum-1, yNum-1, wallMatrix)
|
||||
neIsWall = self.isWall(xNum+1, yNum+1, wallMatrix)
|
||||
seIsWall = self.isWall(xNum+1, yNum-1, wallMatrix)
|
||||
|
||||
# NE quadrant
|
||||
if (not nIsWall) and (not eIsWall):
|
||||
# inner circle
|
||||
circle(screen2, WALL_RADIUS * self.gridSize, wallColor, wallColor, (0,91), 'arc')
|
||||
if (nIsWall) and (not eIsWall):
|
||||
# vertical line
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*WALL_RADIUS, 0)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(-0.5)-1)), wallColor)
|
||||
if (not nIsWall) and (eIsWall):
|
||||
# horizontal line
|
||||
line(add(screen, (0, self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*0.5+1, self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS)), wallColor)
|
||||
if (nIsWall) and (eIsWall) and (not neIsWall):
|
||||
# outer circle
|
||||
circle(add(screen2, (self.gridSize*2*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(-2)*WALL_RADIUS)), WALL_RADIUS * self.gridSize-1, wallColor, wallColor, (180,271), 'arc')
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*2*WALL_RADIUS-1, self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*0.5+1, self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS)), wallColor)
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(-2)*WALL_RADIUS+1)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(-0.5))), wallColor)
|
||||
|
||||
# NW quadrant
|
||||
if (not nIsWall) and (not wIsWall):
|
||||
# inner circle
|
||||
circle(screen2, WALL_RADIUS * self.gridSize, wallColor, wallColor, (90,181), 'arc')
|
||||
if (nIsWall) and (not wIsWall):
|
||||
# vertical line
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS, 0)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(-0.5)-1)), wallColor)
|
||||
if (not nIsWall) and (wIsWall):
|
||||
# horizontal line
|
||||
line(add(screen, (0, self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-0.5)-1, self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS)), wallColor)
|
||||
if (nIsWall) and (wIsWall) and (not nwIsWall):
|
||||
# outer circle
|
||||
circle(add(screen2, (self.gridSize*(-2)*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(-2)*WALL_RADIUS)), WALL_RADIUS * self.gridSize-1, wallColor, wallColor, (270,361), 'arc')
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-2)*WALL_RADIUS+1, self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-0.5), self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS)), wallColor)
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(-2)*WALL_RADIUS+1)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(-0.5))), wallColor)
|
||||
|
||||
# SE quadrant
|
||||
if (not sIsWall) and (not eIsWall):
|
||||
# inner circle
|
||||
circle(screen2, WALL_RADIUS * self.gridSize, wallColor, wallColor, (270,361), 'arc')
|
||||
if (sIsWall) and (not eIsWall):
|
||||
# vertical line
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*WALL_RADIUS, 0)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(0.5)+1)), wallColor)
|
||||
if (not sIsWall) and (eIsWall):
|
||||
# horizontal line
|
||||
line(add(screen, (0, self.gridSize*(1)*WALL_RADIUS)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*0.5+1, self.gridSize*(1)*WALL_RADIUS)), wallColor)
|
||||
if (sIsWall) and (eIsWall) and (not seIsWall):
|
||||
# outer circle
|
||||
circle(add(screen2, (self.gridSize*2*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(2)*WALL_RADIUS)), WALL_RADIUS * self.gridSize-1, wallColor, wallColor, (90,181), 'arc')
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*2*WALL_RADIUS-1, self.gridSize*(1)*WALL_RADIUS)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*0.5, self.gridSize*(1)*WALL_RADIUS)), wallColor)
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(2)*WALL_RADIUS-1)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(0.5))), wallColor)
|
||||
|
||||
# SW quadrant
|
||||
if (not sIsWall) and (not wIsWall):
|
||||
# inner circle
|
||||
circle(screen2, WALL_RADIUS * self.gridSize, wallColor, wallColor, (180,271), 'arc')
|
||||
if (sIsWall) and (not wIsWall):
|
||||
# vertical line
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS, 0)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(0.5)+1)), wallColor)
|
||||
if (not sIsWall) and (wIsWall):
|
||||
# horizontal line
|
||||
line(add(screen, (0, self.gridSize*(1)*WALL_RADIUS)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-0.5)-1, self.gridSize*(1)*WALL_RADIUS)), wallColor)
|
||||
if (sIsWall) and (wIsWall) and (not swIsWall):
|
||||
# outer circle
|
||||
circle(add(screen2, (self.gridSize*(-2)*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(2)*WALL_RADIUS)), WALL_RADIUS * self.gridSize-1, wallColor, wallColor, (0,91), 'arc')
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-2)*WALL_RADIUS+1, self.gridSize*(1)*WALL_RADIUS)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-0.5), self.gridSize*(1)*WALL_RADIUS)), wallColor)
|
||||
line(add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(2)*WALL_RADIUS-1)), add(screen, (self.gridSize*(-1)*WALL_RADIUS, self.gridSize*(0.5))), wallColor)
|
||||
|
||||
def isWall(self, x, y, walls):
|
||||
if x < 0 or y < 0:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
if x >= walls.width or y >= walls.height:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return walls[x][y]
|
||||
|
||||
def drawFood(self, foodMatrix):
|
||||
foodImages = []
|
||||
color = FOOD_COLOR
|
||||
for xNum, x in enumerate(foodMatrix):
|
||||
if self.capture and (xNum * 2) <= foodMatrix.width:
|
||||
color = TEAM_COLORS[0]
|
||||
if self.capture and (xNum * 2) > foodMatrix.width:
|
||||
color = TEAM_COLORS[1]
|
||||
imageRow = []
|
||||
foodImages.append(imageRow)
|
||||
for yNum, cell in enumerate(x):
|
||||
if cell: # There's food here
|
||||
screen = self.to_screen((xNum, yNum))
|
||||
dot = circle(screen,
|
||||
FOOD_SIZE * self.gridSize,
|
||||
outlineColor=color, fillColor=color,
|
||||
width=1)
|
||||
imageRow.append(dot)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
imageRow.append(None)
|
||||
return foodImages
|
||||
|
||||
def drawCapsules(self, capsules):
|
||||
capsuleImages = {}
|
||||
for capsule in capsules:
|
||||
(screen_x, screen_y) = self.to_screen(capsule)
|
||||
dot = circle((screen_x, screen_y),
|
||||
CAPSULE_SIZE * self.gridSize,
|
||||
outlineColor=CAPSULE_COLOR,
|
||||
fillColor=CAPSULE_COLOR,
|
||||
width=1)
|
||||
capsuleImages[capsule] = dot
|
||||
return capsuleImages
|
||||
|
||||
def removeFood(self, cell, foodImages):
|
||||
x, y = cell
|
||||
remove_from_screen(foodImages[x][y])
|
||||
|
||||
def removeCapsule(self, cell, capsuleImages):
|
||||
x, y = cell
|
||||
remove_from_screen(capsuleImages[(x, y)])
|
||||
|
||||
def drawExpandedCells(self, cells, cellColor=[0.0, 1.0, 0.0]):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Draws an overlay of expanded grid positions for search agents
|
||||
"""
|
||||
n = float(len(cells))
|
||||
baseColor = [1.0, 0.0, 0.0]
|
||||
self.clearExpandedCells()
|
||||
self.expandedCells = []
|
||||
for k, cell in enumerate(cells):
|
||||
screenPos = self.to_screen(cell)
|
||||
cellColor = formatColor(*[(n-k) * c * .5 / n + .25 for c in baseColor])
|
||||
block = square(screenPos,
|
||||
0.5 * self.gridSize,
|
||||
color=cellColor,
|
||||
filled=1, behind=2)
|
||||
self.expandedCells.append(block)
|
||||
if self.frameTime < 0:
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def colorCircleCells(self, cells, fillColor=PALE_PACMAN_COLOR, direction="North", pacman_position=None):
|
||||
endpoints = self.getEndpoints(direction)
|
||||
|
||||
width = PACMAN_OUTLINE_WIDTH
|
||||
|
||||
n = float(len(cells))
|
||||
self.clearExpandedCells()
|
||||
self.expandedCells = []
|
||||
|
||||
cells = list(cells)
|
||||
if pacman_position:
|
||||
cells.remove(pacman_position)
|
||||
|
||||
for k, cell in enumerate(cells):
|
||||
screenPos = self.to_screen(cell)
|
||||
block = circle(screenPos, PACMAN_SCALE * self.gridSize,
|
||||
fillColor=fillColor, outlineColor=fillColor,
|
||||
endpoints=endpoints,
|
||||
width=width)
|
||||
self.expandedCells.append(block)
|
||||
if self.frameTime < 0:
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def colorCircleSquareCells(self, pacman_cells, square_cells=[],
|
||||
circleColor=PALE_PACMAN_COLOR, squareColor=formatColor(0.0, 0.0, 1.0),
|
||||
direction="North", pacman_position=None):
|
||||
endpoints = self.getEndpoints(direction)
|
||||
|
||||
width = PACMAN_OUTLINE_WIDTH
|
||||
|
||||
n = float(len(pacman_cells))
|
||||
self.clearExpandedCells()
|
||||
self.expandedCells = []
|
||||
|
||||
pacman_cells = list(pacman_cells)
|
||||
if pacman_position in pacman_cells:
|
||||
pacman_cells.remove(pacman_position)
|
||||
|
||||
for k, sq_cell in enumerate(square_cells):
|
||||
screenPos = self.to_screen(sq_cell)
|
||||
block = square(screenPos,
|
||||
0.5 * self.gridSize,
|
||||
color=squareColor,
|
||||
filled=1, behind=2)
|
||||
self.expandedCells.append(block)
|
||||
if self.frameTime < 0:
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
for k, pacman_cell in enumerate(pacman_cells):
|
||||
screenPos = self.to_screen(pacman_cell)
|
||||
cir = circle(screenPos, PACMAN_SCALE * self.gridSize,
|
||||
fillColor=circleColor, outlineColor=circleColor,
|
||||
endpoints=endpoints,
|
||||
width=width)
|
||||
self.expandedCells.append(cir)
|
||||
if self.frameTime < 0:
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def colorSquareCells(self, cells, baseColor=[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Draws an overlay of expanded grid positions for search agents
|
||||
"""
|
||||
n = float(len(cells))
|
||||
self.clearExpandedCells()
|
||||
self.expandedCells = []
|
||||
if isinstance(baseColor, list):
|
||||
cellColor = formatColor(*baseColor)
|
||||
for k, cell in enumerate(cells):
|
||||
screenPos = self.to_screen(cell)
|
||||
block = square(screenPos,
|
||||
0.5 * self.gridSize,
|
||||
color=cellColor,
|
||||
filled=1, behind=2)
|
||||
self.expandedCells.append(block)
|
||||
if self.frameTime < 0:
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
def clearExpandedCells(self):
|
||||
if 'expandedCells' in dir(self) and len(self.expandedCells) > 0:
|
||||
for cell in self.expandedCells:
|
||||
remove_from_screen(cell)
|
||||
|
||||
def clearCells(self, cells):
|
||||
for cell in cells:
|
||||
remove_from_screen(cell)
|
||||
|
||||
def updateDistributions(self, distributions):
|
||||
"Draws an agent's belief distributions"
|
||||
# copy all distributions so we don't change their state
|
||||
distributions = [x.copy() for x in distributions]
|
||||
if self.distributionImages == None:
|
||||
self.drawDistributions(self.previousState)
|
||||
for x in range(len(self.distributionImages)):
|
||||
for y in range(len(self.distributionImages[0])):
|
||||
image = self.distributionImages[x][y]
|
||||
weights = [dist[(x, y)] for dist in distributions]
|
||||
|
||||
if sum(weights) != 0:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# Fog of war
|
||||
color = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
|
||||
colors = GHOST_VEC_COLORS[1:] # With Pacman
|
||||
if self.capture:
|
||||
colors = GHOST_VEC_COLORS
|
||||
for weight, gcolor in zip(weights, colors):
|
||||
color = [min(1.0, c + 0.95 * g * weight ** .3) for c,g in zip(color, gcolor)]
|
||||
changeColor(image, formatColor(*color))
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FirstPersonPacmanGraphics(PacmanGraphics):
|
||||
def __init__(self, zoom=1.0, showGhosts=True, capture=False, frameTime=0):
|
||||
PacmanGraphics.__init__(self, zoom, frameTime=frameTime)
|
||||
self.showGhosts = showGhosts
|
||||
self.capture = capture
|
||||
|
||||
def initialize(self, state, isBlue=False):
|
||||
|
||||
self.isBlue = isBlue
|
||||
PacmanGraphics.startGraphics(self, state)
|
||||
# Initialize distribution images
|
||||
walls = state.layout.walls
|
||||
dist = []
|
||||
self.layout = state.layout
|
||||
|
||||
# Draw the rest
|
||||
self.distributionImages = None # initialize lazily
|
||||
self.drawStaticObjects(state)
|
||||
self.drawAgentObjects(state)
|
||||
|
||||
# Information
|
||||
self.previousState = state
|
||||
|
||||
def lookAhead(self, config, state):
|
||||
if config.getDirection() == 'Stop':
|
||||
return
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# Draw relevant ghosts
|
||||
allGhosts = state.getGhostStates()
|
||||
visibleGhosts = state.getVisibleGhosts()
|
||||
for i, ghost in enumerate(allGhosts):
|
||||
if ghost in visibleGhosts:
|
||||
self.drawGhost(ghost, i)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.currentGhostImages[i] = None
|
||||
|
||||
def getGhostColor(self, ghost, ghostIndex):
|
||||
return GHOST_COLORS[ghostIndex]
|
||||
|
||||
def getPosition(self, ghostState):
|
||||
if not self.showGhosts and not ghostState.isPacman and ghostState.getPosition()[1] > 1:
|
||||
return (-1000, -1000)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return PacmanGraphics.getPosition(self, ghostState)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def add(x, y):
|
||||
return (x[0] + y[0], x[1] + y[1])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Saving graphical output
|
||||
# -----------------------
|
||||
# Note: to make an animated gif from this postscript output, try the command:
|
||||
# convert -delay 7 -loop 1 -compress lzw -layers optimize frame* out.gif
|
||||
# convert is part of imagemagick (freeware)
|
||||
|
||||
SAVE_POSTSCRIPT = False
|
||||
POSTSCRIPT_OUTPUT_DIR = 'frames'
|
||||
FRAME_NUMBER = 0
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def saveFrame():
|
||||
"Saves the current graphical output as a postscript file"
|
||||
global SAVE_POSTSCRIPT, FRAME_NUMBER, POSTSCRIPT_OUTPUT_DIR
|
||||
if not SAVE_POSTSCRIPT:
|
||||
return
|
||||
if not os.path.exists(POSTSCRIPT_OUTPUT_DIR):
|
||||
os.mkdir(POSTSCRIPT_OUTPUT_DIR)
|
||||
name = os.path.join(POSTSCRIPT_OUTPUT_DIR, 'frame_%08d.ps' % FRAME_NUMBER)
|
||||
FRAME_NUMBER += 1
|
||||
writePostscript(name) # writes the current canvas
|
||||
448
logic/graphicsUtils.py
Normal file
448
logic/graphicsUtils.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,448 @@
|
||||
# graphicsUtils.py
|
||||
# ----------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import string
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import types
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import tkinter
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
tkinter = None
|
||||
import os.path
|
||||
|
||||
_Windows = sys.platform == 'win32' # True if on Win95/98/NT
|
||||
|
||||
_root_window = None # The root window for graphics output
|
||||
_canvas = None # The canvas which holds graphics
|
||||
_canvas_xs = None # Size of canvas object
|
||||
_canvas_ys = None
|
||||
_canvas_x = None # Current position on canvas
|
||||
_canvas_y = None
|
||||
_canvas_col = None # Current colour (set to black below)
|
||||
_canvas_tsize = 12
|
||||
_canvas_tserifs = 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def formatColor(r, g, b):
|
||||
return '#%02x%02x%02x' % (int(r * 255), int(g * 255), int(b * 255))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def colorToVector(color):
|
||||
return [int(x, 16) / 256.0 for x in [color[1:3], color[3:5], color[5:7]]]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if _Windows:
|
||||
_canvas_tfonts = ['times new roman', 'lucida console']
|
||||
else:
|
||||
_canvas_tfonts = ['times', 'lucidasans-24']
|
||||
pass # XXX need defaults here
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sleep(secs):
|
||||
global _root_window
|
||||
if _root_window == None:
|
||||
time.sleep(secs)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
_root_window.update_idletasks()
|
||||
_root_window.after(int(1000 * secs), _root_window.quit)
|
||||
_root_window.mainloop()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def begin_graphics(width=640, height=480, color=formatColor(0, 0, 0), title=None):
|
||||
|
||||
global _root_window, _canvas, _canvas_x, _canvas_y, _canvas_xs, _canvas_ys, _bg_color
|
||||
|
||||
# Check for duplicate call
|
||||
if _root_window is not None:
|
||||
# Lose the window.
|
||||
_root_window.destroy()
|
||||
|
||||
# Save the canvas size parameters
|
||||
_canvas_xs, _canvas_ys = width - 1, height - 1
|
||||
_canvas_x, _canvas_y = 0, _canvas_ys
|
||||
_bg_color = color
|
||||
|
||||
# Create the root window
|
||||
_root_window = tkinter.Tk()
|
||||
_root_window.protocol('WM_DELETE_WINDOW', _destroy_window)
|
||||
_root_window.title(title or 'Graphics Window')
|
||||
_root_window.resizable(0, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create the canvas object
|
||||
try:
|
||||
_canvas = tkinter.Canvas(_root_window, width=width, height=height)
|
||||
_canvas.pack()
|
||||
draw_background()
|
||||
_canvas.update()
|
||||
except:
|
||||
_root_window = None
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
# Bind to key-down and key-up events
|
||||
_root_window.bind("<KeyPress>", _keypress)
|
||||
_root_window.bind("<KeyRelease>", _keyrelease)
|
||||
_root_window.bind("<FocusIn>", _clear_keys)
|
||||
_root_window.bind("<FocusOut>", _clear_keys)
|
||||
_root_window.bind("<Button-1>", _leftclick)
|
||||
_root_window.bind("<Button-2>", _rightclick)
|
||||
_root_window.bind("<Button-3>", _rightclick)
|
||||
_root_window.bind("<Control-Button-1>", _ctrl_leftclick)
|
||||
_clear_keys()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_leftclick_loc = None
|
||||
_rightclick_loc = None
|
||||
_ctrl_leftclick_loc = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _leftclick(event):
|
||||
global _leftclick_loc
|
||||
_leftclick_loc = (event.x, event.y)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _rightclick(event):
|
||||
global _rightclick_loc
|
||||
_rightclick_loc = (event.x, event.y)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _ctrl_leftclick(event):
|
||||
global _ctrl_leftclick_loc
|
||||
_ctrl_leftclick_loc = (event.x, event.y)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def wait_for_click():
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
global _leftclick_loc
|
||||
global _rightclick_loc
|
||||
global _ctrl_leftclick_loc
|
||||
if _leftclick_loc != None:
|
||||
val = _leftclick_loc
|
||||
_leftclick_loc = None
|
||||
return val, 'left'
|
||||
if _rightclick_loc != None:
|
||||
val = _rightclick_loc
|
||||
_rightclick_loc = None
|
||||
return val, 'right'
|
||||
if _ctrl_leftclick_loc != None:
|
||||
val = _ctrl_leftclick_loc
|
||||
_ctrl_leftclick_loc = None
|
||||
return val, 'ctrl_left'
|
||||
sleep(0.05)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def draw_background():
|
||||
corners = [(0, 0), (0, _canvas_ys), (_canvas_xs, _canvas_ys), (_canvas_xs, 0)]
|
||||
polygon(corners, _bg_color, fillColor=_bg_color, filled=True, smoothed=False)
|
||||
|
||||
def _destroy_window(event=None):
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
# global _root_window
|
||||
# _root_window.destroy()
|
||||
# _root_window = None
|
||||
#print("DESTROY")
|
||||
|
||||
def end_graphics():
|
||||
global _root_window, _canvas, _mouse_enabled
|
||||
try:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
sleep(1)
|
||||
if _root_window != None:
|
||||
_root_window.destroy()
|
||||
except SystemExit as e:
|
||||
print('Ending graphics raised an exception:', e)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
_root_window = None
|
||||
_canvas = None
|
||||
_mouse_enabled = 0
|
||||
_clear_keys()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def clear_screen(background=None):
|
||||
global _canvas_x, _canvas_y
|
||||
_canvas.delete('all')
|
||||
draw_background()
|
||||
_canvas_x, _canvas_y = 0, _canvas_ys
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def polygon(coords, outlineColor, fillColor=None, filled=1, smoothed=1, behind=0, width=1):
|
||||
c = []
|
||||
for coord in coords:
|
||||
c.append(coord[0])
|
||||
c.append(coord[1])
|
||||
if fillColor == None:
|
||||
fillColor = outlineColor
|
||||
if filled == 0:
|
||||
fillColor = ""
|
||||
poly = _canvas.create_polygon(c, outline=outlineColor, fill=fillColor, smooth=smoothed, width=width)
|
||||
if behind > 0:
|
||||
_canvas.tag_lower(poly, behind) # Higher should be more visible
|
||||
return poly
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def square(pos, r, color, filled=1, behind=0):
|
||||
x, y = pos
|
||||
coords = [(x - r, y - r), (x + r, y - r), (x + r, y + r), (x - r, y + r)]
|
||||
return polygon(coords, color, color, filled, 0, behind=behind)
|
||||
|
||||
def circle(pos, r, outlineColor, fillColor=None, endpoints=None, style='pieslice', width=2):
|
||||
x, y = pos
|
||||
x0, x1 = x - r - 1, x + r
|
||||
y0, y1 = y - r - 1, y + r
|
||||
if endpoints == None:
|
||||
e = [0, 359]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
e = list(endpoints)
|
||||
while e[0] > e[1]:
|
||||
e[1] = e[1] + 360
|
||||
|
||||
return _canvas.create_arc(x0, y0, x1, y1, outline=outlineColor, fill=fillColor or outlineColor,
|
||||
extent=e[1] - e[0], start=e[0], style=style, width=width)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def image(pos, file="../../blueghost.gif"):
|
||||
x, y = pos
|
||||
# img = PhotoImage(file=file)
|
||||
return _canvas.create_image(x, y, image=tkinter.PhotoImage(file=file), anchor=tkinter.NW)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def refresh():
|
||||
_canvas.update_idletasks()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def moveCircle(id, pos, r, endpoints=None):
|
||||
global _canvas_x, _canvas_y
|
||||
|
||||
x, y = pos
|
||||
# x0, x1 = x - r, x + r + 1
|
||||
# y0, y1 = y - r, y + r + 1
|
||||
x0, x1 = x - r - 1, x + r
|
||||
y0, y1 = y - r - 1, y + r
|
||||
if endpoints == None:
|
||||
e = [0, 359]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
e = list(endpoints)
|
||||
while e[0] > e[1]:
|
||||
e[1] = e[1] + 360
|
||||
|
||||
if os.path.isfile('flag'):
|
||||
edit(id, ('extent', e[1] - e[0]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
edit(id, ('start', e[0]), ('extent', e[1] - e[0]))
|
||||
move_to(id, x0, y0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def edit(id, *args):
|
||||
_canvas.itemconfigure(id, **dict(args))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def text(pos, color, contents, font='Helvetica', size=12, style='normal', anchor="nw"):
|
||||
global _canvas_x, _canvas_y
|
||||
x, y = pos
|
||||
font = (font, str(size), style)
|
||||
return _canvas.create_text(x, y, fill=color, text=contents, font=font, anchor=anchor)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def changeText(id, newText, font=None, size=12, style='normal'):
|
||||
_canvas.itemconfigure(id, text=newText)
|
||||
if font != None:
|
||||
_canvas.itemconfigure(id, font=(font, '-%d' % size, style))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def changeColor(id, newColor):
|
||||
_canvas.itemconfigure(id, fill=newColor)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def line(here, there, color=formatColor(0, 0, 0), width=2):
|
||||
x0, y0 = here[0], here[1]
|
||||
x1, y1 = there[0], there[1]
|
||||
return _canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1, fill=color, width=width)
|
||||
|
||||
##############################################################################
|
||||
### Keypress handling ########################################################
|
||||
##############################################################################
|
||||
|
||||
# We bind to key-down and key-up events.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_keysdown = {}
|
||||
_keyswaiting = {}
|
||||
# This holds an unprocessed key release. We delay key releases by up to
|
||||
# one call to keys_pressed() to get round a problem with auto repeat.
|
||||
_got_release = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _keypress(event):
|
||||
global _got_release
|
||||
# remap_arrows(event)
|
||||
_keysdown[event.keysym] = 1
|
||||
_keyswaiting[event.keysym] = 1
|
||||
# print(event.char, event.keycode)
|
||||
_got_release = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _keyrelease(event):
|
||||
global _got_release
|
||||
# remap_arrows(event)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
del _keysdown[event.keysym]
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
_got_release = 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def remap_arrows(event):
|
||||
# TURN ARROW PRESSES INTO LETTERS (SHOULD BE IN KEYBOARD AGENT)
|
||||
if event.char in ['a', 's', 'd', 'w']:
|
||||
return
|
||||
if event.keycode in [37, 101]: # LEFT ARROW (win / x)
|
||||
event.char = 'a'
|
||||
if event.keycode in [38, 99]: # UP ARROW
|
||||
event.char = 'w'
|
||||
if event.keycode in [39, 102]: # RIGHT ARROW
|
||||
event.char = 'd'
|
||||
if event.keycode in [40, 104]: # DOWN ARROW
|
||||
event.char = 's'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _clear_keys(event=None):
|
||||
global _keysdown, _got_release, _keyswaiting
|
||||
_keysdown = {}
|
||||
_keyswaiting = {}
|
||||
_got_release = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def keys_pressed(d_o_e=lambda arg: _root_window.dooneevent(arg),
|
||||
d_w=tkinter._tkinter.DONT_WAIT if tkinter else None):
|
||||
d_o_e(d_w)
|
||||
if _got_release:
|
||||
d_o_e(d_w)
|
||||
return list(_keysdown.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def keys_waiting():
|
||||
global _keyswaiting
|
||||
keys = list(_keyswaiting.keys())
|
||||
_keyswaiting = {}
|
||||
return keys
|
||||
|
||||
# Block for a list of keys...
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def wait_for_keys():
|
||||
keys = []
|
||||
while keys == []:
|
||||
keys = keys_pressed()
|
||||
sleep(0.05)
|
||||
return keys
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def remove_from_screen(x,
|
||||
d_o_e=lambda arg: _root_window.dooneevent(arg),
|
||||
d_w=tkinter._tkinter.DONT_WAIT if tkinter else None):
|
||||
_canvas.delete(x)
|
||||
d_o_e(d_w)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _adjust_coords(coord_list, x, y):
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(coord_list), 2):
|
||||
coord_list[i] = coord_list[i] + x
|
||||
coord_list[i + 1] = coord_list[i + 1] + y
|
||||
return coord_list
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def move_to(object, x, y=None,
|
||||
d_o_e=lambda arg: _root_window.dooneevent(arg),
|
||||
d_w=tkinter._tkinter.DONT_WAIT if tkinter else None):
|
||||
if y is None:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
x, y = x
|
||||
except:
|
||||
raise Exception('incomprehensible coordinates')
|
||||
|
||||
horiz = True
|
||||
newCoords = []
|
||||
current_x, current_y = _canvas.coords(object)[0:2] # first point
|
||||
for coord in _canvas.coords(object):
|
||||
if horiz:
|
||||
inc = x - current_x
|
||||
else:
|
||||
inc = y - current_y
|
||||
horiz = not horiz
|
||||
|
||||
newCoords.append(coord + inc)
|
||||
|
||||
_canvas.coords(object, *newCoords)
|
||||
d_o_e(d_w)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def move_by(object, x, y=None,
|
||||
d_o_e=lambda arg: _root_window.dooneevent(arg),
|
||||
d_w=tkinter._tkinter.DONT_WAIT if tkinter else None, lift=False):
|
||||
if y is None:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
x, y = x
|
||||
except:
|
||||
raise Exception('incomprehensible coordinates')
|
||||
|
||||
horiz = True
|
||||
newCoords = []
|
||||
for coord in _canvas.coords(object):
|
||||
if horiz:
|
||||
inc = x
|
||||
else:
|
||||
inc = y
|
||||
horiz = not horiz
|
||||
|
||||
newCoords.append(coord + inc)
|
||||
|
||||
_canvas.coords(object, *newCoords)
|
||||
d_o_e(d_w)
|
||||
if lift:
|
||||
_canvas.tag_raise(object)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def writePostscript(filename):
|
||||
"Writes the current canvas to a postscript file."
|
||||
psfile = open(filename, 'w')
|
||||
psfile.write(_canvas.postscript(pageanchor='sw',
|
||||
y='0.c',
|
||||
x='0.c'))
|
||||
psfile.close()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ghost_shape = [
|
||||
(0, - 0.5),
|
||||
(0.25, - 0.75),
|
||||
(0.5, - 0.5),
|
||||
(0.75, - 0.75),
|
||||
(0.75, 0.5),
|
||||
(0.5, 0.75),
|
||||
(- 0.5, 0.75),
|
||||
(- 0.75, 0.5),
|
||||
(- 0.75, - 0.75),
|
||||
(- 0.5, - 0.5),
|
||||
(- 0.25, - 0.75)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
begin_graphics()
|
||||
clear_screen()
|
||||
ghost_shape = [(x * 10 + 20, y * 10 + 20) for x, y in ghost_shape]
|
||||
g = polygon(ghost_shape, formatColor(1, 1, 1))
|
||||
move_to(g, (50, 50))
|
||||
circle((150, 150), 20, formatColor(0.7, 0.3, 0.0), endpoints=[15, - 15])
|
||||
sleep(2)
|
||||
95
logic/keyboardAgents.py
Normal file
95
logic/keyboardAgents.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
# keyboardAgents.py
|
||||
# -----------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from game import Agent
|
||||
from game import Directions
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class KeyboardAgent(Agent):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
An agent controlled by the keyboard.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# NOTE: Arrow keys also work.
|
||||
WEST_KEY = 'a'
|
||||
EAST_KEY = 'd'
|
||||
NORTH_KEY = 'w'
|
||||
SOUTH_KEY = 's'
|
||||
STOP_KEY = 'q'
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, index=0):
|
||||
|
||||
self.lastMove = Directions.STOP
|
||||
self.index = index
|
||||
self.keys = []
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
from graphicsUtils import keys_waiting
|
||||
from graphicsUtils import keys_pressed
|
||||
keys = keys_waiting() + keys_pressed()
|
||||
if keys != []:
|
||||
self.keys = keys
|
||||
|
||||
legal = state.getLegalActions(self.index)
|
||||
move = self.getMove(legal)
|
||||
|
||||
if move == Directions.STOP:
|
||||
# Try to move in the same direction as before
|
||||
if self.lastMove in legal:
|
||||
move = self.lastMove
|
||||
|
||||
if (self.STOP_KEY in self.keys) and Directions.STOP in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.STOP
|
||||
|
||||
if move not in legal:
|
||||
move = random.choice(legal)
|
||||
|
||||
self.lastMove = move
|
||||
return move
|
||||
|
||||
def getMove(self, legal):
|
||||
move = Directions.STOP
|
||||
if (self.WEST_KEY in self.keys or 'Left' in self.keys) and Directions.WEST in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.WEST
|
||||
if (self.EAST_KEY in self.keys or 'Right' in self.keys) and Directions.EAST in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.EAST
|
||||
if (self.NORTH_KEY in self.keys or 'Up' in self.keys) and Directions.NORTH in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.NORTH
|
||||
if (self.SOUTH_KEY in self.keys or 'Down' in self.keys) and Directions.SOUTH in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.SOUTH
|
||||
return move
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class KeyboardAgent2(KeyboardAgent):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A second agent controlled by the keyboard.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# NOTE: Arrow keys also work.
|
||||
WEST_KEY = 'j'
|
||||
EAST_KEY = "l"
|
||||
NORTH_KEY = 'i'
|
||||
SOUTH_KEY = 'k'
|
||||
STOP_KEY = 'u'
|
||||
|
||||
def getMove(self, legal):
|
||||
move = Directions.STOP
|
||||
if (self.WEST_KEY in self.keys) and Directions.WEST in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.WEST
|
||||
if (self.EAST_KEY in self.keys) and Directions.EAST in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.EAST
|
||||
if (self.NORTH_KEY in self.keys) and Directions.NORTH in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.NORTH
|
||||
if (self.SOUTH_KEY in self.keys) and Directions.SOUTH in legal:
|
||||
move = Directions.SOUTH
|
||||
return move
|
||||
175
logic/layout.py
Normal file
175
logic/layout.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,175 @@
|
||||
# layout.py
|
||||
# ---------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from util import manhattanDistance
|
||||
from game import Grid
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from functools import reduce
|
||||
|
||||
VISIBILITY_MATRIX_CACHE = {}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Layout:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A Layout manages the static information about the game board.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, layoutText):
|
||||
self.width = len(layoutText[0])
|
||||
self.height = len(layoutText)
|
||||
self.walls = Grid(self.width, self.height, False)
|
||||
self.food = Grid(self.width, self.height, False)
|
||||
self.capsules = []
|
||||
self.agentPositions = []
|
||||
self.numGhosts = 0
|
||||
self.processLayoutText(layoutText)
|
||||
self.layoutText = layoutText
|
||||
self.totalFood = len(self.food.asList())
|
||||
# self.initializeVisibilityMatrix()
|
||||
|
||||
def getNumGhosts(self):
|
||||
return self.numGhosts
|
||||
|
||||
def initializeVisibilityMatrix(self):
|
||||
global VISIBILITY_MATRIX_CACHE
|
||||
if reduce(str.__add__, self.layoutText) not in VISIBILITY_MATRIX_CACHE:
|
||||
from game import Directions
|
||||
vecs = [(-0.5, 0), (0.5, 0),(0, -0.5),(0, 0.5)]
|
||||
dirs = [Directions.NORTH, Directions.SOUTH, Directions.WEST, Directions.EAST]
|
||||
vis = Grid(self.width, self.height, {Directions.NORTH:set(), Directions.SOUTH:set(), Directions.EAST:set(), Directions.WEST:set(), Directions.STOP:set()})
|
||||
for x in range(self.width):
|
||||
for y in range(self.height):
|
||||
if self.walls[x][y] == False:
|
||||
for vec, direction in zip(vecs, dirs):
|
||||
dx, dy = vec
|
||||
nextx, nexty = x + dx, y + dy
|
||||
while (nextx + nexty) != int(nextx) + int(nexty) or not self.walls[int(nextx)][int(nexty)]:
|
||||
vis[x][y][direction].add((nextx, nexty))
|
||||
nextx, nexty = x + dx, y + dy
|
||||
self.visibility = vis
|
||||
VISIBILITY_MATRIX_CACHE[reduce(str.__add__, self.layoutText)] = vis
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.visibility = VISIBILITY_MATRIX_CACHE[reduce(str.__add__, self.layoutText)]
|
||||
|
||||
def isWall(self, pos):
|
||||
x, col = pos
|
||||
return self.walls[x][col]
|
||||
|
||||
def get_all_coords_list(self):
|
||||
all_coords_list = []
|
||||
for x in range(self.width):
|
||||
for y in range(self.height):
|
||||
all_coords_list.append((x, y))
|
||||
return all_coords_list
|
||||
|
||||
def get_non_outer_wall_coords_list(self):
|
||||
outer_wall_coords_list = []
|
||||
for x in range(self.width):
|
||||
for y in range(self.height):
|
||||
if ((not (x == 0 or x == self.width - 1))
|
||||
and (not (y == 0 or y == self.height - 1))):
|
||||
outer_wall_coords_list.append((x, y))
|
||||
return outer_wall_coords_list
|
||||
|
||||
def getRandomLegalPosition(self):
|
||||
x = random.choice(list(range(self.width)))
|
||||
y = random.choice(list(range(self.height)))
|
||||
while self.isWall((x, y)):
|
||||
x = random.choice(list(range(self.width)))
|
||||
y = random.choice(list(range(self.height)))
|
||||
return (x, y)
|
||||
|
||||
def getRandomCorner(self):
|
||||
poses = [(1, 1), (1, self.height - 2), (self.width - 2, 1), (self.width - 2, self.height - 2)]
|
||||
return random.choice(poses)
|
||||
|
||||
def getFurthestCorner(self, pacPos):
|
||||
poses = [(1, 1), (1, self.height - 2), (self.width - 2, 1), (self.width - 2, self.height - 2)]
|
||||
dist, pos = max([(manhattanDistance(p, pacPos), p) for p in poses])
|
||||
return pos
|
||||
|
||||
def isVisibleFrom(self, ghostPos, pacPos, pacDirection):
|
||||
row, col = [int(x) for x in pacPos]
|
||||
return ghostPos in self.visibility[row][col][pacDirection]
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
return "\n".join(self.layoutText)
|
||||
|
||||
def deepCopy(self):
|
||||
return Layout(self.layoutText[:])
|
||||
|
||||
def processLayoutText(self, layoutText):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Coordinates are flipped from the input format to the (x,y) convention here
|
||||
|
||||
The shape of the maze. Each character
|
||||
represents a different type of object.
|
||||
% - Wall
|
||||
. - Food
|
||||
o - Capsule
|
||||
G - Ghost
|
||||
P - Pacman
|
||||
Other characters are ignored.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
maxY = self.height - 1
|
||||
for y in range(self.height):
|
||||
for x in range(self.width):
|
||||
layoutChar = layoutText[maxY - y][x]
|
||||
self.processLayoutChar(x, y, layoutChar)
|
||||
self.agentPositions.sort()
|
||||
self.agentPositions = [(i == 0, pos) for i, pos in self.agentPositions]
|
||||
|
||||
def processLayoutChar(self, x, y, layoutChar):
|
||||
if layoutChar == '%':
|
||||
self.walls[x][y] = True
|
||||
elif layoutChar == '.':
|
||||
self.food[x][y] = True
|
||||
elif layoutChar == 'o':
|
||||
self.capsules.append((x, y))
|
||||
elif layoutChar == 'P':
|
||||
self.agentPositions.append((0, (x, y)))
|
||||
elif layoutChar in ['G']:
|
||||
self.agentPositions.append((1, (x, y)))
|
||||
self.numGhosts += 1
|
||||
elif layoutChar in ['1', '2', '3', '4']:
|
||||
self.agentPositions.append((int(layoutChar), (x, y)))
|
||||
self.numGhosts += 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def getLayout(name, back=2):
|
||||
if name.endswith('.lay'):
|
||||
layout = tryToLoad('layouts/' + name)
|
||||
if layout == None:
|
||||
layout = tryToLoad(name)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
layout = tryToLoad('layouts/' + name + '.lay')
|
||||
if layout == None:
|
||||
layout = tryToLoad(name + '.lay')
|
||||
if layout == None and back >= 0:
|
||||
curdir = os.path.abspath('.')
|
||||
os.chdir('..')
|
||||
layout = getLayout(name, back - 1)
|
||||
os.chdir(curdir)
|
||||
return layout
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def tryToLoad(fullname):
|
||||
if(not os.path.exists(fullname)):
|
||||
return None
|
||||
f = open(fullname)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return Layout([line.strip() for line in f])
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
f.close()
|
||||
37
logic/layouts/bigCorners.lay
Normal file
37
logic/layouts/bigCorners.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%. % %.%
|
||||
% %%%%% % %%% %%% %%%%%%% % %
|
||||
% % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%%%% %%%%% %%% % % % %%% %%%%% % %%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%% % % % %%% %%%%% %%% % %%% %%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%% %%%%%%%%% %%%%%%% %%% %%% % % % %
|
||||
% % % % % % %
|
||||
% % %%%%% % %%% % % %%% % %%% %%% % %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % %%%%%%% % %%%%%%%%% %%% % %%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%% %%% % %%%%% %%%%% %%% %%% %%%%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % % % % %%% %%% %%% % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % % % %% % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % %%%%% % %%% %%% % %%% %%% %%%%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%% % % % %%% %%% %%%%%%%%% % %%%
|
||||
% % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% % % %%% %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
% % % %%%%% %%% % % % % %%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % %%% %%% % % % %%%%%%%%% %%% % % %
|
||||
% % % % % % %P % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%% %%% %%% % %%% % % %%%%% % %%%%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%% % %%%%% %%%%% %%% %%% % %%% % %%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % %%% % % % % %%%%%%%%% % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
% % % %%% %%% %%%%%%% %%% %%% %%% %
|
||||
%.% % % % % .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
37
logic/layouts/bigMaze.lay
Normal file
37
logic/layouts/bigMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%%%%%% % %%% % %%% %%% %%%%%%% % %
|
||||
% % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%%%% %%%%% %%% % % % %%% %%%%% % %%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%% % % % %%% %%%%% %%% % %%% %%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%% %%%%%%%%% %%%%%%% %%% %%% % % % %
|
||||
% % % % % % %
|
||||
% % %%%%% % %%% % % %%% % %%% %%% % %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % %%%%%%% % %%%%%%%%% %%% % %%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%% %%% % %%%%% %%%%% %%% %%% %%%%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % % % %%% %%% %%% %%% % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%% %%%%%%% % % %%%%% %%% % %%% %%%%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%%%% % % %%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%% % %%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%% %%%%% %%%%%%%%% %%%%% % % %%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % %%%%% %%% % % % % %%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % %%% %%% % % % %%%%%%%%% %%% % % %
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%% %%% %%%%% %%% % % %%%%% % %%%%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % %
|
||||
%%% % %%%%% %%%%% %%% %%% % %%% % %%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% % %%% % % % % %%%%%%%%% % % % % % %
|
||||
% % % % % %
|
||||
% % % % %%% %%% %%%%%%% %%% %%% %%% %
|
||||
%.% % % % % % % % P%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
8
logic/layouts/bigSafeSearch.lay
Normal file
8
logic/layouts/bigSafeSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%.%.........%% G % o%%%%.....%
|
||||
%.%.%%%%%%%.%%%%%% %%%%%%%.%%.%
|
||||
%............%...%............%
|
||||
%%%%%...%%%.. ..%.%...%.%%%
|
||||
%o%%%.%%%%%.%%%%%%%.%%%.%.%%%%%
|
||||
% ..........Po...%...%. o%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
15
logic/layouts/bigSearch.lay
Normal file
15
logic/layouts/bigSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%.....%.................%.....%
|
||||
%.%%%.%.%%%.%%%%%%%.%%%.%.....%
|
||||
%.%...%.%......%......%.%.....%
|
||||
%...%%%.%.%%%%.%.%%%%...%%%...%
|
||||
%%%.%.%.%.%......%..%.%...%.%%%
|
||||
%...%.%%%.%.%%% %%%.%.%%%.%...%
|
||||
%.%%%.......% %.......%%%.%
|
||||
%...%.%%%%%.%%%%%%%.%.%%%.%...%
|
||||
%%%.%...%.%....%....%.%...%.%%%
|
||||
%...%%%.%.%%%%.%.%%%%.%.%%%...%
|
||||
%.......%......%......%.....%.%
|
||||
%.....%.%%%.%%%%%%%.%%%.%.%%%.%
|
||||
%.....%........P....%...%.....%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
14
logic/layouts/boxSearch.lay
Normal file
14
logic/layouts/boxSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%. . . . . % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
%. . . . . %G%
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
%. . . . . % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
%. . . . . % %
|
||||
% P %G%
|
||||
%. . . . . % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
%. . . . . % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/capsuleClassic.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/capsuleClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%G. G ....%
|
||||
%.% % %%%%%% %.%%.%
|
||||
%.%o% % o% %.o%.%
|
||||
%.%%%.% %%% %..%.%
|
||||
%..... P %..%G%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
9
logic/layouts/contestClassic.lay
Normal file
9
logic/layouts/contestClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%o...%........%...o%
|
||||
%.%%.%.%%..%%.%.%%.%
|
||||
%...... G GG%......%
|
||||
%.%.%%.%% %%%.%%.%.%
|
||||
%.%....% ooo%.%..%.%
|
||||
%.%.%%.% %% %.%.%%.%
|
||||
%o%......P....%....%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
11
logic/layouts/contoursMaze.lay
Normal file
11
logic/layouts/contoursMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%. %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
8
logic/layouts/greedySearch.lay
Normal file
8
logic/layouts/greedySearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
%....%
|
||||
% %%.%
|
||||
% %%.%
|
||||
%.P .%
|
||||
%.%%%%
|
||||
%....%
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
4
logic/layouts/maze1x2.lay
Normal file
4
logic/layouts/maze1x2.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
%%%
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%P%
|
||||
%%%
|
||||
4
logic/layouts/maze2x2.lay
Normal file
4
logic/layouts/maze2x2.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
%. %
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
4
logic/layouts/maze2x2_2.lay
Normal file
4
logic/layouts/maze2x2_2.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
%%P%
|
||||
%% %
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
4
logic/layouts/maze2x2_3.lay
Normal file
4
logic/layouts/maze2x2_3.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
%% %
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_5_cross.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_5_cross.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_5_t.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_5_t.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_6.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_6.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
%% P%
|
||||
% %%
|
||||
%% %
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_7.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_7.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_8.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/maze3x3_8.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
6
logic/layouts/maze3x4_4.lay
Normal file
6
logic/layouts/maze3x4_4.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
%%P%%
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
6
logic/layouts/maze3x4_9.lay
Normal file
6
logic/layouts/maze3x4_9.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
% %P%
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
6
logic/layouts/maze4x4_13.lay
Normal file
6
logic/layouts/maze4x4_13.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
% %% %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
4
logic/layouts/mazeDown.lay
Normal file
4
logic/layouts/mazeDown.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
%P%%
|
||||
%. %
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
4
logic/layouts/mazeLshape.lay
Normal file
4
logic/layouts/mazeLshape.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
%.%%
|
||||
%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/mazeSearch1.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/mazeSearch1.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%.%% %%.%
|
||||
%.%. .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/mazeSearch2.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/mazeSearch2.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%.......%
|
||||
%%%%.%% %
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
4
logic/layouts/mazeUshape.lay
Normal file
4
logic/layouts/mazeUshape.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%.%P%
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
11
logic/layouts/mediumClassic.lay
Normal file
11
logic/layouts/mediumClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%o...%........%....%
|
||||
%.%%.%.%%%%%%.%.%%.%
|
||||
%.%..............%.%
|
||||
%.%.%%.%% %%.%%.%.%
|
||||
%......%G G%......%
|
||||
%.%.%%.%%%%%%.%%.%.%
|
||||
%.%..............%.%
|
||||
%.%%.%.%%%%%%.%.%%.%
|
||||
%....%...P....%...o%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
14
logic/layouts/mediumCorners.lay
Normal file
14
logic/layouts/mediumCorners.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%. % % % %.%
|
||||
% % % %%%%%% %%%%%%% % %
|
||||
% % % % % %
|
||||
%%%%% %%%%% %%% %% %%%%% % %%%
|
||||
% % % % % % % % %
|
||||
% %%% % % % %%%%%%%% %%% %%% %
|
||||
% % %% % % % %
|
||||
%%% % %%%%%%% %%%% %%% % % % %
|
||||
% % %% % % %
|
||||
% % %%%%% % %%%% % %%% %%% % %
|
||||
% % % % % % %%% %
|
||||
%. %P%%%%% % %%% % .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
18
logic/layouts/mediumDottedMaze.lay
Normal file
18
logic/layouts/mediumDottedMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%% %%%%%%%% %
|
||||
% %% % % %%% %%% %% ... %
|
||||
% %% % % % % %%%% %%%%%%%%% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %% % % % % % %% %% %% ... %
|
||||
% %% % % % % % %%%% %%% %%%%%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % %% %%%%%%%% ... %
|
||||
% %% % % %%%%%%%% %% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %% % %% %%%%%%%%% %% ... %
|
||||
% %%%%%% %%%%%%% %% %%%%%% %
|
||||
%%%%%% % %%%% %% % ... %
|
||||
% %%%%%% %%%%% % %% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %%%%%% % %%%%% %% %
|
||||
% %%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%% %% %% %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%% %
|
||||
%. %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% ...... %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
18
logic/layouts/mediumMaze.lay
Normal file
18
logic/layouts/mediumMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%% %
|
||||
% %% % % %%%%%%% %% %
|
||||
% %% % % % % %%%% %%%%%%%%% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %% % % % % %% %% %
|
||||
% %% % % % % % %%%% %%% %%%%%% %
|
||||
% % % % % % %% %%%%%%%% %
|
||||
% %% % % %%%%%%%% %% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %% % %% %%%%%%%%% %% %
|
||||
% %%%%%% %%%%%%% %% %%%%%% %
|
||||
%%%%%% % %%%% %% % %
|
||||
% %%%%%% %%%%% % %% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %%%%%% % %%%%% %% %
|
||||
% %%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%% %% %% %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%% %
|
||||
%. %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
6
logic/layouts/mediumSafeSearch.lay
Normal file
6
logic/layouts/mediumSafeSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%.% ....%% G %%%%%% o%%.%
|
||||
%.%o%%%%%%%.%%%%%%% %%%%%.%
|
||||
% %%%.%%%%%.%%%%%%%.%%%.%.%%%.%
|
||||
% ..........Po...%.........%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
18
logic/layouts/mediumScaryMaze.lay
Normal file
18
logic/layouts/mediumScaryMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%% %%%%%%%% %
|
||||
% %% % % %%% %%% %%GG %
|
||||
% %% % % % % %%%% %%%%%%%%% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %% % % % % % %%GG %% %
|
||||
% %% % % % % % %%%%% %%% %%%%%% %
|
||||
% %% % % % % %% %%%%%%%%% %
|
||||
% %% % % %%%%%%%% %% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %% % %% %%%%%%%%% %% %
|
||||
% %%% %% %%%%%%% %% %%%%%% %
|
||||
%%%%%% % % %% %% %
|
||||
% %%%%%% %% %% %% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %%%%%% % %%%%% %% %
|
||||
% %%%% %%%%% %%%%%% %
|
||||
%%%%%%%% % %%%%%% %
|
||||
%. %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
8
logic/layouts/mediumSearch.lay
Normal file
8
logic/layouts/mediumSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%............%%%%%............%
|
||||
%%%.%...%%%.........%.%...%.%%%
|
||||
%...%%%.%.%%%%.%.%%%%%%.%%%...%
|
||||
%.%.....%......%......%.....%.%
|
||||
%.%%%.%%%%%.%%%%%%%.%%%.%.%%%%%
|
||||
%.....%........P....%...%.....%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/minimaxClassic.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/minimaxClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%.P G%
|
||||
% %.%G%%%
|
||||
%G %%%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/oddSearch.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/oddSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%...%.........%%...%
|
||||
%.%.%.%%%%%%%%%%.%.%
|
||||
%..................%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%.%.%%%%%%%P%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%....... %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
9
logic/layouts/openClassic.lay
Normal file
9
logic/layouts/openClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% P.... .... .. %
|
||||
% .. ... ... ... .. %
|
||||
% ... ... ... .. %
|
||||
% ... .... G .. %
|
||||
% ... ... ... .. %
|
||||
% ... ... ... .. %
|
||||
% ....... .... ..o%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
23
logic/layouts/openMaze.lay
Normal file
23
logic/layouts/openMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
% % % %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%. %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/openSearch.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/openSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%..................%
|
||||
%..................%
|
||||
%........P.........%
|
||||
%..................%
|
||||
%..................%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
27
logic/layouts/originalClassic.lay
Normal file
27
logic/layouts/originalClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%............%%............%
|
||||
%.%%%%.%%%%%.%%.%%%%%.%%%%.%
|
||||
%o%%%%.%%%%%.%%.%%%%%.%%%%o%
|
||||
%.%%%%.%%%%%.%%.%%%%%.%%%%.%
|
||||
%..........................%
|
||||
%.%%%%.%%.%%%%%%%%.%%.%%%%.%
|
||||
%.%%%%.%%.%%%%%%%%.%%.%%%%.%
|
||||
%......%%....%%....%%......%
|
||||
%%%%%%.%%%%% %% %%%%%.%%%%%%
|
||||
%%%%%%.%%%%% %% %%%%%.%%%%%%
|
||||
%%%%%%.% %.%%%%%%
|
||||
%%%%%%.% %%%% %%%% %.%%%%%%
|
||||
% . %G GG G% . %
|
||||
%%%%%%.% %%%%%%%%%% %.%%%%%%
|
||||
%%%%%%.% %.%%%%%%
|
||||
%%%%%%.% %%%%%%%%%% %.%%%%%%
|
||||
%............%%............%
|
||||
%.%%%%.%%%%%.%%.%%%%%.%%%%.%
|
||||
%.%%%%.%%%%%.%%.%%%%%.%%%%.%
|
||||
%o..%%....... .......%%..o%
|
||||
%%%.%%.%%.%%%%%%%%.%%.%%.%%%
|
||||
%%%.%%.%%.%%%%%%%%.%%.%%.%%%
|
||||
%......%%....%%....%%......%
|
||||
%.%%%%%%%%%%.%%.%%%%%%%%%%.%
|
||||
%.............P............%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/patrolling1.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/patrolling1.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
% .%
|
||||
% G%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/patrolling2.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/patrolling2.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
% .%
|
||||
% G %
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/patrolling3.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/patrolling3.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
%...%
|
||||
%.G.%
|
||||
%..P%
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
6
logic/layouts/patrolling4.lay
Normal file
6
logic/layouts/patrolling4.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
% . %
|
||||
%G %
|
||||
%G %
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
6
logic/layouts/patrolling5.lay
Normal file
6
logic/layouts/patrolling5.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
% . %
|
||||
%G G%
|
||||
% GG %
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
6
logic/layouts/patrolling6.lay
Normal file
6
logic/layouts/patrolling6.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
%....%
|
||||
%G G%
|
||||
%.GG.%
|
||||
%..P.%
|
||||
%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/patrolling7.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/patrolling7.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%..G ..%
|
||||
%%%%.%% %
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%.%% %%.%
|
||||
%.%. .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/patrolling8.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/patrolling8.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%..G ..%
|
||||
%%%%.%% %
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%.%% %%.%
|
||||
%.%.G .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/patrolling9.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/patrolling9.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%
|
||||
%% . %
|
||||
%G G .%
|
||||
% %%G %
|
||||
% G%
|
||||
% P%.%
|
||||
%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/powerClassic.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/powerClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%o....o%GGGG%o....o%
|
||||
%..%...%% %%...%..%
|
||||
%.%o.%........%.o%.%
|
||||
%.o%.%.%%%%%%.%.%o.%
|
||||
%........P.........%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/smallClassic.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/smallClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%......%G G%......%
|
||||
%.%%...%% %%...%%.%
|
||||
%.%o.%........%.o%.%
|
||||
%.%%.%.%%%%%%.%.%%.%
|
||||
%........P.........%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
10
logic/layouts/smallMaze.lay
Normal file
10
logic/layouts/smallMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% %% % % %
|
||||
% %%%%%% % %%%%%% %
|
||||
%%%%%% P % %
|
||||
% % %%%%%% %% %%%%%
|
||||
% %%%% % % %
|
||||
% %%% %%% % %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%% %
|
||||
%. %% %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
10
logic/layouts/smallModifiedMaze.lay
Normal file
10
logic/layouts/smallModifiedMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% %% %
|
||||
% %%%%%% %
|
||||
%%%%%% P%
|
||||
% % %%%%%%
|
||||
% %%%% % %
|
||||
% %%%%
|
||||
%%%% %%%% %
|
||||
%. %%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
15
logic/layouts/smallSafeSearch.lay
Normal file
15
logic/layouts/smallSafeSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%.. % G %
|
||||
%%% %%%%%
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%%%%%%% %
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% %%%%% %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
%%%%% % %
|
||||
% %o%
|
||||
% %%%%%%%
|
||||
% .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%.%
|
||||
%Po .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/smallSearch.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/smallSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%. ...P .%
|
||||
%.%%.%%.%%.%%.%% %.%
|
||||
% %% %..... %.%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
10
logic/layouts/testClassic.lay
Normal file
10
logic/layouts/testClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
% . %
|
||||
%.G.%
|
||||
% . %
|
||||
%. .%
|
||||
% %
|
||||
% .%
|
||||
% %
|
||||
%P .%
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
3
logic/layouts/testMaze.lay
Normal file
3
logic/layouts/testMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%. P%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/testSearch.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/testSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
%.P %
|
||||
%%% %
|
||||
%. %
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
3
logic/layouts/threeByOneMaze.lay
Normal file
3
logic/layouts/threeByOneMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
%. P%
|
||||
%%%%%
|
||||
8
logic/layouts/tinyCorners.lay
Normal file
8
logic/layouts/tinyCorners.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%. .%
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
% %%%% %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
% % %%%%
|
||||
%.% .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/tinyMaze.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/tinyMaze.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%
|
||||
% P%
|
||||
% %%% %
|
||||
% % %
|
||||
%% %%
|
||||
%. %%%%
|
||||
%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/tinySafeSearch.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/tinySafeSearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% G %...%
|
||||
%%%%%%% %
|
||||
%Po %
|
||||
%.%%.%%.%
|
||||
%.%%....%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/tinySearch.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/tinySearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%.. ..%
|
||||
%%%%.%% %
|
||||
% P %
|
||||
%.%% %%.%
|
||||
%.%. .%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
5
logic/layouts/trappedClassic.lay
Normal file
5
logic/layouts/trappedClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%
|
||||
% P G%
|
||||
%G%%%%%%
|
||||
%.... %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%
|
||||
13
logic/layouts/trickyClassic.lay
Normal file
13
logic/layouts/trickyClassic.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%o...%........%...o%
|
||||
%.%%.%.%%..%%.%.%%.%
|
||||
%.%.....%..%.....%.%
|
||||
%.%.%%.%% %%.%%.%.%
|
||||
%...... GGGG%.%....%
|
||||
%.%....%%%%%%.%..%.%
|
||||
%.%....% oo%.%..%.%
|
||||
%.%....% %%%%.%..%.%
|
||||
%.%...........%..%.%
|
||||
%.%%.%.%%%%%%.%.%%.%
|
||||
%o...%...P....%...o%
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
7
logic/layouts/trickySearch.lay
Normal file
7
logic/layouts/trickySearch.lay
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
%. ..% %
|
||||
%.%%.%%.%%.%%.%% % %
|
||||
% P % %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %
|
||||
%..... %
|
||||
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
|
||||
728
logic/logic.py
Normal file
728
logic/logic.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,728 @@
|
||||
# logic.py
|
||||
# --------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""Representations and Inference for the CS 188 Logic Project
|
||||
|
||||
Code originally from https://code.google.com/p/aima-python/
|
||||
Modified heavily with additional convenience classes and functions as well
|
||||
as an interface to the pycosat (picoSAT wrapper) library.
|
||||
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pycosat.
|
||||
Original package contained implementations of functions and data structures
|
||||
for Knowledge bases and First-Order Logic.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import itertools, re
|
||||
from typing import Tuple
|
||||
import agents
|
||||
from logic_utils import *
|
||||
import pycosat
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
class Expr:
|
||||
"""A symbolic mathematical expression. We use this class for logical
|
||||
expressions, and for terms within logical expressions. In general, an
|
||||
Expr has an op (operator) and a list of args. The op can be:
|
||||
Null-ary (no args) op:
|
||||
A number, representing the number itself. (e.g. Expr(42) => 42)
|
||||
A symbol, representing a variable or constant (e.g. Expr('F') => F)
|
||||
Unary (1 arg) op:
|
||||
'~', '-', representing NOT, negation (e.g. Expr('~', Expr('P')) => ~P)
|
||||
Binary (2 arg) op:
|
||||
'>>', '<<', representing forward and backward implication
|
||||
'+', '-', '*', '/', '**', representing arithmetic operators
|
||||
'<', '>', '>=', '<=', representing comparison operators
|
||||
'<=>', '^', representing logical equality and XOR
|
||||
N-ary (0 or more args) op:
|
||||
'&', '|', representing conjunction and disjunction
|
||||
A symbol, representing a function term or FOL proposition
|
||||
|
||||
Exprs can be constructed with operator overloading: if x and y are Exprs,
|
||||
then so are x + y and x & y, etc. Also, if F and x are Exprs, then so is
|
||||
F(x); it works by overloading the __call__ method of the Expr F. Note
|
||||
that in the Expr that is created by F(x), the op is the str 'F', not the
|
||||
Expr F. See http://www.python.org/doc/current/ref/specialnames.html
|
||||
to learn more about operator overloading in Python.
|
||||
|
||||
WARNING: x == y and x != y are NOT Exprs. The reason is that we want
|
||||
to write code that tests 'if x == y:' and if x == y were the same
|
||||
as Expr('==', x, y), then the result would always be true; not what a
|
||||
programmer would expect. But we still need to form Exprs representing
|
||||
equalities and disequalities. We concentrate on logical equality (or
|
||||
equivalence) and logical disequality (or XOR). You have 3 choices:
|
||||
(1) Expr('<=>', x, y) and Expr('^', x, y)
|
||||
Note that ^ is bitwise XOR in Python (and Java and C++)
|
||||
(2) expr('x <=> y') and expr('x =/= y').
|
||||
See the doc string for the function expr.
|
||||
(3) (x % y) and (x ^ y).
|
||||
It is very ugly to have (x % y) mean (x <=> y), but we need
|
||||
SOME operator to make (2) work, and this seems the best choice.
|
||||
|
||||
WARNING: if x is an Expr, then so is x + 1, because the int 1 gets
|
||||
coerced to an Expr by the constructor. But 1 + x is an error, because
|
||||
1 doesn't know how to add an Expr. (Adding an __radd__ method to Expr
|
||||
wouldn't help, because int.__add__ is still called first.) Therefore,
|
||||
you should use Expr(1) + x instead, or ONE + x, or expr('1 + x').
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize a counter object
|
||||
counter = 0
|
||||
def __init__(self, op, *args):
|
||||
"Op is a string or number; args are Exprs (or are coerced to Exprs)."
|
||||
assert isinstance(op, str) or (isnumber(op) and not args)
|
||||
self.op = num_or_str(op)
|
||||
self.args = tuple(map(expr, args)) ## Coerce args to Exprs
|
||||
if not args and not is_prop_symbol(self.op):
|
||||
raise SyntaxError("Unacceptable symbol base name (%s). Name must start with an upper-case alphabetic character that and is not TRUE or FALSE. Furthermore, only the following are allowed: capital and lower case alphabetic, 0-9, _, \",\", [, and ]." % self.op)
|
||||
# Increment the counter when an object is created
|
||||
type(self).counter += 1
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, *args):
|
||||
"""Self must be a symbol with no args, such as Expr('F'). Create a new
|
||||
Expr with 'F' as op and the args as arguments."""
|
||||
assert is_symbol(self.op) and not self.args
|
||||
return Expr(self.op, *args)
|
||||
|
||||
def __repr__(self):
|
||||
"Show something like 'P' or 'P(x, y)', or '~P' or '(P | Q | R)'"
|
||||
if not self.args: # Constant or proposition with arity 0
|
||||
return str(self.op)
|
||||
elif is_symbol(self.op): # Functional or propositional operator
|
||||
return '%s(%s)' % (self.op, ', '.join(map(repr, self.args)))
|
||||
elif len(self.args) == 1: # Prefix operator
|
||||
return self.op + repr(self.args[0])
|
||||
else: # Infix operator
|
||||
return '(%s)' % (' '+self.op+' ').join(map(repr, self.args))
|
||||
|
||||
def __eq__(self, other):
|
||||
"""x and y are equal iff their ops and args are equal."""
|
||||
return (other is self) or (isinstance(other, Expr)
|
||||
and self.op == other.op and self.args == other.args)
|
||||
|
||||
def __ne__(self, other):
|
||||
return not self.__eq__(other)
|
||||
|
||||
def __hash__(self):
|
||||
"Need a hash method so Exprs can live in dicts."
|
||||
return hash(self.op) ^ hash(tuple(self.args))
|
||||
|
||||
# See http://www.python.org/doc/current/lib/module-operator.html
|
||||
# Not implemented: not, abs, pos, concat, contains, *item, *slice
|
||||
def __lt__(self, other): return Expr('<', self, other)
|
||||
def __le__(self, other): return Expr('<=', self, other)
|
||||
def __ge__(self, other): return Expr('>=', self, other)
|
||||
def __gt__(self, other): return Expr('>', self, other)
|
||||
def __add__(self, other): return Expr('+', self, other)
|
||||
def __sub__(self, other): return Expr('-', self, other)
|
||||
def __and__(self, other): return Expr('&', self, other)
|
||||
def __div__(self, other): return Expr('/', self, other)
|
||||
def __truediv__(self, other):return Expr('/', self, other)
|
||||
def __invert__(self): return Expr('~', self)
|
||||
def __lshift__(self, other): return Expr('<<', self, other)
|
||||
def __rshift__(self, other): return Expr('>>', self, other)
|
||||
def __mul__(self, other): return Expr('*', self, other)
|
||||
def __neg__(self): return Expr('-', self)
|
||||
def __or__(self, other): return Expr('|', self, other)
|
||||
def __pow__(self, other): return Expr('**', self, other)
|
||||
def __xor__(self, other): return Expr('^', self, other)
|
||||
def __mod__(self, other): return Expr('<=>', self, other)
|
||||
|
||||
class PropSymbolExpr(Expr):
|
||||
"""An extension of Expr intended to represent a symbol. This SymbolExpr
|
||||
is a convenience for naming symbols, especially symbols whose names
|
||||
indicate an indexed value (e.g. Position[x,y] or Fluent[t]).
|
||||
Symbol name must begin with a capital letter. This class helps to add
|
||||
brackets with enumerated indices to the end of the name.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# copied from logicPlan.py; preferably do this better
|
||||
pacman_str = 'P'
|
||||
food_str = 'FOOD'
|
||||
wall_str = 'WALL'
|
||||
DIRECTIONS = {'North', 'South', 'East', 'West'}
|
||||
# rules
|
||||
double_index = {pacman_str, food_str, wall_str}
|
||||
time_index = {pacman_str, food_str} | DIRECTIONS
|
||||
all_checked = double_index | time_index
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, sym_str: str, *index: Tuple[int], time: int = None):
|
||||
"""Constructor taking a propositional logic symbol name and an optional set of index values,
|
||||
creating a symbol with the base name followed by brackets with the specific
|
||||
indices.
|
||||
sym_str: String representing base name for symbol. Must begin with a capital letter.
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
>>> red = PropSymbolExpr("R")
|
||||
>>> print(red)
|
||||
R
|
||||
>>> turnLeft7 = PropSymbolExpr("Left",7)
|
||||
>>> print(turnLeft7)
|
||||
Left[7]
|
||||
>>> pos_2_3 = PropSymbolExpr("P",2,3)
|
||||
>>> print(pos_2_3)
|
||||
P[2,3]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not is_prop_symbol(sym_str):
|
||||
raise SyntaxError("Unacceptable symbol base name (%s). Name must start with an upper-case alphabetic character that and is not TRUE or FALSE. Furthermore, only the following are allowed: capital and lower case alphabetic, 0-9, _, \",\", [, and ]." % sym_str)
|
||||
if sym_str in self.all_checked:
|
||||
if sym_str in self.double_index:
|
||||
if len(index) != 2:
|
||||
raise SyntaxError("Unexpected " + sym_str + " Symbol. Was expecting 2 coordinates.")
|
||||
elif len(index) != 0:
|
||||
raise SyntaxError("Unexpected " + sym_str + " Symbol. Was expecting 0 coordinates.")
|
||||
if sym_str in self.time_index:
|
||||
if time == None:
|
||||
raise SyntaxError("Unexpected " + sym_str + " Symbol. Was expecting time stamp.")
|
||||
elif time != None:
|
||||
raise SyntaxError("Unexpected " + sym_str + " Symbol. Was expecting no time stamp.")
|
||||
self.sym_str = sym_str
|
||||
self.indicies = index
|
||||
self.time = time
|
||||
if len(index) > 0:
|
||||
if len(index) > 4:
|
||||
raise SyntaxError("Too many arguments to SymbolExpr constructor. SymbolExpr(symbol_str, [index1], [index2], [index3], [index4], time=[time]), or fewer indicies -- possibly 0.")
|
||||
if len(index) == 1:
|
||||
sym_str = '%s[%d]' % (sym_str, *index)
|
||||
elif len(index) == 2:
|
||||
sym_str = '%s[%d,%d]' % (sym_str, *index)
|
||||
elif len(index) == 3:
|
||||
sym_str = '%s[%d,%d,%d]' % (sym_str, *index)
|
||||
elif len(index) == 4:
|
||||
sym_str = '%s[%d,%d,%d,%d]' % (sym_str, *index)
|
||||
if time != None:
|
||||
sym_str = '%s_%d' % (sym_str, int(time))
|
||||
Expr.__init__(self, sym_str)
|
||||
|
||||
def getBaseName(self):
|
||||
return self.sym_str
|
||||
|
||||
def getIndex(self):
|
||||
return self.indicies
|
||||
|
||||
def getTime(self):
|
||||
return self.time
|
||||
|
||||
def parseExpr(symbol):
|
||||
"""A simple expression parser, takes in a PropSymbolExpr and returns
|
||||
its deconstruction in the form ( sym_str, indices, time ).
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
>>> parseExpr("North[3]")
|
||||
('North', None, (3))
|
||||
>>> parseExpr("A")
|
||||
(A, None, ())
|
||||
>>> parseExpr("P[3,4]_1")
|
||||
('P', 1, (3, 4))
|
||||
"""
|
||||
tokens = re.split(r"_", str(symbol))
|
||||
time = None
|
||||
if len(tokens) == 2:
|
||||
symbol = tokens[0]
|
||||
time = int(tokens[1])
|
||||
|
||||
tokens = re.findall(r"[\w]+", str(symbol))
|
||||
if len(tokens) == 1:
|
||||
return (tokens[0], (), time)
|
||||
return (tokens[0], tuple(map(int,tokens[1:])), time)
|
||||
|
||||
def expr(s):
|
||||
"""Create an Expr representing a logic expression by parsing the input
|
||||
string. Symbols and numbers are automatically converted to Exprs.
|
||||
In addition you can use alternative spellings of these operators:
|
||||
'x ==> y' parses as (x >> y) # Implication
|
||||
'x <== y' parses as (x << y) # Reverse implication
|
||||
'x <=> y' parses as (x % y) # Logical equivalence
|
||||
'x =/= y' parses as (x ^ y) # Logical disequality (xor)
|
||||
But BE CAREFUL; precedence of implication is wrong. expr('P & Q ==> R & S')
|
||||
is ((P & (Q >> R)) & S); so you must use expr('(P & Q) ==> (R & S)').
|
||||
>>> expr('P <=> Q(1)')
|
||||
(P <=> Q(1))
|
||||
>>> expr('P & Q | ~R(x, F(x))')
|
||||
((P & Q) | ~R(x, F(x)))
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(s, Expr): return s
|
||||
if isnumber(s): return Expr(s)
|
||||
## Replace the alternative spellings of operators with canonical spellings
|
||||
s = s.replace('==>', '>>').replace('<==', '<<')
|
||||
s = s.replace('<=>', '%').replace('=/=', '^')
|
||||
## Replace a symbol or number, such as 'P' with 'Expr("P")'
|
||||
s = re.sub(r'([a-zA-Z0-9_.]+)', r'Expr("\1")', s)
|
||||
## Now eval the string. (A security hole; do not use with an adversary.)
|
||||
return eval(s, {'Expr':Expr})
|
||||
|
||||
def is_symbol(s):
|
||||
"A string s is a symbol if it starts with an alphabetic char."
|
||||
return isinstance(s, str) and s[:1].isalpha()
|
||||
|
||||
def is_var_symbol(s):
|
||||
"A logic variable symbol is an initial-lowercase string."
|
||||
return is_symbol(s) and s[0].islower()
|
||||
|
||||
def is_prop_symbol(s):
|
||||
"""A proposition logic symbol is an initial-uppercase string other than
|
||||
TRUE or FALSE."""
|
||||
return is_symbol(s) and s[0].isupper() and s != 'TRUE' and s != 'FALSE' and re.match(r'[a-zA-Z0-9_\[\],]*$', s)
|
||||
|
||||
def variables(s):
|
||||
"""Return a set of the variables in expression s.
|
||||
>>> ppset(variables(F(x, A, y)))
|
||||
set([x, y])
|
||||
>>> ppset(variables(F(G(x), z)))
|
||||
set([x, z])
|
||||
>>> ppset(variables(expr('F(x, x) & G(x, y) & H(y, z) & R(A, z, z)')))
|
||||
set([x, y, z])
|
||||
"""
|
||||
result = set([])
|
||||
def walk(s):
|
||||
if is_variable(s):
|
||||
result.add(s)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for arg in s.args:
|
||||
walk(arg)
|
||||
walk(s)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
def is_definite_clause(s):
|
||||
"""returns True for exprs s of the form A & B & ... & C ==> D,
|
||||
where all literals are positive. In clause form, this is
|
||||
~A | ~B | ... | ~C | D, where exactly one clause is positive.
|
||||
>>> is_definite_clause(expr('Farmer(Mac)'))
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> is_definite_clause(expr('~Farmer(Mac)'))
|
||||
False
|
||||
>>> is_definite_clause(expr('(Farmer(f) & Rabbit(r)) ==> Hates(f, r)'))
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> is_definite_clause(expr('(Farmer(f) & ~Rabbit(r)) ==> Hates(f, r)'))
|
||||
False
|
||||
>>> is_definite_clause(expr('(Farmer(f) | Rabbit(r)) ==> Hates(f, r)'))
|
||||
False
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if is_symbol(s.op):
|
||||
return True
|
||||
elif s.op == '>>':
|
||||
antecedent, consequent = s.args
|
||||
return (is_symbol(consequent.op)
|
||||
and every(lambda arg: is_symbol(arg.op), conjuncts(antecedent)))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_definite_clause(s):
|
||||
"Return the antecedents and the consequent of a definite clause."
|
||||
assert is_definite_clause(s)
|
||||
if is_symbol(s.op):
|
||||
return [], s
|
||||
else:
|
||||
antecedent, consequent = s.args
|
||||
return conjuncts(antecedent), consequent
|
||||
|
||||
## Useful constant Exprs used in examples and code:
|
||||
class SpecialExpr(Expr):
|
||||
"""Exists solely to allow the normal Expr constructor to assert valid symbol
|
||||
syntax while still having some way to create the constants
|
||||
TRUE, FALSE, ZERO, ONE, and, TWO
|
||||
"""
|
||||
def __init__(self, op, *args):
|
||||
"Op is a string or number; args are Exprs (or are coerced to Exprs)."
|
||||
assert isinstance(op, str) or (isnumber(op) and not args)
|
||||
self.op = num_or_str(op)
|
||||
self.args = tuple(map(expr, args)) ## Coerce args to Exprs
|
||||
|
||||
TRUE, FALSE = tuple(map(SpecialExpr, ['TRUE', 'FALSE']))
|
||||
ZERO, ONE, TWO = tuple(map(SpecialExpr, [0, 1, 2]))
|
||||
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, P, Q = tuple(map(Expr, 'ABCDEFGPQ'))
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
def prop_symbols(x):
|
||||
"Return a list of all propositional symbols in x."
|
||||
if not isinstance(x, Expr):
|
||||
return []
|
||||
elif is_prop_symbol(x.op):
|
||||
return [x]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return list(set(symbol for arg in x.args
|
||||
for symbol in prop_symbols(arg)))
|
||||
|
||||
def pl_true(exp, model={}):
|
||||
"""Return True if the propositional logic expression is true in the model,
|
||||
and False if it is false. If the model does not specify the value for
|
||||
every proposition, this may return None to indicate 'not obvious';
|
||||
this may happen even when the expression is tautological."""
|
||||
op, args = exp.op, exp.args
|
||||
if exp == TRUE:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
elif exp == FALSE:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
elif is_prop_symbol(op):
|
||||
return model.get(exp)
|
||||
elif op == '~':
|
||||
p = pl_true(args[0], model)
|
||||
if p is None: return None
|
||||
else: return not p
|
||||
elif op == '|':
|
||||
result = False
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
p = pl_true(arg, model)
|
||||
if p is True: return True
|
||||
if p is None: result = None
|
||||
return result
|
||||
elif op == '&':
|
||||
result = True
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
p = pl_true(arg, model)
|
||||
if p is False: return False
|
||||
if p is None: result = None
|
||||
return result
|
||||
p, q = args
|
||||
if op == '>>':
|
||||
return pl_true(~p | q, model)
|
||||
elif op == '<<':
|
||||
return pl_true(p | ~q, model)
|
||||
pt = pl_true(p, model)
|
||||
if pt is None: return None
|
||||
qt = pl_true(q, model)
|
||||
if qt is None: return None
|
||||
if op == '<=>':
|
||||
return pt == qt
|
||||
elif op == '^':
|
||||
return pt != qt
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError("illegal operator in logic expression" + str(exp))
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
## Convert to Conjunctive Normal Form (CNF)
|
||||
|
||||
def to_cnf(s):
|
||||
"""Convert a propositional logical sentence s to conjunctive normal form.
|
||||
That is, to the form ((A | ~B | ...) & (B | C | ...) & ...) [p. 253]
|
||||
>>> to_cnf("~(B|C)")
|
||||
(~B & ~C)
|
||||
>>> to_cnf("B <=> (P1|P2)")
|
||||
((~P1 | B) & (~P2 | B) & (P1 | P2 | ~B))
|
||||
>>> to_cnf("a | (b & c) | d")
|
||||
((b | a | d) & (c | a | d))
|
||||
>>> to_cnf("A & (B | (D & E))")
|
||||
(A & (D | B) & (E | B))
|
||||
>>> to_cnf("A | (B | (C | (D & E)))")
|
||||
((D | A | B | C) & (E | A | B | C))
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(s, str): s = expr(s)
|
||||
s = eliminate_implications(s) # Steps 1, 2 from p. 253
|
||||
s = move_not_inwards(s) # Step 3
|
||||
s = distribute_and_over_or(s) # Step 4
|
||||
return s
|
||||
|
||||
def eliminate_implications(s):
|
||||
"""Change >>, <<, and <=> into &, |, and ~. That is, return an Expr
|
||||
that is equivalent to s, but has only &, |, and ~ as logical operators.
|
||||
>>> eliminate_implications(A >> (~B << C))
|
||||
((~B | ~C) | ~A)
|
||||
>>> eliminate_implications(A ^ B)
|
||||
((A & ~B) | (~A & B))
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not s.args or is_symbol(s.op): return s ## (Atoms are unchanged.)
|
||||
args = tuple(map(eliminate_implications, s.args))
|
||||
a, b = args[0], args[-1]
|
||||
if s.op == '>>':
|
||||
return (b | ~a)
|
||||
elif s.op == '<<':
|
||||
return (a | ~b)
|
||||
elif s.op == '<=>':
|
||||
return (a | ~b) & (b | ~a)
|
||||
elif s.op == '^':
|
||||
assert len(args) == 2 ## TODO: relax this restriction
|
||||
return (a & ~b) | (~a & b)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert s.op in ('&', '|', '~')
|
||||
return Expr(s.op, *args)
|
||||
|
||||
def move_not_inwards(s):
|
||||
"""Rewrite sentence s by moving negation sign inward.
|
||||
>>> move_not_inwards(~(A | B))
|
||||
(~A & ~B)
|
||||
>>> move_not_inwards(~(A & B))
|
||||
(~A | ~B)
|
||||
>>> move_not_inwards(~(~(A | ~B) | ~~C))
|
||||
((A | ~B) & ~C)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if s.op == '~':
|
||||
NOT = lambda b: move_not_inwards(~b)
|
||||
a = s.args[0]
|
||||
if a.op == '~': return move_not_inwards(a.args[0]) # ~~A ==> A
|
||||
if a.op =='&': return associate('|', tuple(map(NOT, a.args)))
|
||||
if a.op =='|': return associate('&', tuple(map(NOT, a.args)))
|
||||
return s
|
||||
elif is_symbol(s.op) or not s.args:
|
||||
return s
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return Expr(s.op, *map(move_not_inwards, s.args))
|
||||
|
||||
def distribute_and_over_or(s):
|
||||
"""Given a sentence s consisting of conjunctions and disjunctions
|
||||
of literals, return an equivalent sentence in CNF.
|
||||
>>> distribute_and_over_or((A & B) | C)
|
||||
((A | C) & (B | C))
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if s.op == '|':
|
||||
s = associate('|', s.args)
|
||||
if s.op != '|':
|
||||
return distribute_and_over_or(s)
|
||||
if len(s.args) == 0:
|
||||
return FALSE
|
||||
if len(s.args) == 1:
|
||||
return distribute_and_over_or(s.args[0])
|
||||
conj = find_if((lambda d: d.op == '&'), s.args)
|
||||
if not conj:
|
||||
return s
|
||||
others = [a for a in s.args if a is not conj]
|
||||
rest = associate('|', others)
|
||||
return associate('&', [distribute_and_over_or(c|rest)
|
||||
for c in conj.args])
|
||||
elif s.op == '&':
|
||||
return associate('&', map(distribute_and_over_or, s.args))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return s
|
||||
|
||||
def associate(op, args):
|
||||
"""Given an associative op, return an expression with the same
|
||||
meaning as Expr(op, *args), but flattened -- that is, with nested
|
||||
instances of the same op promoted to the top level.
|
||||
>>> associate('&', [(A&B),(B|C),(B&C)])
|
||||
(A & B & (B | C) & B & C)
|
||||
>>> associate('|', [A|(B|(C|(A&B)))])
|
||||
(A | B | C | (A & B))
|
||||
"""
|
||||
args = dissociate(op, args)
|
||||
if len(args) == 0:
|
||||
return _op_identity[op]
|
||||
elif len(args) == 1:
|
||||
return args[0]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return Expr(op, *args)
|
||||
|
||||
_op_identity = {'&':TRUE, '|':FALSE, '+':ZERO, '*':ONE}
|
||||
|
||||
def conjoin(exprs, *args):
|
||||
"""Given a list of expressions, returns their conjunction. Can be called either
|
||||
with one argument that is a list of expressions, or with several arguments that
|
||||
are each an expression.
|
||||
If exprs is a singular expression or contains only one expression, return that
|
||||
expression directly.
|
||||
If exprs is an empty list, throw an error.
|
||||
>>> conjoin([(A&B),(B|C),(B&C)])
|
||||
(A & B & (B | C) & B & C)
|
||||
>>> conjoin((A&B), (B|C), (B&C))
|
||||
(A & B & (B | C) & B & C)
|
||||
>>> conjoin([A])
|
||||
A
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if args:
|
||||
return conjoin([exprs] + list(args))
|
||||
if (type(exprs) != list):
|
||||
return exprs
|
||||
|
||||
assert len(exprs) > 0, "List to conjoin cannot be empty."
|
||||
|
||||
# It is a list. Enforce everything in the list is an Expr
|
||||
for expr in exprs:
|
||||
assert isinstance(expr, Expr), "An item in list to conjoin is not an Expr."
|
||||
|
||||
if (len(exprs) == 1):
|
||||
return exprs[0]
|
||||
return associate('&', exprs)
|
||||
|
||||
def disjoin(exprs, *args):
|
||||
"""Given a list of expressions, returns their disjunction. Can be called either
|
||||
with one argument that is a list of expressions, or with several arguments that
|
||||
are each an expression.
|
||||
If exprs is a singular expression or contains only one expression, return that
|
||||
expression directly.
|
||||
If exprs is an empty list, throw an error.
|
||||
>>> disjoin([C, (A&B), (D&E)])
|
||||
(C | (A & B) | (D & E))
|
||||
>>> disjoin(C, (A&B), (D&E))
|
||||
(C | (A & B) | (D & E))
|
||||
>>> disjoin([C])
|
||||
D
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if args:
|
||||
return disjoin([exprs] + list(args))
|
||||
if (type(exprs) != list):
|
||||
return exprs
|
||||
|
||||
assert len(exprs) > 0, "List to disjoin cannot be empty."
|
||||
|
||||
# It is a list. Enforce everything in the list is an Expr
|
||||
for expr in exprs:
|
||||
assert isinstance(expr, Expr), "An item in list to disjoin is not an Expr."
|
||||
|
||||
if (len(exprs) == 1):
|
||||
return exprs[0]
|
||||
return associate('|', exprs)
|
||||
|
||||
def dissociate(op, args):
|
||||
"""Given an associative op, return a flattened list result such
|
||||
that Expr(op, *result) means the same as Expr(op, *args)."""
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
def collect(subargs):
|
||||
for arg in subargs:
|
||||
if arg.op == op: collect(arg.args)
|
||||
else: result.append(arg)
|
||||
collect(args)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
def conjuncts(s):
|
||||
"""Return a list of the conjuncts in the sentence s.
|
||||
>>> conjuncts(A & B)
|
||||
[A, B]
|
||||
>>> conjuncts(A | B)
|
||||
[(A | B)]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return dissociate('&', [s])
|
||||
|
||||
def disjuncts(s):
|
||||
"""Return a list of the disjuncts in the sentence s.
|
||||
>>> disjuncts(A | B)
|
||||
[A, B]
|
||||
>>> disjuncts(A & B)
|
||||
[(A & B)]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return dissociate('|', [s])
|
||||
|
||||
def is_valid_cnf(exp):
|
||||
if not isinstance(exp, Expr):
|
||||
print("Input is not an expression.")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
clauses = conjuncts(exp);
|
||||
|
||||
for c in clauses:
|
||||
literals = disjuncts(c)
|
||||
|
||||
for lit in literals:
|
||||
if len(lit.args) == 0:
|
||||
symbol = lit;
|
||||
elif len(lit.args) == 1:
|
||||
symbol = lit.args[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(symbol.args) != 0:
|
||||
print("Found a NOT outside of %s" % symbol)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Found %s where only a literal should be." % lit)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
symbol_str = str(symbol)
|
||||
|
||||
if not is_symbol(symbol_str):
|
||||
print("%s is not a valid symbol." % symbol_str)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
elif not symbol_str[0].isupper():
|
||||
print("The symbol %s must begin with an upper-case letter." % symbol_str)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
elif symbol_str == 'TRUE':
|
||||
print("TRUE is not a valid symbol.")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
elif symbol_str == 'FALSE':
|
||||
print("FALSE is not a valid symbol.")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# pycosat python wrapper around PicoSAT software.
|
||||
# https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pycosat
|
||||
|
||||
def pycoSAT(expr):
|
||||
"""Check satisfiability of an expression.
|
||||
Given a CNF expression, returns a model that causes the input expression
|
||||
to be true. Returns false if it cannot find a satisfible model.
|
||||
A model is simply a dictionary with Expr symbols as keys with corresponding values
|
||||
that are booleans: True if that symbol is true in the model and False if it is
|
||||
false in the model.
|
||||
Calls the pycosat solver: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pycosat
|
||||
>>> ppsubst(pycoSAT(A&~B))
|
||||
{A: True, B: False}
|
||||
>>> pycoSAT(P&~P)
|
||||
False
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
clauses = conjuncts(expr)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load symbol dictionary
|
||||
symbol_dict = mapSymbolAndIndices(clauses)
|
||||
# Convert Expr to integers
|
||||
clauses_int = exprClausesToIndexClauses(clauses, symbol_dict)
|
||||
|
||||
model_int = pycosat.solve(clauses_int)
|
||||
|
||||
if model_int == 'UNSAT' or model_int == 'UNKNOWN':
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
model = indexModelToExprModel(model_int, symbol_dict)
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
def mapSymbolAndIndices(clauses):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Create a dictionary that maps each clause to an integer index.
|
||||
Uses a bidirectional dictionary {key1:value1, value1:key1, ...} for quick
|
||||
access from symbol to index and index to symbol.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
symbol_dict = {}
|
||||
idx = 1
|
||||
for clause in clauses:
|
||||
symbols = prop_symbols(clause)
|
||||
for symbol in symbols:
|
||||
if symbol not in symbol_dict:
|
||||
symbol_dict[symbol] = idx
|
||||
symbol_dict[idx] = symbol
|
||||
idx +=1
|
||||
|
||||
return symbol_dict
|
||||
|
||||
def exprClausesToIndexClauses(clauses, symbol_dict):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Convert each Expr in a list of clauses (CNF) into its corresponding index in
|
||||
the symbol_dict (see mapSymbolAndIndices)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
clauses_int = []
|
||||
for c in clauses:
|
||||
c_disj = disjuncts(c)
|
||||
|
||||
c_int = []
|
||||
for lit in c_disj:
|
||||
# If literal is symbol, convert to index and add it.
|
||||
# Otherwise it is ~symbol, in which case, we extract the symbol,
|
||||
# convert it to index, and add the negative of the index
|
||||
if len(lit.args) == 0:
|
||||
c_int += [symbol_dict[lit]]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
c_int += [-symbol_dict[lit.args[0]]]
|
||||
clauses_int += [c_int]
|
||||
|
||||
return clauses_int
|
||||
|
||||
def indexModelToExprModel(model_int, symbol_dict):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Convert a model with indices into a model with the corresponding Expr in
|
||||
the symbol_dict (see mapSymbolAndIndices)
|
||||
>>>
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model = {}
|
||||
for lit_int in model_int:
|
||||
if lit_int > 0:
|
||||
model[symbol_dict[lit_int]] = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model[symbol_dict[-lit_int]] = False
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
622
logic/logicAgents.py
Normal file
622
logic/logicAgents.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,622 @@
|
||||
# logicAgents.py
|
||||
# --------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This file contains all of the agents that can be selected to control Pacman. To
|
||||
select an agent, use the '-p' option when running pacman.py. Arguments can be
|
||||
passed to your agent using '-a'. For example, to load a LogicAgent that uses
|
||||
logicPlan.positionLogicPlan, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
> python pacman.py -p LogicAgent -a fn=positionLogicPlan
|
||||
|
||||
Commands to invoke other planning methods can be found in the project
|
||||
description.
|
||||
|
||||
You should NOT change code in this file
|
||||
|
||||
Good luck and happy planning!
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from game import Directions
|
||||
from game import Agent
|
||||
from game import Actions
|
||||
from game import Grid
|
||||
from graphicsUtils import *
|
||||
import graphicsDisplay
|
||||
import util
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
import logicPlan
|
||||
import random
|
||||
|
||||
class GoWestAgent(Agent):
|
||||
"An agent that goes West until it can't."
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
"The agent receives a GameState (defined in pacman.py)."
|
||||
if Directions.WEST in state.getLegalPacmanActions():
|
||||
return Directions.WEST
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return Directions.STOP
|
||||
|
||||
#######################################################
|
||||
# This portion is written for you, but will only work #
|
||||
# after you fill in parts of logicPlan.py #
|
||||
#######################################################
|
||||
|
||||
class LogicAgent(Agent):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This very general logic agent finds a path using a supplied planning
|
||||
algorithm for a supplied planning problem, then returns actions to follow that
|
||||
path.
|
||||
|
||||
As a default, this agent runs positionLogicPlan on a
|
||||
PositionPlanningProblem to find location (1,1)
|
||||
|
||||
Options for fn include:
|
||||
positionLogicPlan or plp
|
||||
foodLogicPlan or flp
|
||||
foodGhostLogicPlan or fglp
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note: You should NOT change any code in LogicAgent
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, fn='positionLogicPlan', prob='PositionPlanningProblem', plan_mod=logicPlan):
|
||||
# Warning: some advanced Python magic is employed below to find the right functions and problems
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the planning function from the name and heuristic
|
||||
if fn not in dir(plan_mod):
|
||||
raise AttributeError(fn + ' is not a planning function in logicPlan.py.')
|
||||
func = getattr(plan_mod, fn)
|
||||
self.planningFunction = lambda x: func(x)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the planning problem type from the name
|
||||
if prob not in globals().keys() or not prob.endswith('Problem'):
|
||||
raise AttributeError(prob + ' is not a planning problem type in logicAgents.py.')
|
||||
self.planType = globals()[prob]
|
||||
self.live_checking = False
|
||||
print('[LogicAgent] using problem type ' + prob)
|
||||
|
||||
def registerInitialState(self, state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This is the first time that the agent sees the layout of the game
|
||||
board. Here, we choose a path to the goal. In this phase, the agent
|
||||
should compute the path to the goal and store it in a local variable.
|
||||
All of the work is done in this method!
|
||||
|
||||
state: a GameState object (pacman.py)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self.planningFunction == None:
|
||||
raise Exception("No planning function provided for LogicAgent")
|
||||
starttime = time.time()
|
||||
problem = self.planType(state) # Makes a new planning problem
|
||||
|
||||
self.actions = [] # In case planningFunction times out
|
||||
self.actions = self.planningFunction(problem) # Find a path
|
||||
if self.actions == None:
|
||||
raise Exception('Studenct code supplied None instead of result')
|
||||
totalCost = problem.getCostOfActions(self.actions)
|
||||
print('Path found with total cost of %d in %.1f seconds' % (totalCost, time.time() - starttime))
|
||||
# TODO Drop
|
||||
if '_expanded' in dir(problem):
|
||||
print('Nodes expanded: %d' % problem._expanded)
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the next action in the path chosen earlier (in
|
||||
registerInitialState). Return Directions.STOP if there is no further
|
||||
action to take.
|
||||
|
||||
state: a GameState object (pacman.py)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# import ipdb; ipdb.set_trace()
|
||||
if 'actionIndex' not in dir(self): self.actionIndex = 0
|
||||
i = self.actionIndex
|
||||
self.actionIndex += 1
|
||||
if i < len(self.actions):
|
||||
return self.actions[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('Oh no! The Pacman agent created a plan that was too short!')
|
||||
print()
|
||||
return None
|
||||
# return Directions.STOP
|
||||
|
||||
class CheckSatisfiabilityAgent(LogicAgent):
|
||||
def __init__(self, fn='checkLocationSatisfiability', prob='LocMapProblem', plan_mod=logicPlan):
|
||||
# Warning: some advanced Python magic is employed below to find the right functions and problems
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the planning function from the name and heuristic
|
||||
if fn not in dir(plan_mod):
|
||||
raise AttributeError(fn + ' is not a planning function in logicPlan.py.')
|
||||
func = getattr(plan_mod, fn)
|
||||
self.planningFunction = lambda x: func(*x)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the planning problem type from the name
|
||||
if prob not in globals().keys() or not prob.endswith('Problem'):
|
||||
raise AttributeError(prob + ' is not a planning problem type in logicAgents.py.')
|
||||
self.planType = globals()[prob]
|
||||
print('[LogicAgent] using problem type ' + prob)
|
||||
self.live_checking = False
|
||||
|
||||
def registerInitialState(self, state):
|
||||
if self.planningFunction == None:
|
||||
raise Exception("No planning function provided for LogicAgent")
|
||||
starttime = time.time()
|
||||
self.problem = self.planType(state) # Makes a new planning problem
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
return "EndGame"
|
||||
|
||||
class LocalizeMapAgent(LogicAgent):
|
||||
"""Parent class for localization, mapping, and slam"""
|
||||
def __init__(self, fn='positionLogicPlan', prob='LocMapProblem', plan_mod=logicPlan, display=None, scripted_actions=[]):
|
||||
# Warning: some advanced Python magic is employed below to find the right functions and problems
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the planning function from the name and heuristic
|
||||
if fn not in dir(plan_mod):
|
||||
raise AttributeError(fn + ' is not a planning function in logicPlan.py.')
|
||||
func = getattr(plan_mod, fn)
|
||||
self.planningFunction = lambda x, y: func(x, y)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the planning problem type from the name
|
||||
if prob not in globals().keys() or not prob.endswith('Problem'):
|
||||
raise AttributeError(prob + ' is not a planning problem type in logicAgents.py.')
|
||||
self.planType = globals()[prob]
|
||||
print('[LogicAgent] using problem type ' + prob)
|
||||
self.visited_states = []
|
||||
self.display = display
|
||||
self.scripted_actions = scripted_actions
|
||||
self.live_checking = True
|
||||
|
||||
def resetLocation(self):
|
||||
self.visited_states = []
|
||||
self.state = self.problem.getStartState()
|
||||
self.visited_states.append(self.state)
|
||||
|
||||
def addNoOp_t0(self):
|
||||
self.visited_states = [self.visited_states[0]] + list(self.visited_states)
|
||||
self.actions.insert(0, "Stop")
|
||||
|
||||
def registerInitialState(self, state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This is the first time that the agent sees the layout of the game
|
||||
board. Here, we choose a path to the goal. In this phase, the agent
|
||||
should compute the path to the goal and store it in a local variable.
|
||||
All of the work is done in this method!
|
||||
|
||||
state: a GameState object (pacman.py)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self.planningFunction == None:
|
||||
raise Exception("No planning function provided for LogicAgent")
|
||||
starttime = time.time()
|
||||
problem = self.planType(state) # Makes a new planning problem
|
||||
|
||||
self.problem = problem
|
||||
self.state = self.problem.getStartState()
|
||||
|
||||
self.actions = self.scripted_actions
|
||||
self.resetLocation()
|
||||
self.planning_fn_output = self.planningFunction(problem, self)
|
||||
# self.addNoOp_t0()
|
||||
|
||||
def get_known_walls_non_walls_from_known_map(self, known_map):
|
||||
# map is 1 for known wall, 0 for
|
||||
if known_map == None:
|
||||
raise Exception('Student code supplied None instead of a 2D known map')
|
||||
known_walls = [[(True if entry==1 else False) for entry in row] for row in known_map]
|
||||
known_non_walls = [[(True if entry==0 else False) for entry in row] for row in known_map]
|
||||
return known_walls, known_non_walls
|
||||
|
||||
class LocalizationLogicAgent(LocalizeMapAgent):
|
||||
def __init__(self, fn='localization', prob='LocalizationProblem', plan_mod=logicPlan, display=None, scripted_actions=[]):
|
||||
super(LocalizationLogicAgent, self).__init__(fn, prob, plan_mod, display, scripted_actions)
|
||||
self.num_timesteps = len(scripted_actions) if scripted_actions else 5
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the next action in the path chosen earlier (in
|
||||
registerInitialState). Return Directions.STOP if there is no further
|
||||
action to take.
|
||||
|
||||
state: a GameState object (pacman.py)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# import ipdb; ipdb.set_trace()
|
||||
if 'actionIndex' not in dir(self): self.actionIndex = 0
|
||||
i = self.actionIndex
|
||||
self.actionIndex += 1
|
||||
|
||||
planning_fn_output = None
|
||||
if i < self.num_timesteps:
|
||||
proposed_action = self.actions[i]
|
||||
planning_fn_output = next(self.planning_fn_output)
|
||||
if planning_fn_output == None:
|
||||
raise Exception('Studenct code supplied None instead of result')
|
||||
if isinstance(self.display, graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics):
|
||||
self.drawPossibleStates(planning_fn_output, direction=self.actions[i])
|
||||
elif i < len(self.actions):
|
||||
proposed_action = self.actions[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
proposed_action = "EndGame"
|
||||
|
||||
return proposed_action, planning_fn_output
|
||||
|
||||
def moveToNextState(self, action):
|
||||
oldX, oldY = self.state
|
||||
dx, dy = Actions.directionToVector(action)
|
||||
x, y = int(oldX + dx), int(oldY + dy)
|
||||
if self.problem.walls[x][y]:
|
||||
raise AssertionError("Taking an action that goes into wall")
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.state = (x, y)
|
||||
self.visited_states.append(self.state)
|
||||
|
||||
def getPercepts(self):
|
||||
x, y = self.state
|
||||
north_iswall = self.problem.walls[x][y+1]
|
||||
south_iswall = self.problem.walls[x][y-1]
|
||||
east_iswall = self.problem.walls[x+1][y]
|
||||
west_iswall = self.problem.walls[x-1][y]
|
||||
return [north_iswall, south_iswall, east_iswall, west_iswall]
|
||||
|
||||
def getValidActions(self):
|
||||
x, y = self.state
|
||||
actions = []
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x][y+1]: actions.append('North')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x][y-1]: actions.append('South')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x+1][y]: actions.append('East')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x-1][y]: actions.append('West')
|
||||
return actions
|
||||
|
||||
def drawPossibleStates(self, possibleLocations=None, direction="North", pacman_position=None):
|
||||
import __main__
|
||||
self.display.clearExpandedCells() # Erase previous colors
|
||||
self.display.colorCircleCells(possibleLocations, direction=direction, pacman_position=pacman_position)
|
||||
|
||||
class MappingLogicAgent(LocalizeMapAgent):
|
||||
def __init__(self, fn='mapping', prob='MappingProblem', plan_mod=logicPlan, display=None, scripted_actions=[]):
|
||||
super(MappingLogicAgent, self).__init__(fn, prob, plan_mod, display, scripted_actions)
|
||||
self.num_timesteps = len(scripted_actions) if scripted_actions else 10
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the next action in the path chosen earlier (in
|
||||
registerInitialState). Return Directions.STOP if there is no further
|
||||
action to take.
|
||||
|
||||
state: a GameState object (pacman.py)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if 'actionIndex' not in dir(self): self.actionIndex = 0
|
||||
i = self.actionIndex
|
||||
self.actionIndex += 1
|
||||
|
||||
planning_fn_output = None
|
||||
if i < self.num_timesteps:
|
||||
proposed_action = self.actions[i]
|
||||
planning_fn_output = next(self.planning_fn_output)
|
||||
if isinstance(self.display, graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics):
|
||||
self.drawWallBeliefs(planning_fn_output, self.actions[i], self.visited_states[:i])
|
||||
elif i < len(self.actions):
|
||||
proposed_action = self.actions[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
proposed_action = "EndGame"
|
||||
|
||||
return proposed_action, planning_fn_output
|
||||
|
||||
def moveToNextState(self, action):
|
||||
oldX, oldY = self.state
|
||||
dx, dy = Actions.directionToVector(action)
|
||||
x, y = int(oldX + dx), int(oldY + dy)
|
||||
if self.problem.walls[x][y]:
|
||||
raise AssertionError("Taking an action that goes into wall")
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.state = (x, y)
|
||||
self.visited_states.append(self.state)
|
||||
|
||||
def getPercepts(self):
|
||||
x, y = self.state
|
||||
north_iswall = self.problem.walls[x][y+1]
|
||||
south_iswall = self.problem.walls[x][y-1]
|
||||
east_iswall = self.problem.walls[x+1][y]
|
||||
west_iswall = self.problem.walls[x-1][y]
|
||||
return [north_iswall, south_iswall, east_iswall, west_iswall]
|
||||
|
||||
def getValidActions(self):
|
||||
x, y = self.state
|
||||
actions = []
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x][y+1]: actions.append('North')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x][y-1]: actions.append('South')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x+1][y]: actions.append('East')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x-1][y]: actions.append('West')
|
||||
return actions
|
||||
|
||||
def drawWallBeliefs(self, known_map=None, direction="North", visited_states_to_render=[]):
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import __main__
|
||||
from graphicsUtils import draw_background, refresh
|
||||
known_walls, known_non_walls = self.get_known_walls_non_walls_from_known_map(known_map)
|
||||
wallGrid = Grid(self.problem.walls.width, self.problem.walls.height, initialValue=False)
|
||||
wallGrid.data = known_walls
|
||||
allTrueWallGrid = Grid(self.problem.walls.width, self.problem.walls.height, initialValue=True)
|
||||
self.display.clearExpandedCells() # Erase previous colors
|
||||
self.display.drawWalls(wallGrid, formatColor(.9,0,0), allTrueWallGrid)
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
class SLAMLogicAgent(LocalizeMapAgent):
|
||||
def __init__(self, fn='slam', prob='SLAMProblem', plan_mod=logicPlan, display=None, scripted_actions=[]):
|
||||
super(SLAMLogicAgent, self).__init__(fn, prob, plan_mod, display, scripted_actions)
|
||||
self.scripted_actions = scripted_actions
|
||||
self.num_timesteps = len(self.scripted_actions) if self.scripted_actions else 10
|
||||
self.live_checking = True
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the next action in the path chosen earlier (in
|
||||
registerInitialState). Return Directions.STOP if there is no further
|
||||
action to take.
|
||||
|
||||
state: a GameState object (pacman.py)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# import ipdb; ipdb.set_trace()
|
||||
if 'actionIndex' not in dir(self): self.actionIndex = 0
|
||||
i = self.actionIndex
|
||||
self.actionIndex += 1
|
||||
pacman_loc = self.visited_states[i]
|
||||
|
||||
planning_fn_output = None
|
||||
if i < self.num_timesteps:
|
||||
proposed_action = self.actions[i]
|
||||
planning_fn_output = next(self.planning_fn_output)
|
||||
if planning_fn_output == None:
|
||||
raise Exception('Studenct code supplied None instead of result')
|
||||
if isinstance(self.display, graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics):
|
||||
self.drawWallandPositionBeliefs(
|
||||
known_map=planning_fn_output[0],
|
||||
possibleLocations=planning_fn_output[1],
|
||||
direction=self.actions[i])
|
||||
elif i < len(self.actions):
|
||||
proposed_action = self.actions[i]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
proposed_action = "EndGame"
|
||||
|
||||
# SLAM needs to handle illegal actions
|
||||
if proposed_action not in self.getValidActions(pacman_loc) and proposed_action not in ["Stop", "EndGame"]:
|
||||
proposed_action = "Stop"
|
||||
|
||||
return proposed_action, planning_fn_output
|
||||
|
||||
def moveToNextState(self, action):
|
||||
oldX, oldY = self.state
|
||||
dx, dy = Actions.directionToVector(action)
|
||||
x, y = int(oldX + dx), int(oldY + dy)
|
||||
if self.problem.walls[x][y]:
|
||||
# raise AssertionError("Taking an action that goes into wall")
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.state = (x, y)
|
||||
self.visited_states.append(self.state)
|
||||
|
||||
def getPercepts(self):
|
||||
x, y = self.state
|
||||
north_iswall = self.problem.walls[x][y+1]
|
||||
south_iswall = self.problem.walls[x][y-1]
|
||||
east_iswall = self.problem.walls[x+1][y]
|
||||
west_iswall = self.problem.walls[x-1][y]
|
||||
num_adj_walls = sum([north_iswall, south_iswall, east_iswall, west_iswall])
|
||||
# percept format: [adj_to_>=1_wall, adj_to_>=2_wall, adj_to_>=3_wall]
|
||||
percept = [num_adj_walls >= i for i in range(1, 4)]
|
||||
return percept
|
||||
|
||||
def getValidActions(self, state=None):
|
||||
if not state:
|
||||
state = self.state
|
||||
x, y = state
|
||||
actions = []
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x][y+1]: actions.append('North')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x][y-1]: actions.append('South')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x+1][y]: actions.append('East')
|
||||
if not self.problem.walls[x-1][y]: actions.append('West')
|
||||
return actions
|
||||
|
||||
def drawWallandPositionBeliefs(self, known_map=None, possibleLocations=None,
|
||||
direction="North", visited_states_to_render=[], pacman_position=None):
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import __main__
|
||||
from graphicsUtils import draw_background, refresh
|
||||
known_walls, known_non_walls = self.get_known_walls_non_walls_from_known_map(known_map)
|
||||
wallGrid = Grid(self.problem.walls.width, self.problem.walls.height, initialValue=False)
|
||||
wallGrid.data = known_walls
|
||||
allTrueWallGrid = Grid(self.problem.walls.width, self.problem.walls.height, initialValue=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Recover list of non-wall coords:
|
||||
non_wall_coords = []
|
||||
for x in range(len(known_non_walls)):
|
||||
for y in range(len(known_non_walls[x])):
|
||||
if known_non_walls[x][y] == 1:
|
||||
non_wall_coords.append((x, y))
|
||||
|
||||
self.display.clearExpandedCells() # Erase previous colors
|
||||
|
||||
self.display.drawWalls(wallGrid, formatColor(.9,0,0), allTrueWallGrid)
|
||||
self.display.colorCircleSquareCells(possibleLocations, square_cells=non_wall_coords, direction=direction, pacman_position=pacman_position)
|
||||
refresh()
|
||||
|
||||
class PositionPlanningProblem(logicPlan.PlanningProblem):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A planning problem defines the state space, start state, goal test, successor
|
||||
function and cost function. This planning problem can be used to find paths
|
||||
to a particular point on the pacman board.
|
||||
|
||||
The state space consists of (x,y) positions in a pacman game.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: this planning problem is fully specified; you should NOT change it.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, gameState, costFn = lambda x: 1, goal=(1,1), start=None, warn=True, visualize=True):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Stores the start and goal.
|
||||
|
||||
gameState: A GameState object (pacman.py)
|
||||
costFn: A function from a planning state (tuple) to a non-negative number
|
||||
goal: A position in the gameState
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.walls = gameState.getWalls()
|
||||
self.startState = gameState.getPacmanPosition()
|
||||
if start != None: self.startState = start
|
||||
self.goal = goal
|
||||
self.costFn = costFn
|
||||
self.visualize = visualize
|
||||
if warn and (gameState.getNumFood() != 1 or not gameState.hasFood(*goal)):
|
||||
print('Warning: this does not look like a regular position planning maze')
|
||||
|
||||
# For display purposes
|
||||
self._visited, self._visitedlist, self._expanded = {}, [], 0 # DO NOT CHANGE
|
||||
|
||||
def getStartState(self):
|
||||
return self.startState
|
||||
|
||||
def getGoalState(self):
|
||||
return self.goal
|
||||
|
||||
def getCostOfActions(self, actions):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the cost of a particular sequence of actions. If those actions
|
||||
include an illegal move, return 999999.
|
||||
|
||||
This is included in the logic project solely for autograding purposes.
|
||||
You should not be calling it.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if actions == None: return 999999
|
||||
x,y= self.getStartState()
|
||||
cost = 0
|
||||
for action in actions:
|
||||
# Check figure out the next state and see whether it's legal
|
||||
dx, dy = Actions.directionToVector(action)
|
||||
x, y = int(x + dx), int(y + dy)
|
||||
if self.walls[x][y]: return 999999
|
||||
cost += self.costFn((x,y))
|
||||
return cost
|
||||
|
||||
def getWidth(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the width of the playable grid (does not include the external wall)
|
||||
Possible x positions for agents will be in range [1,width]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.walls.width-2
|
||||
|
||||
def getHeight(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the height of the playable grid (does not include the external wall)
|
||||
Possible y positions for agents will be in range [1,height]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.walls.height-2
|
||||
|
||||
def manhattanHeuristic(position, problem, info={}):
|
||||
"The Manhattan distance heuristic for a PositionPlanningProblem"
|
||||
xy1 = position
|
||||
xy2 = problem.goal
|
||||
return abs(xy1[0] - xy2[0]) + abs(xy1[1] - xy2[1])
|
||||
|
||||
def euclideanHeuristic(position, problem, info={}):
|
||||
"The Euclidean distance heuristic for a PositionPlanningProblem"
|
||||
xy1 = position
|
||||
xy2 = problem.goal
|
||||
return ( (xy1[0] - xy2[0]) ** 2 + (xy1[1] - xy2[1]) ** 2 ) ** 0.5
|
||||
|
||||
class LocMapProblem:
|
||||
"""Parent class for Localization, Mapping, and SLAM."""
|
||||
def __init__(self, gameState, costFn = lambda x: 1, goal=(1,1), start=None, warn=True, visualize=True):
|
||||
self.walls = gameState.getWalls()
|
||||
self.startState = gameState.getPacmanPosition()
|
||||
if start != None: self.startState = start
|
||||
self._visited, self._visitedlist, self._expanded = {}, [], 0 # DO NOT CHANGE
|
||||
|
||||
def getStartState(self):
|
||||
return self.startState
|
||||
|
||||
def getWidth(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the width of the playable grid (does not include the external wall)
|
||||
Possible x positions for agents will be in range [1,width]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.walls.width-2
|
||||
|
||||
def getHeight(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the height of the playable grid (does not include the external wall)
|
||||
Possible y positions for agents will be in range [1,height]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.walls.height-2
|
||||
|
||||
class LocalizationProblem(LocMapProblem):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
class MappingProblem(LocMapProblem):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
class SLAMProblem(LocMapProblem):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
class FoodPlanningProblem:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A planning problem associated with finding the a path that collects all of the
|
||||
food (dots) in a Pacman game.
|
||||
|
||||
A planning state in this problem is a tuple ( pacmanPosition, foodGrid ) where
|
||||
pacmanPosition: a tuple (x,y) of integers specifying Pacman's position
|
||||
foodGrid: a Grid (see game.py) of either True or False, specifying remaining food
|
||||
"""
|
||||
def __init__(self, startingGameState):
|
||||
self.start = (startingGameState.getPacmanPosition(), startingGameState.getFood())
|
||||
self.walls = startingGameState.getWalls()
|
||||
self.startingGameState = startingGameState
|
||||
self._expanded = 0 # DO NOT CHANGE
|
||||
self.heuristicInfo = {} # A dictionary for the heuristic to store information
|
||||
|
||||
def getStartState(self):
|
||||
return self.start
|
||||
|
||||
def getCostOfActions(self, actions):
|
||||
"""Returns the cost of a particular sequence of actions. If those actions
|
||||
include an illegal move, return 999999.
|
||||
|
||||
This is included in the logic project solely for autograding purposes.
|
||||
You should not be calling it.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
x,y= self.getStartState()[0]
|
||||
cost = 0
|
||||
for action in actions:
|
||||
# figure out the next state and see whether it's legal
|
||||
dx, dy = Actions.directionToVector(action)
|
||||
x, y = int(x + dx), int(y + dy)
|
||||
if self.walls[x][y]:
|
||||
return 999999
|
||||
cost += 1
|
||||
return cost
|
||||
|
||||
def getWidth(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the width of the playable grid (does not include the external wall)
|
||||
Possible x positions for agents will be in range [1,width]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.walls.width-2
|
||||
|
||||
def getHeight(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the height of the playable grid (does not include the external wall)
|
||||
Possible y positions for agents will be in range [1,height]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.walls.height-2
|
||||
648
logic/logicPlan.py
Normal file
648
logic/logicPlan.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,648 @@
|
||||
# logicPlan.py
|
||||
# ------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
In logicPlan.py, you will implement logic planning methods which are called by
|
||||
Pacman agents (in logicAgents.py).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, Callable, Generator, Any
|
||||
import util
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import logic
|
||||
import game
|
||||
|
||||
from logic import conjoin, disjoin
|
||||
from logic import PropSymbolExpr, Expr, to_cnf, pycoSAT, parseExpr, pl_true
|
||||
|
||||
import itertools
|
||||
import copy
|
||||
|
||||
pacman_str = 'P'
|
||||
food_str = 'FOOD'
|
||||
wall_str = 'WALL'
|
||||
pacman_wall_str = pacman_str + wall_str
|
||||
DIRECTIONS = ['North', 'South', 'East', 'West']
|
||||
blocked_str_map = dict([(direction, (direction + "_blocked").upper()) for direction in DIRECTIONS])
|
||||
geq_num_adj_wall_str_map = dict([(num, "GEQ_{}_adj_walls".format(num)) for num in range(1, 4)])
|
||||
DIR_TO_DXDY_MAP = {'North':(0, 1), 'South':(0, -1), 'East':(1, 0), 'West':(-1, 0)}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# QUESTION 1
|
||||
|
||||
def sentence1() -> Expr:
|
||||
"""Returns a Expr instance that encodes that the following expressions are all true.
|
||||
|
||||
A or B
|
||||
(not A) if and only if ((not B) or C)
|
||||
(not A) or (not B) or C
|
||||
"""
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sentence2() -> Expr:
|
||||
"""Returns a Expr instance that encodes that the following expressions are all true.
|
||||
|
||||
C if and only if (B or D)
|
||||
A implies ((not B) and (not D))
|
||||
(not (B and (not C))) implies A
|
||||
(not D) implies C
|
||||
"""
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sentence3() -> Expr:
|
||||
"""Using the symbols PacmanAlive_1 PacmanAlive_0, PacmanBorn_0, and PacmanKilled_0,
|
||||
created using the PropSymbolExpr constructor, return a PropSymbolExpr
|
||||
instance that encodes the following English sentences (in this order):
|
||||
|
||||
Pacman is alive at time 1 if and only if Pacman was alive at time 0 and it was
|
||||
not killed at time 0 or it was not alive at time 0 and it was born at time 0.
|
||||
|
||||
Pacman cannot both be alive at time 0 and be born at time 0.
|
||||
|
||||
Pacman is born at time 0.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
def findModel(sentence: Expr) -> Dict[Expr, bool]:
|
||||
"""Given a propositional logic sentence (i.e. a Expr instance), returns a satisfying
|
||||
model if one exists. Otherwise, returns False.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
cnf_sentence = to_cnf(sentence)
|
||||
return pycoSAT(cnf_sentence)
|
||||
|
||||
def findModelUnderstandingCheck() -> Dict[Expr, bool]:
|
||||
"""Returns the result of findModel(Expr('a')) if lower cased expressions were allowed.
|
||||
You should not use findModel or Expr in this method.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
a = Expr('A')
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
print("a.__dict__ is:", a.__dict__) # might be helpful for getting ideas
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
def entails(premise: Expr, conclusion: Expr) -> bool:
|
||||
"""Returns True if the premise entails the conclusion and False otherwise.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
def plTrueInverse(assignments: Dict[Expr, bool], inverse_statement: Expr) -> bool:
|
||||
"""Returns True if the (not inverse_statement) is True given assignments and False otherwise.
|
||||
pl_true may be useful here; see logic.py for its description.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# QUESTION 2
|
||||
|
||||
def atLeastOne(literals: List[Expr]) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Given a list of Expr literals (i.e. in the form A or ~A), return a single
|
||||
Expr instance in CNF (conjunctive normal form) that represents the logic
|
||||
that at least one of the literals ist is true.
|
||||
>>> A = PropSymbolExpr('A');
|
||||
>>> B = PropSymbolExpr('B');
|
||||
>>> symbols = [A, B]
|
||||
>>> atleast1 = atLeastOne(symbols)
|
||||
>>> model1 = {A:False, B:False}
|
||||
>>> print(pl_true(atleast1,model1))
|
||||
False
|
||||
>>> model2 = {A:False, B:True}
|
||||
>>> print(pl_true(atleast1,model2))
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> model3 = {A:True, B:True}
|
||||
>>> print(pl_true(atleast1,model2))
|
||||
True
|
||||
"""
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def atMostOne(literals: List[Expr]) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Given a list of Expr literals, return a single Expr instance in
|
||||
CNF (conjunctive normal form) that represents the logic that at most one of
|
||||
the expressions in the list is true.
|
||||
itertools.combinations may be useful here.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def exactlyOne(literals: List[Expr]) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Given a list of Expr literals, return a single Expr instance in
|
||||
CNF (conjunctive normal form)that represents the logic that exactly one of
|
||||
the expressions in the list is true.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# QUESTION 3
|
||||
|
||||
def pacmanSuccessorAxiomSingle(x: int, y: int, time: int, walls_grid: List[List[bool]]=None) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Successor state axiom for state (x,y,t) (from t-1), given the board (as a
|
||||
grid representing the wall locations).
|
||||
Current <==> (previous position at time t-1) & (took action to move to x, y)
|
||||
Available actions are ['North', 'East', 'South', 'West']
|
||||
Note that STOP is not an available action.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
now, last = time, time - 1
|
||||
possible_causes: List[Expr] = [] # enumerate all possible causes for P[x,y]_t
|
||||
# the if statements give a small performance boost and are required for q4 and q5 correctness
|
||||
if walls_grid[x][y+1] != 1:
|
||||
possible_causes.append( PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y+1, time=last)
|
||||
& PropSymbolExpr('South', time=last))
|
||||
if walls_grid[x][y-1] != 1:
|
||||
possible_causes.append( PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y-1, time=last)
|
||||
& PropSymbolExpr('North', time=last))
|
||||
if walls_grid[x+1][y] != 1:
|
||||
possible_causes.append( PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x+1, y, time=last)
|
||||
& PropSymbolExpr('West', time=last))
|
||||
if walls_grid[x-1][y] != 1:
|
||||
possible_causes.append( PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x-1, y, time=last)
|
||||
& PropSymbolExpr('East', time=last))
|
||||
if not possible_causes:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def SLAMSuccessorAxiomSingle(x: int, y: int, time: int, walls_grid: List[List[bool]]) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Similar to `pacmanSuccessorStateAxioms` but accounts for illegal actions
|
||||
where the pacman might not move timestep to timestep.
|
||||
Available actions are ['North', 'East', 'South', 'West']
|
||||
"""
|
||||
now, last = time, time - 1
|
||||
moved_causes: List[Expr] = [] # enumerate all possible causes for P[x,y]_t, assuming moved to having moved
|
||||
if walls_grid[x][y+1] != 1:
|
||||
moved_causes.append( PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y+1, time=last)
|
||||
& PropSymbolExpr('South', time=last))
|
||||
if walls_grid[x][y-1] != 1:
|
||||
moved_causes.append( PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y-1, time=last)
|
||||
& PropSymbolExpr('North', time=last))
|
||||
if walls_grid[x+1][y] != 1:
|
||||
moved_causes.append( PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x+1, y, time=last)
|
||||
& PropSymbolExpr('West', time=last))
|
||||
if walls_grid[x-1][y] != 1:
|
||||
moved_causes.append( PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x-1, y, time=last)
|
||||
& PropSymbolExpr('East', time=last))
|
||||
if not moved_causes:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
moved_causes_sent: Expr = conjoin([~PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y, time=last) , ~PropSymbolExpr(wall_str, x, y), disjoin(moved_causes)])
|
||||
|
||||
failed_move_causes: List[Expr] = [] # using merged variables, improves speed significantly
|
||||
auxilary_expression_definitions: List[Expr] = []
|
||||
for direction in DIRECTIONS:
|
||||
dx, dy = DIR_TO_DXDY_MAP[direction]
|
||||
wall_dir_clause = PropSymbolExpr(wall_str, x + dx, y + dy) & PropSymbolExpr(direction, time=last)
|
||||
wall_dir_combined_literal = PropSymbolExpr(wall_str + direction, x + dx, y + dy, time=last)
|
||||
failed_move_causes.append(wall_dir_combined_literal)
|
||||
auxilary_expression_definitions.append(wall_dir_combined_literal % wall_dir_clause)
|
||||
|
||||
failed_move_causes_sent: Expr = conjoin([
|
||||
PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y, time=last),
|
||||
disjoin(failed_move_causes)])
|
||||
|
||||
return conjoin([PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y, time=now) % disjoin([moved_causes_sent, failed_move_causes_sent])] + auxilary_expression_definitions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pacphysicsAxioms(t: int, all_coords: List[Tuple], non_outer_wall_coords: List[Tuple], walls_grid: List[List] = None, sensorModel: Callable = None, successorAxioms: Callable = None) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Given:
|
||||
t: timestep
|
||||
all_coords: list of (x, y) coordinates of the entire problem
|
||||
non_outer_wall_coords: list of (x, y) coordinates of the entire problem,
|
||||
excluding the outer border (these are the actual squares pacman can
|
||||
possibly be in)
|
||||
walls_grid: 2D array of either -1/0/1 or T/F. Used only for successorAxioms.
|
||||
Do NOT use this when making possible locations for pacman to be in.
|
||||
sensorModel(t, non_outer_wall_coords) -> Expr: function that generates
|
||||
the sensor model axioms. If None, it's not provided, so shouldn't be run.
|
||||
successorAxioms(t, walls_grid, non_outer_wall_coords) -> Expr: function that generates
|
||||
the sensor model axioms. If None, it's not provided, so shouldn't be run.
|
||||
Return a logic sentence containing all of the following:
|
||||
- for all (x, y) in all_coords:
|
||||
If a wall is at (x, y) --> Pacman is not at (x, y)
|
||||
- Pacman is at exactly one of the squares at timestep t.
|
||||
- Pacman takes exactly one action at timestep t.
|
||||
- Results of calling sensorModel(...), unless None.
|
||||
- Results of calling successorAxioms(...), describing how Pacman can end in various
|
||||
locations on this time step. Consider edge cases. Don't call if None.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
pacphysics_sentences = []
|
||||
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
return conjoin(pacphysics_sentences)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def checkLocationSatisfiability(x1_y1: Tuple[int, int], x0_y0: Tuple[int, int], action0, action1, problem):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Given:
|
||||
- x1_y1 = (x1, y1), a potential location at time t = 1
|
||||
- x0_y0 = (x0, y0), Pacman's location at time t = 0
|
||||
- action0 = one of the four items in DIRECTIONS, Pacman's action at time t = 0
|
||||
- action1 = to ensure match with autograder solution
|
||||
- problem = an instance of logicAgents.LocMapProblem
|
||||
Note:
|
||||
- there's no sensorModel because we know everything about the world
|
||||
- the successorAxioms should be allLegalSuccessorAxioms where needed
|
||||
Return:
|
||||
- a model where Pacman is at (x1, y1) at time t = 1
|
||||
- a model where Pacman is not at (x1, y1) at time t = 1
|
||||
"""
|
||||
walls_grid = problem.walls
|
||||
walls_list = walls_grid.asList()
|
||||
all_coords = list(itertools.product(range(problem.getWidth()+2), range(problem.getHeight()+2)))
|
||||
non_outer_wall_coords = list(itertools.product(range(1, problem.getWidth()+1), range(1, problem.getHeight()+1)))
|
||||
KB = []
|
||||
x0, y0 = x0_y0
|
||||
x1, y1 = x1_y1
|
||||
|
||||
# We know which coords are walls:
|
||||
map_sent = [PropSymbolExpr(wall_str, x, y) for x, y in walls_list]
|
||||
KB.append(conjoin(map_sent))
|
||||
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# QUESTION 4
|
||||
|
||||
def positionLogicPlan(problem) -> List:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Given an instance of a PositionPlanningProblem, return a list of actions that lead to the goal.
|
||||
Available actions are ['North', 'East', 'South', 'West']
|
||||
Note that STOP is not an available action.
|
||||
Overview: add knowledge incrementally, and query for a model each timestep. Do NOT use pacphysicsAxioms.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
walls_grid = problem.walls
|
||||
width, height = problem.getWidth(), problem.getHeight()
|
||||
walls_list = walls_grid.asList()
|
||||
x0, y0 = problem.startState
|
||||
xg, yg = problem.goal
|
||||
|
||||
# Get lists of possible locations (i.e. without walls) and possible actions
|
||||
all_coords = list(itertools.product(range(width + 2),
|
||||
range(height + 2)))
|
||||
non_wall_coords = [loc for loc in all_coords if loc not in walls_list]
|
||||
actions = [ 'North', 'South', 'East', 'West' ]
|
||||
KB = []
|
||||
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# QUESTION 5
|
||||
|
||||
def foodLogicPlan(problem) -> List:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Given an instance of a FoodPlanningProblem, return a list of actions that help Pacman
|
||||
eat all of the food.
|
||||
Available actions are ['North', 'East', 'South', 'West']
|
||||
Note that STOP is not an available action.
|
||||
Overview: add knowledge incrementally, and query for a model each timestep. Do NOT use pacphysicsAxioms.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
walls = problem.walls
|
||||
width, height = problem.getWidth(), problem.getHeight()
|
||||
walls_list = walls.asList()
|
||||
(x0, y0), food = problem.start
|
||||
food = food.asList()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get lists of possible locations (i.e. without walls) and possible actions
|
||||
all_coords = list(itertools.product(range(width + 2), range(height + 2)))
|
||||
|
||||
non_wall_coords = [loc for loc in all_coords if loc not in walls_list]
|
||||
actions = [ 'North', 'South', 'East', 'West' ]
|
||||
|
||||
KB = []
|
||||
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# QUESTION 6
|
||||
|
||||
def localization(problem, agent) -> Generator:
|
||||
'''
|
||||
problem: a LocalizationProblem instance
|
||||
agent: a LocalizationLogicAgent instance
|
||||
'''
|
||||
walls_grid = problem.walls
|
||||
walls_list = walls_grid.asList()
|
||||
all_coords = list(itertools.product(range(problem.getWidth()+2), range(problem.getHeight()+2)))
|
||||
non_outer_wall_coords = list(itertools.product(range(1, problem.getWidth()+1), range(1, problem.getHeight()+1)))
|
||||
|
||||
KB = []
|
||||
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
for t in range(agent.num_timesteps):
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
yield possible_locations
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# QUESTION 7
|
||||
|
||||
def mapping(problem, agent) -> Generator:
|
||||
'''
|
||||
problem: a MappingProblem instance
|
||||
agent: a MappingLogicAgent instance
|
||||
'''
|
||||
pac_x_0, pac_y_0 = problem.startState
|
||||
KB = []
|
||||
all_coords = list(itertools.product(range(problem.getWidth()+2), range(problem.getHeight()+2)))
|
||||
non_outer_wall_coords = list(itertools.product(range(1, problem.getWidth()+1), range(1, problem.getHeight()+1)))
|
||||
|
||||
# map describes what we know, for GUI rendering purposes. -1 is unknown, 0 is open, 1 is wall
|
||||
known_map = [[-1 for y in range(problem.getHeight()+2)] for x in range(problem.getWidth()+2)]
|
||||
|
||||
# Pacman knows that the outer border of squares are all walls
|
||||
outer_wall_sent = []
|
||||
for x, y in all_coords:
|
||||
if ((x == 0 or x == problem.getWidth() + 1)
|
||||
or (y == 0 or y == problem.getHeight() + 1)):
|
||||
known_map[x][y] = 1
|
||||
outer_wall_sent.append(PropSymbolExpr(wall_str, x, y))
|
||||
KB.append(conjoin(outer_wall_sent))
|
||||
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
for t in range(agent.num_timesteps):
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
yield known_map
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# QUESTION 8
|
||||
|
||||
def slam(problem, agent) -> Generator:
|
||||
'''
|
||||
problem: a SLAMProblem instance
|
||||
agent: a SLAMLogicAgent instance
|
||||
'''
|
||||
pac_x_0, pac_y_0 = problem.startState
|
||||
KB = []
|
||||
all_coords = list(itertools.product(range(problem.getWidth()+2), range(problem.getHeight()+2)))
|
||||
non_outer_wall_coords = list(itertools.product(range(1, problem.getWidth()+1), range(1, problem.getHeight()+1)))
|
||||
|
||||
# map describes what we know, for GUI rendering purposes. -1 is unknown, 0 is open, 1 is wall
|
||||
known_map = [[-1 for y in range(problem.getHeight()+2)] for x in range(problem.getWidth()+2)]
|
||||
|
||||
# We know that the outer_coords are all walls.
|
||||
outer_wall_sent = []
|
||||
for x, y in all_coords:
|
||||
if ((x == 0 or x == problem.getWidth() + 1)
|
||||
or (y == 0 or y == problem.getHeight() + 1)):
|
||||
known_map[x][y] = 1
|
||||
outer_wall_sent.append(PropSymbolExpr(wall_str, x, y))
|
||||
KB.append(conjoin(outer_wall_sent))
|
||||
|
||||
"*** BEGIN YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
for t in range(agent.num_timesteps):
|
||||
"*** END YOUR CODE HERE ***"
|
||||
yield (known_map, possible_locations)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Abbreviations
|
||||
plp = positionLogicPlan
|
||||
loc = localization
|
||||
mp = mapping
|
||||
flp = foodLogicPlan
|
||||
# Sometimes the logic module uses pretty deep recursion on long expressions
|
||||
sys.setrecursionlimit(100000)
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Important expression generating functions, useful to read for understanding of this project.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sensorAxioms(t: int, non_outer_wall_coords: List[Tuple[int, int]]) -> Expr:
|
||||
all_percept_exprs = []
|
||||
combo_var_def_exprs = []
|
||||
for direction in DIRECTIONS:
|
||||
percept_exprs = []
|
||||
dx, dy = DIR_TO_DXDY_MAP[direction]
|
||||
for x, y in non_outer_wall_coords:
|
||||
combo_var = PropSymbolExpr(pacman_wall_str, x, y, x + dx, y + dy, time=t)
|
||||
percept_exprs.append(combo_var)
|
||||
combo_var_def_exprs.append(combo_var % (
|
||||
PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y, time=t) & PropSymbolExpr(wall_str, x + dx, y + dy)))
|
||||
|
||||
percept_unit_clause = PropSymbolExpr(blocked_str_map[direction], time = t)
|
||||
all_percept_exprs.append(percept_unit_clause % disjoin(percept_exprs))
|
||||
|
||||
return conjoin(all_percept_exprs + combo_var_def_exprs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def fourBitPerceptRules(t: int, percepts: List) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Localization and Mapping both use the 4 bit sensor, which tells us True/False whether
|
||||
a wall is to pacman's north, south, east, and west.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
assert isinstance(percepts, list), "Percepts must be a list."
|
||||
assert len(percepts) == 4, "Percepts must be a length 4 list."
|
||||
|
||||
percept_unit_clauses = []
|
||||
for wall_present, direction in zip(percepts, DIRECTIONS):
|
||||
percept_unit_clause = PropSymbolExpr(blocked_str_map[direction], time=t)
|
||||
if not wall_present:
|
||||
percept_unit_clause = ~PropSymbolExpr(blocked_str_map[direction], time=t)
|
||||
percept_unit_clauses.append(percept_unit_clause) # The actual sensor readings
|
||||
return conjoin(percept_unit_clauses)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def numAdjWallsPerceptRules(t: int, percepts: List) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
SLAM uses a weaker numAdjWallsPerceptRules sensor, which tells us how many walls pacman is adjacent to
|
||||
in its four directions.
|
||||
000 = 0 adj walls.
|
||||
100 = 1 adj wall.
|
||||
110 = 2 adj walls.
|
||||
111 = 3 adj walls.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
assert isinstance(percepts, list), "Percepts must be a list."
|
||||
assert len(percepts) == 3, "Percepts must be a length 3 list."
|
||||
|
||||
percept_unit_clauses = []
|
||||
for i, percept in enumerate(percepts):
|
||||
n = i + 1
|
||||
percept_literal_n = PropSymbolExpr(geq_num_adj_wall_str_map[n], time=t)
|
||||
if not percept:
|
||||
percept_literal_n = ~percept_literal_n
|
||||
percept_unit_clauses.append(percept_literal_n)
|
||||
return conjoin(percept_unit_clauses)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def SLAMSensorAxioms(t: int, non_outer_wall_coords: List[Tuple[int, int]]) -> Expr:
|
||||
all_percept_exprs = []
|
||||
combo_var_def_exprs = []
|
||||
for direction in DIRECTIONS:
|
||||
percept_exprs = []
|
||||
dx, dy = DIR_TO_DXDY_MAP[direction]
|
||||
for x, y in non_outer_wall_coords:
|
||||
combo_var = PropSymbolExpr(pacman_wall_str, x, y, x + dx, y + dy, time=t)
|
||||
percept_exprs.append(combo_var)
|
||||
combo_var_def_exprs.append(combo_var % (PropSymbolExpr(pacman_str, x, y, time=t) & PropSymbolExpr(wall_str, x + dx, y + dy)))
|
||||
|
||||
blocked_dir_clause = PropSymbolExpr(blocked_str_map[direction], time=t)
|
||||
all_percept_exprs.append(blocked_dir_clause % disjoin(percept_exprs))
|
||||
|
||||
percept_to_blocked_sent = []
|
||||
for n in range(1, 4):
|
||||
wall_combos_size_n = itertools.combinations(blocked_str_map.values(), n)
|
||||
n_walls_blocked_sent = disjoin([
|
||||
conjoin([PropSymbolExpr(blocked_str, time=t) for blocked_str in wall_combo])
|
||||
for wall_combo in wall_combos_size_n])
|
||||
# n_walls_blocked_sent is of form: (N & S) | (N & E) | ...
|
||||
percept_to_blocked_sent.append(
|
||||
PropSymbolExpr(geq_num_adj_wall_str_map[n], time=t) % n_walls_blocked_sent)
|
||||
|
||||
return conjoin(all_percept_exprs + combo_var_def_exprs + percept_to_blocked_sent)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def allLegalSuccessorAxioms(t: int, walls_grid: List[List], non_outer_wall_coords: List[Tuple[int, int]]) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""walls_grid can be a 2D array of ints or bools."""
|
||||
all_xy_succ_axioms = []
|
||||
for x, y in non_outer_wall_coords:
|
||||
xy_succ_axiom = pacmanSuccessorAxiomSingle(
|
||||
x, y, t, walls_grid)
|
||||
if xy_succ_axiom:
|
||||
all_xy_succ_axioms.append(xy_succ_axiom)
|
||||
return conjoin(all_xy_succ_axioms)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def SLAMSuccessorAxioms(t: int, walls_grid: List[List], non_outer_wall_coords: List[Tuple[int, int]]) -> Expr:
|
||||
"""walls_grid can be a 2D array of ints or bools."""
|
||||
all_xy_succ_axioms = []
|
||||
for x, y in non_outer_wall_coords:
|
||||
xy_succ_axiom = SLAMSuccessorAxiomSingle(
|
||||
x, y, t, walls_grid)
|
||||
if xy_succ_axiom:
|
||||
all_xy_succ_axioms.append(xy_succ_axiom)
|
||||
return conjoin(all_xy_succ_axioms)
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Various useful functions, are not needed for completing the project but may be useful for debugging
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def modelToString(model: Dict[Expr, bool]) -> str:
|
||||
"""Converts the model to a string for printing purposes. The keys of a model are
|
||||
sorted before converting the model to a string.
|
||||
|
||||
model: Either a boolean False or a dictionary of Expr symbols (keys)
|
||||
and a corresponding assignment of True or False (values). This model is the output of
|
||||
a call to pycoSAT.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if model == False:
|
||||
return "False"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Dictionary
|
||||
modelList = sorted(model.items(), key=lambda item: str(item[0]))
|
||||
return str(modelList)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def extractActionSequence(model: Dict[Expr, bool], actions: List) -> List:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Convert a model in to an ordered list of actions.
|
||||
model: Propositional logic model stored as a dictionary with keys being
|
||||
the symbol strings and values being Boolean: True or False
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
>>> model = {"North[2]":True, "P[3,4,0]":True, "P[3,3,0]":False, "West[0]":True, "GhostScary":True, "West[2]":False, "South[1]":True, "East[0]":False}
|
||||
>>> actions = ['North', 'South', 'East', 'West']
|
||||
>>> plan = extractActionSequence(model, actions)
|
||||
>>> print(plan)
|
||||
['West', 'South', 'North']
|
||||
"""
|
||||
plan = [None for _ in range(len(model))]
|
||||
for sym, val in model.items():
|
||||
parsed = parseExpr(sym)
|
||||
if type(parsed) == tuple and parsed[0] in actions and val:
|
||||
action, _, time = parsed
|
||||
plan[time] = action
|
||||
#return list(filter(lambda x: x is not None, plan))
|
||||
return [x for x in plan if x is not None]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Helpful Debug Method
|
||||
def visualizeCoords(coords_list, problem) -> None:
|
||||
wallGrid = game.Grid(problem.walls.width, problem.walls.height, initialValue=False)
|
||||
for (x, y) in itertools.product(range(problem.getWidth()+2), range(problem.getHeight()+2)):
|
||||
if (x, y) in coords_list:
|
||||
wallGrid.data[x][y] = True
|
||||
print(wallGrid)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Helpful Debug Method
|
||||
def visualizeBoolArray(bool_arr, problem) -> None:
|
||||
wallGrid = game.Grid(problem.walls.width, problem.walls.height, initialValue=False)
|
||||
wallGrid.data = copy.deepcopy(bool_arr)
|
||||
print(wallGrid)
|
||||
|
||||
class PlanningProblem:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This class outlines the structure of a planning problem, but doesn't implement
|
||||
any of the methods (in object-oriented terminology: an abstract class).
|
||||
|
||||
You do not need to change anything in this class, ever.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def getStartState(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the start state for the planning problem.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
def getGhostStartStates(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a list containing the start state for each ghost.
|
||||
Only used in problems that use ghosts (FoodGhostPlanningProblem)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
def getGoalState(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns goal state for problem. Note only defined for problems that have
|
||||
a unique goal state such as PositionPlanningProblem
|
||||
"""
|
||||
util.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
767
logic/logic_planTestClasses.py
Normal file
767
logic/logic_planTestClasses.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,767 @@
|
||||
# logic_planTestClasses.py
|
||||
# ------------------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import testClasses
|
||||
|
||||
import textDisplay
|
||||
import graphicsDisplay
|
||||
import layout
|
||||
import pacman
|
||||
import logicAgents
|
||||
from logicPlan import PlanningProblem
|
||||
import logicPlan
|
||||
|
||||
import itertools
|
||||
|
||||
# Simple test case which evals an arbitrary piece of python code.
|
||||
# The test is correct if the output of the code given the student's
|
||||
# solution matches that of the instructor's.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EvalTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(EvalTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.preamble = compile(testDict.get('preamble', ""), "%s.preamble" % self.getPath(), 'exec')
|
||||
self.test = compile(testDict['test'], "%s.test" % self.getPath(), 'eval')
|
||||
self.success = testDict['success']
|
||||
self.failure = testDict['failure']
|
||||
|
||||
def evalCode(self, moduleDict):
|
||||
bindings = dict(moduleDict)
|
||||
exec(self.preamble, bindings)
|
||||
return str(eval(self.test, bindings))
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
result = self.evalCode(moduleDict)
|
||||
if result == solutionDict['result']:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\t%s' % self.success)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\t%s' % self.failure)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent result: "%s"' % result)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tcorrect result: "%s"' % solutionDict['result'])
|
||||
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
handle.write('# The result of evaluating the test must equal the below when cast to a string.\n')
|
||||
|
||||
handle.write('result: "%s"\n' % self.evalCode(moduleDict))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
class LogicTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(LogicTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.preamble = compile(testDict.get('preamble', ""), "%s.preamble" % self.getPath(), 'exec')
|
||||
self.test = compile(testDict['test'], "%s.test" % self.getPath(), 'eval')
|
||||
self.success = testDict['success']
|
||||
self.failure = testDict['failure']
|
||||
|
||||
def evalCode(self, moduleDict):
|
||||
bindings = dict(moduleDict)
|
||||
exec(self.preamble, bindings)
|
||||
return eval(self.test, bindings)
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
result = self.evalCode(moduleDict)
|
||||
result = map(lambda x: str(x), result)
|
||||
result = ' '.join(result)
|
||||
|
||||
if result == solutionDict['result']:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\t%s' % self.success)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
for i in range(100):
|
||||
solI = 'result' + str(i)
|
||||
if solI not in solutionDict:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if result == solutionDict[solI]:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\t%s' % self.success)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\t%s' % self.failure)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent result: "%s"' % result)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tcorrect result: "%s"' % solutionDict['result'])
|
||||
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
handle.write('# The result of evaluating the test must equal the below when cast to a string.\n')
|
||||
solution = self.evalCode(moduleDict)
|
||||
solution = map(lambda x: str(x), solution)
|
||||
handle.write('result: "%s"\n' % ' '.join(solution))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
class PacphysicsTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(PacphysicsTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.layoutText = testDict['layout']
|
||||
self.layoutName = testDict['layoutName']
|
||||
self.t = int(testDict['t'])
|
||||
self.soln_labels = ["pacphysicsAxioms"]
|
||||
self.axiom_type = testDict['axiomType']
|
||||
if self.axiom_type == 'sensor':
|
||||
self.sensorAxioms = logicPlan.sensorAxioms
|
||||
self.successorAxioms = logicPlan.allLegalSuccessorAxioms
|
||||
elif self.axiom_type == 'slam':
|
||||
self.sensorAxioms = logicPlan.SLAMSensorAxioms
|
||||
self.successorAxioms = logicPlan.SLAMSuccessorAxioms
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise Exception('Bad test case!')
|
||||
|
||||
def solution(self, logicPlan):
|
||||
lay = layout.Layout([l.strip() for l in self.layoutText.split('\n')])
|
||||
walls_list = lay.walls.data
|
||||
all_coords = lay.get_all_coords_list()
|
||||
non_outer_wall_coords = lay.get_non_outer_wall_coords_list()
|
||||
pacphysics_axioms = logicPlan.pacphysicsAxioms(self.t, all_coords, non_outer_wall_coords, walls_list, self.sensorAxioms, self.successorAxioms)
|
||||
return pacphysics_axioms
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('Testing pacphysicsAxioms')
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
gold_solution = solutionDict[self.soln_labels[0]]
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
gold_soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined = str(gold_solution)[1:-1].split(" & ")
|
||||
soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined = str(solution)[1:-1].split(" & ")
|
||||
|
||||
# Check student used conjoin correctly; this is a weak check
|
||||
# after <=>, we get Action) | (Wall expresisons due to SLAM successor
|
||||
for soln_clause in soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined:
|
||||
if "<=>" in soln_clause:
|
||||
if self.axiom_type == 'sensor':
|
||||
continue
|
||||
else:
|
||||
break
|
||||
contains_open_parens = ("(" in soln_clause[1:-1]) or ("(" in soln_clause[1:-1])
|
||||
if contains_open_parens:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution does not combine sentences properly.')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tMake sure you append the items to join with "and",'
|
||||
' and conjoin at the end.')
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
# Check number of clauses is correct.
|
||||
gold_soln_num_clauses_conjoined = len(gold_soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined)
|
||||
soln_num_clauses_conjoined = len(soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined)
|
||||
|
||||
if gold_soln_num_clauses_conjoined != soln_num_clauses_conjoined:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tNumber of clauses being conjoined in student solution: {}'.format(
|
||||
soln_num_clauses_conjoined))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tNumber of clauses being conjoined in correct solution: {}'.format(
|
||||
gold_soln_num_clauses_conjoined))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
for gold_clause in gold_soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined:
|
||||
if gold_clause not in soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution does not contain clause {}'.format(gold_clause))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
if set(soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined) != set(gold_soln_clauses_list_being_conjoined):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution on clause set comparison')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution: {}'.format(solution))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution: {}'.format(gold_solution))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
if sorted(str(solution)) != sorted(str(gold_solution)):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution on character list comparison')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution: {}'.format(solution))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution: {}'.format(gold_solution))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
# open file and write comments
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Solving problem", self.layoutName)
|
||||
print(self.layoutText)
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Problem solved")
|
||||
|
||||
handle.write('{}: "{}"\n'.format(self.soln_labels[0], str(solution)))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
class LocationSatisfiabilityTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(LocationSatisfiabilityTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.layoutText = testDict['layout']
|
||||
self.layoutName = testDict['layoutName']
|
||||
self.x0_y0 = eval(testDict['x0_y0'])
|
||||
self.action0 = testDict['action0']
|
||||
self.x1_y1 = eval(testDict['x1_y1'])
|
||||
self.action1 = testDict['action1']
|
||||
self.soln_labels = ["model_at_x1_y1_1", "model_not_at_x1_y1_1"]
|
||||
|
||||
def solution(self, logicPlan):
|
||||
lay = layout.Layout([l.strip() for l in self.layoutText.split('\n')])
|
||||
pac = logicAgents.CheckSatisfiabilityAgent('checkLocationSatisfiability', 'LocMapProblem', logicPlan)
|
||||
ghosts = []
|
||||
disp = textDisplay.NullGraphics()
|
||||
games = next(pacman.runGames(lay, pac, ghosts, disp, 1, False, catchExceptions=True, timeout=180))
|
||||
loc_sat_models = logicPlan.checkLocationSatisfiability(self.x1_y1, self.x0_y0, self.action0, self.action1, pac.problem)
|
||||
return loc_sat_models
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('Testing checkLocationSatisfiability')
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
for i, solution_i in enumerate(solution):
|
||||
gold_solution_i = solutionDict[self.soln_labels[i]]
|
||||
solution_i = logicPlan.modelToString(solution_i)
|
||||
|
||||
if gold_solution_i == "False" and solution_i != "False":
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution for {}'.format(self.soln_labels[i]))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent model found satisfiable solution but no satisfiable solution exists.')
|
||||
return False
|
||||
elif gold_solution_i != "False" and solution_i == "False":
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution for {}'.format(self.soln_labels[i]))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent model found no satisfiable solution when a satisfiable solution exists.')
|
||||
return False
|
||||
elif gold_solution_i == "False" and solution_i == "False":
|
||||
continue
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
gold_solution_i_str_pairs_list = gold_solution_i[2:-2].split("), (")
|
||||
gold_solution_i_tuples_list = [tuple(pair.split(", ")) for pair in gold_solution_i_str_pairs_list]
|
||||
gold_solution_i_dict = dict(gold_solution_i_tuples_list)
|
||||
solution_i_str_pairs_list = solution_i[2:-2].split("), (")
|
||||
solution_i_tuples_list = [tuple(pair.split(", ")) for pair in solution_i_str_pairs_list]
|
||||
solution_i_dict = dict(solution_i_tuples_list)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if student has all of the correct variables.
|
||||
gold_solution_i_num_vars = len(gold_solution_i_tuples_list)
|
||||
solution_i_num_vars = len(solution_i_tuples_list)
|
||||
if gold_solution_i_num_vars != solution_i_num_vars:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tNumber of variables in student solution: {}'.format(
|
||||
solution_i_num_vars))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tNumber of variables in correct solution: {}'.format(
|
||||
gold_solution_i_num_vars))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
for gold_solution_var in gold_solution_i_dict:
|
||||
if gold_solution_var not in solution_i_dict:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution does not contain the same variables as correct solution')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution variable missing in student solution: {}'.format(
|
||||
gold_solution_var))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
# Some miscellaneous inequality; return which variables are different between solution and student.
|
||||
for key in gold_solution_i_dict:
|
||||
if gold_solution_i_dict[key] != solution_i_dict[key]:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent model does not assign the correct value for variable {}'.format(key))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent value for {}: {}'.format(key, solution_i_dict[key]))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect value for {}: {}'.format(key, gold_solution_i_dict[key]))
|
||||
if "WALL" in key:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tDouble check that you are loading the map properly.')
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
if str(solution_i) != str(gold_solution_i):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution for {}'.format(self.soln_labels[i]))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution: {}'.format(solution_i))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution: {}'.format(gold_solution_i))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
# open file and write comments
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Solving problem", self.layoutName)
|
||||
print(self.layoutText)
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Problem solved")
|
||||
|
||||
for i, solution_i in enumerate(solution):
|
||||
handle.write('{}: "{}"\n'.format(self.soln_labels[i], logicPlan.modelToString(solution_i)))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PositionProblemTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(PositionProblemTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.layoutText = testDict['layout']
|
||||
self.layoutName = testDict['layoutName']
|
||||
|
||||
def solution(self, logicPlan):
|
||||
lay = layout.Layout([l.strip() for l in self.layoutText.split('\n')])
|
||||
pac = logicAgents.LogicAgent('plp', 'PositionPlanningProblem', logicPlan)
|
||||
ghosts = []
|
||||
disp = textDisplay.NullGraphics()
|
||||
games = next(pacman.runGames(lay, pac, ghosts, disp, 1, False, catchExceptions=True, timeout=300))
|
||||
gameState = games[0].state
|
||||
return (gameState.isWin(), gameState.getScore(), pac.actions)
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
gold_path = solutionDict['solution_path']
|
||||
gold_score = int(solutionDict['solution_score'])
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
if not solution[0] or solution[1] < gold_score:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tpacman layout:\t\t%s' % self.layoutName)
|
||||
if solution[0]:
|
||||
result_str = "wins"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
result_str = "loses"
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent solution result: Pacman %s' % result_str)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent solution score: %d' % solution[1])
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent solution path: %s' % ' '.join(solution[2]))
|
||||
if solution[1] < gold_score:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('Optimal solution not found.')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tcorrect solution score: %d' % gold_score)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tcorrect solution path: %s' % gold_path)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tpacman layout:\t\t%s' % self.layoutName)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tsolution score:\t\t%d' % gold_score)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tsolution path:\t\t%s' % gold_path)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
# open file and write comments
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Solving problem", self.layoutName)
|
||||
print(self.layoutText)
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Problem solved")
|
||||
|
||||
handle.write('solution_win: "%s"\n' % str(solution[0]))
|
||||
handle.write('solution_score: "%d"\n' % solution[1])
|
||||
handle.write('solution_path: "%s"\n' % ' '.join(solution[2]))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FoodProblemTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(FoodProblemTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.layoutText = testDict['layout']
|
||||
self.layoutName = testDict['layoutName']
|
||||
|
||||
def solution(self, logicPlan):
|
||||
lay = layout.Layout([l.strip() for l in self.layoutText.split('\n')])
|
||||
pac = logicAgents.LogicAgent('flp', 'FoodPlanningProblem', logicPlan)
|
||||
ghosts = []
|
||||
disp = textDisplay.NullGraphics()
|
||||
games = next(pacman.runGames(lay, pac, ghosts, disp, 1, False, catchExceptions=True, timeout=300))
|
||||
gameState = games[0].state
|
||||
return (gameState.isWin(), gameState.getScore(), pac.actions)
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
gold_path = solutionDict['solution_path']
|
||||
gold_score = int(solutionDict['solution_score'])
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
if not solution[0] or solution[1] < gold_score:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tpacman layout:\t\t%s' % self.layoutName)
|
||||
if solution[0]:
|
||||
result_str = "wins"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
result_str = "loses"
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent solution result: Pacman %s' % result_str)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent solution score: %d' % solution[1])
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent solution path: %s' % ' '.join(solution[2]))
|
||||
if solution[1] < gold_score:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('Optimal solution not found.')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tcorrect solution score: %d' % gold_score)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tcorrect solution path: %s' % gold_path)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tpacman layout:\t\t%s' % self.layoutName)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tsolution score:\t\t%d' % gold_score)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tsolution path:\t\t%s' % gold_path)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
# open file and write comments
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Solving problem", self.layoutName)
|
||||
print(self.layoutText)
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Problem solved")
|
||||
|
||||
handle.write('solution_win: "%s"\n' % str(solution[0]))
|
||||
handle.write('solution_score: "%d"\n' % solution[1])
|
||||
handle.write('solution_path: "%s"\n' % ' '.join(solution[2]))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LocalizationProblemTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(LocalizationProblemTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.layoutText = testDict['layout']
|
||||
self.layoutName = testDict['layoutName']
|
||||
self.scriptedActions = eval(testDict['actions'])
|
||||
|
||||
def solution(self, logicPlan):
|
||||
lay = layout.Layout([l.strip() for l in self.layoutText.split('\n')])
|
||||
ghosts = []
|
||||
# TODO: Figure out if we can use no-graphics cleaner
|
||||
disp = self.question.display
|
||||
if isinstance(disp, graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics): # autograder.py has incorrect options
|
||||
disp = graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics(frameTime=0.5)
|
||||
pac = logicAgents.LocalizationLogicAgent(
|
||||
'loc', 'LocalizationProblem', logicPlan, display=disp, scripted_actions=self.scriptedActions)
|
||||
yield from pacman.runGames(lay, pac, ghosts, disp, 1, False, catchExceptions=True, timeout=300)
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
gold_solution = eval(solutionDict['possible_locations_per_timestep'])
|
||||
|
||||
num_timesteps = 0
|
||||
for t, solution in enumerate(self.solution(logicPlan)):
|
||||
if solution is None:
|
||||
num_timesteps = t
|
||||
break
|
||||
if set(solution) != set(gold_solution[t]):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution at timestep t = {}'.format(t))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution at time t = {}: {}'.format(t, solution))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution at time t = {}: {}'.format(t, gold_solution[t]))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
if num_timesteps != len(gold_solution):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution timestep number: {}'.format(num_timesteps))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution timestep number: {}'.format(len(eval(solutionDict['possible_locations_per_timestep']))))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
# open file and write comments
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Solving problem", self.layoutName)
|
||||
print(self.layoutText)
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Problem solved")
|
||||
|
||||
handle.write('possible_locations_per_timestep: "{}"\n'.format(str(solution)))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
class MappingProblemTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(MappingProblemTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.layoutText = testDict['layout']
|
||||
self.layoutName = testDict['layoutName']
|
||||
self.scriptedActions = eval(testDict['actions'])
|
||||
self.solution_label = 'known_map_per_timestep'
|
||||
|
||||
def solution(self, logicPlan):
|
||||
lay = layout.Layout([l.strip() for l in self.layoutText.split('\n')])
|
||||
ghosts = []
|
||||
# TODO: Figure out if we can use no-graphics cleaner
|
||||
disp = self.question.display
|
||||
if isinstance(disp, graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics): # autograder.py has incorrect options
|
||||
disp = graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics(frameTime=0.5, render_walls_beforehand=False)
|
||||
pac = logicAgents.MappingLogicAgent(
|
||||
'mp', 'MappingProblem', logicPlan, display=disp, scripted_actions=self.scriptedActions)
|
||||
yield from pacman.runGames(lay, pac, ghosts, disp, 1, False, catchExceptions=True, timeout=300)
|
||||
|
||||
def check_len(self, grades, soln, gold_soln, str_info=""):
|
||||
if len(soln) != len(gold_soln):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent solution length {}: {}'.format(str_info, len(soln)))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tcorrect solution length {}: {}'.format(str_info, len(gold_soln)))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
gold_solution = eval(solutionDict[self.solution_label])
|
||||
|
||||
num_timesteps = 0
|
||||
|
||||
for t, solution_t in enumerate(self.solution(logicPlan)):
|
||||
if solution_t == None:
|
||||
num_timesteps = t
|
||||
break
|
||||
if not self.check_len(grades, solution_t, gold_solution[t], "at time t = {}".format(t)):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
if solution_t != gold_solution[t]:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution at timestep t = {}'.format(t))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution at time t = {}: {}'.format(t, solution_t))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution at time t = {}: {}'.format(t, gold_solution[t]))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
if num_timesteps != len(gold_solution):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution timestep number: {}'.format(num_timesteps))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution timestep number: {}'.format(len(eval(solutionDict[self.solution_label]))))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
# open file and write comments
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Solving problem", self.layoutName)
|
||||
print(self.layoutText)
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Problem solved")
|
||||
|
||||
handle.write('{}: "{}"\n'.format(self.solution_label, str(solution)))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
class SLAMProblemTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(SLAMProblemTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.layoutText = testDict['layout']
|
||||
self.layoutName = testDict['layoutName']
|
||||
self.scriptedActions = eval(testDict['actions'])
|
||||
self.solution_labels = ['known_map_per_timestep', 'possible_locations_per_timestep']
|
||||
|
||||
def solution(self, logicPlan):
|
||||
lay = layout.Layout([l.strip() for l in self.layoutText.split('\n')])
|
||||
ghosts = []
|
||||
# TODO: Figure out if we can use no-graphics cleaner
|
||||
disp = self.question.display
|
||||
if isinstance(disp, graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics): # autograder.py has incorrect options
|
||||
disp = graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics(frameTime=0.5, render_walls_beforehand=False)
|
||||
pac = logicAgents.SLAMLogicAgent(
|
||||
'slam', 'SLAMProblem', logicPlan, display=disp, scripted_actions=self.scriptedActions)
|
||||
yield from pacman.runGames(lay, pac, ghosts, disp, 1, False, catchExceptions=True, timeout=1800)
|
||||
|
||||
def check_len(self, grades, soln, gold_soln, str_info=""):
|
||||
if len(soln) != len(gold_soln):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tstudent solution length {}: {}'.format(str_info, len(soln)))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tcorrect solution length {}: {}'.format(str_info, len(gold_soln)))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
num_timesteps = 0
|
||||
for t, solutions_at_t in enumerate(self.solution(logicPlan)):
|
||||
if solutions_at_t is None:
|
||||
num_timesteps = t
|
||||
break
|
||||
for soln_label, solution in zip(self.solution_labels, solutions_at_t):
|
||||
gold_solution = eval(solutionDict[soln_label])
|
||||
|
||||
if solution != gold_solution[t]:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution at timestep t = {}'.format(t))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution for {} at time t = {}: {}'.format(soln_label, t, solution))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution for {} at time t = {}: {}'.format(soln_label, t, gold_solution[t]))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
if num_timesteps != len(eval(solutionDict[self.solution_labels[0]])):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution differed from autograder solution')
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tStudent solution timestep number: {}'.format(num_timesteps))
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\tCorrect solution timestep number: {}'.format(len(eval(solutionDict[self.solution_labels[0]]))))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
logicPlan = moduleDict['logicPlan']
|
||||
# open file and write comments
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Solving problem", self.layoutName)
|
||||
print(self.layoutText)
|
||||
|
||||
solution = self.solution(logicPlan)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Problem solved")
|
||||
|
||||
for soln_label, solution_i in zip(self.solution_labels, solution):
|
||||
handle.write('{}: "{}"\n'.format(soln_label, str(solution_i)))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
class LogicStatementTest(testClasses.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
super(LogicStatementTest, self).__init__(question, testDict)
|
||||
self.preamble = compile(testDict.get('preamble', ""), "%s.preamble" % self.getPath(), 'exec')
|
||||
self.test = compile(testDict['test'], "%s.test" % self.getPath(), 'eval')
|
||||
self.pairs = testDict['pairs']
|
||||
self.success = testDict['success']
|
||||
self.failure = testDict['failure']
|
||||
|
||||
def evalCode(self, moduleDict):
|
||||
bindings = dict(moduleDict)
|
||||
exec(self.preamble, bindings)
|
||||
return eval(self.test, bindings)
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
bindings = dict(moduleDict)
|
||||
exec(self.preamble, bindings)
|
||||
truths = eval(self.test, bindings)
|
||||
model_truth_pairs = eval(self.pairs, bindings)
|
||||
if str(truths) == solutionDict['result']:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('\t%s' % self.success)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
solution_truths = eval(solutionDict['result'])
|
||||
firstError = 1
|
||||
while truths[firstError-1] == solution_truths[firstError-1]:
|
||||
firstError += 1
|
||||
model = model_truth_pairs[firstError-1][0]
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: %s' % self.path)
|
||||
# grades.addMessage('\t%s' % self.failure)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('Your solution\'s first error occurred on model %d.' % firstError)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('MODEL: %s' % model)
|
||||
grades.addMessage('The correct answer is %s but you returned %s.' % (solution_truths[firstError-1], truths[firstError-1]))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
handle = open(filePath, 'w')
|
||||
handle.write('# This is the solution file for %s.\n' % self.path)
|
||||
handle.write('# The result of evaluating the test must equal the below when cast to a string.\n')
|
||||
|
||||
handle.write('result: "%s"\n' % self.evalCode(moduleDict))
|
||||
handle.close()
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
770
logic/logic_utils.py
Normal file
770
logic/logic_utils.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,770 @@
|
||||
# logic_utils.py
|
||||
# --------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""Provide some widely useful utilities. Safe for "from logic_utils import *".
|
||||
|
||||
Code originally from https://code.google.com/p/aima-python/
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import generators
|
||||
import operator, math, random, copy, sys, os.path, bisect, re
|
||||
from functools import reduce
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Simple Data Structures: infinity, Dict, Struct
|
||||
|
||||
infinity = 1.0e400
|
||||
|
||||
def Dict(**entries):
|
||||
"""Create a dict out of the argument=value arguments.
|
||||
>>> Dict(a=1, b=2, c=3)
|
||||
{'a': 1, 'c': 3, 'b': 2}
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return entries
|
||||
|
||||
class DefaultDict(dict):
|
||||
"""Dictionary with a default value for unknown keys."""
|
||||
def __init__(self, default):
|
||||
self.default = default
|
||||
|
||||
def __getitem__(self, key):
|
||||
if key in self: return self.get(key)
|
||||
return self.setdefault(key, copy.deepcopy(self.default))
|
||||
|
||||
def __copy__(self):
|
||||
copy = DefaultDict(self.default)
|
||||
copy.update(self)
|
||||
return copy
|
||||
|
||||
class Struct:
|
||||
"""Create an instance with argument=value slots.
|
||||
This is for making a lightweight object whose class doesn't matter."""
|
||||
def __init__(self, **entries):
|
||||
self.__dict__.update(entries)
|
||||
|
||||
def __cmp__(self, other):
|
||||
if isinstance(other, Struct):
|
||||
return cmp(self.__dict__, other.__dict__)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return cmp(self.__dict__, other)
|
||||
|
||||
def __repr__(self):
|
||||
args = ['%s=%s' % (k, repr(v)) for (k, v) in vars(self).items()]
|
||||
return 'Struct(%s)' % ', '.join(sorted(args))
|
||||
|
||||
def update(x, **entries):
|
||||
"""Update a dict; or an object with slots; according to entries.
|
||||
>>> update({'a': 1}, a=10, b=20)
|
||||
{'a': 10, 'b': 20}
|
||||
>>> update(Struct(a=1), a=10, b=20)
|
||||
Struct(a=10, b=20)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(x, dict):
|
||||
x.update(entries)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
x.__dict__.update(entries)
|
||||
return x
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Functions on Sequences (mostly inspired by Common Lisp)
|
||||
# NOTE: Sequence functions (count_if, find_if, every, some) take function
|
||||
# argument first (like reduce, filter, and map).
|
||||
|
||||
def removeall(item, seq):
|
||||
"""Return a copy of seq (or string) with all occurences of item removed.
|
||||
>>> removeall(3, [1, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1, 3])
|
||||
[1, 2, 2, 1]
|
||||
>>> removeall(4, [1, 2, 3])
|
||||
[1, 2, 3]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(seq, str):
|
||||
return seq.replace(item, '')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return [x for x in seq if x != item]
|
||||
|
||||
def unique(seq):
|
||||
"""Remove duplicate elements from seq. Assumes hashable elements.
|
||||
>>> unique([1, 2, 3, 2, 1])
|
||||
[1, 2, 3]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return list(set(seq))
|
||||
|
||||
def product(numbers):
|
||||
"""Return the product of the numbers.
|
||||
>>> product([1,2,3,4])
|
||||
24
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return reduce(operator.mul, numbers, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
def count_if(predicate, seq):
|
||||
"""Count the number of elements of seq for which the predicate is true.
|
||||
>>> count_if(callable, [42, None, max, min])
|
||||
2
|
||||
"""
|
||||
f = lambda count, x: count + (not not predicate(x))
|
||||
return reduce(f, seq, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def find_if(predicate, seq):
|
||||
"""If there is an element of seq that satisfies predicate; return it.
|
||||
>>> find_if(callable, [3, min, max])
|
||||
<built-in function min>
|
||||
>>> find_if(callable, [1, 2, 3])
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for x in seq:
|
||||
if predicate(x): return x
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
def every(predicate, seq):
|
||||
"""True if every element of seq satisfies predicate.
|
||||
>>> every(callable, [min, max])
|
||||
1
|
||||
>>> every(callable, [min, 3])
|
||||
0
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for x in seq:
|
||||
if not predicate(x): return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def some(predicate, seq):
|
||||
"""If some element x of seq satisfies predicate(x), return predicate(x).
|
||||
>>> some(callable, [min, 3])
|
||||
1
|
||||
>>> some(callable, [2, 3])
|
||||
0
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for x in seq:
|
||||
px = predicate(x)
|
||||
if px: return px
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def isin(elt, seq):
|
||||
"""Like (elt in seq), but compares with is, not ==.
|
||||
>>> e = []; isin(e, [1, e, 3])
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> isin(e, [1, [], 3])
|
||||
False
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for x in seq:
|
||||
if elt is x: return True
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Functions on sequences of numbers
|
||||
# NOTE: these take the sequence argument first, like min and max,
|
||||
# and like standard math notation: \sigma (i = 1..n) fn(i)
|
||||
# A lot of programing is finding the best value that satisfies some condition;
|
||||
# so there are three versions of argmin/argmax, depending on what you want to
|
||||
# do with ties: return the first one, return them all, or pick at random.
|
||||
|
||||
def argmin(seq, fn):
|
||||
"""Return an element with lowest fn(seq[i]) score; tie goes to first one.
|
||||
>>> argmin(['one', 'to', 'three'], len)
|
||||
'to'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
best = seq[0]; best_score = fn(best)
|
||||
for x in seq:
|
||||
x_score = fn(x)
|
||||
if x_score < best_score:
|
||||
best, best_score = x, x_score
|
||||
return best
|
||||
|
||||
def argmin_list(seq, fn):
|
||||
"""Return a list of elements of seq[i] with the lowest fn(seq[i]) scores.
|
||||
>>> argmin_list(['one', 'to', 'three', 'or'], len)
|
||||
['to', 'or']
|
||||
"""
|
||||
best_score, best = fn(seq[0]), []
|
||||
for x in seq:
|
||||
x_score = fn(x)
|
||||
if x_score < best_score:
|
||||
best, best_score = [x], x_score
|
||||
elif x_score == best_score:
|
||||
best.append(x)
|
||||
return best
|
||||
|
||||
def argmin_random_tie(seq, fn):
|
||||
"""Return an element with lowest fn(seq[i]) score; break ties at random.
|
||||
Thus, for all s,f: argmin_random_tie(s, f) in argmin_list(s, f)"""
|
||||
best_score = fn(seq[0]); n = 0
|
||||
for x in seq:
|
||||
x_score = fn(x)
|
||||
if x_score < best_score:
|
||||
best, best_score = x, x_score; n = 1
|
||||
elif x_score == best_score:
|
||||
n += 1
|
||||
if random.randrange(n) == 0:
|
||||
best = x
|
||||
return best
|
||||
|
||||
def argmax(seq, fn):
|
||||
"""Return an element with highest fn(seq[i]) score; tie goes to first one.
|
||||
>>> argmax(['one', 'to', 'three'], len)
|
||||
'three'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return argmin(seq, lambda x: -fn(x))
|
||||
|
||||
def argmax_list(seq, fn):
|
||||
"""Return a list of elements of seq[i] with the highest fn(seq[i]) scores.
|
||||
>>> argmax_list(['one', 'three', 'seven'], len)
|
||||
['three', 'seven']
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return argmin_list(seq, lambda x: -fn(x))
|
||||
|
||||
def argmax_random_tie(seq, fn):
|
||||
"Return an element with highest fn(seq[i]) score; break ties at random."
|
||||
return argmin_random_tie(seq, lambda x: -fn(x))
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Statistical and mathematical functions
|
||||
|
||||
def histogram(values, mode=0, bin_function=None):
|
||||
"""Return a list of (value, count) pairs, summarizing the input values.
|
||||
Sorted by increasing value, or if mode=1, by decreasing count.
|
||||
If bin_function is given, map it over values first."""
|
||||
if bin_function: values = map(bin_function, values)
|
||||
bins = {}
|
||||
for val in values:
|
||||
bins[val] = bins.get(val, 0) + 1
|
||||
if mode:
|
||||
return sorted(bins.items(), key=lambda x: (x[1],x[0]), reverse=True)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return sorted(bins.items())
|
||||
|
||||
def log2(x):
|
||||
"""Base 2 logarithm.
|
||||
>>> log2(1024)
|
||||
10.0
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return math.log10(x) / math.log10(2)
|
||||
|
||||
def mode(values):
|
||||
"""Return the most common value in the list of values.
|
||||
>>> mode([1, 2, 3, 2])
|
||||
2
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return histogram(values, mode=1)[0][0]
|
||||
|
||||
def median(values):
|
||||
"""Return the middle value, when the values are sorted.
|
||||
If there are an odd number of elements, try to average the middle two.
|
||||
If they can't be averaged (e.g. they are strings), choose one at random.
|
||||
>>> median([10, 100, 11])
|
||||
11
|
||||
>>> median([1, 2, 3, 4])
|
||||
2.5
|
||||
"""
|
||||
n = len(values)
|
||||
values = sorted(values)
|
||||
if n % 2 == 1:
|
||||
return values[n/2]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
middle2 = values[(n/2)-1:(n/2)+1]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return mean(middle2)
|
||||
except TypeError:
|
||||
return random.choice(middle2)
|
||||
|
||||
def mean(values):
|
||||
"""Return the arithmetic average of the values."""
|
||||
return sum(values) / float(len(values))
|
||||
|
||||
def stddev(values, meanval=None):
|
||||
"""The standard deviation of a set of values.
|
||||
Pass in the mean if you already know it."""
|
||||
if meanval is None: meanval = mean(values)
|
||||
return math.sqrt(sum([(x - meanval)**2 for x in values]) / (len(values)-1))
|
||||
|
||||
def dotproduct(X, Y):
|
||||
"""Return the sum of the element-wise product of vectors x and y.
|
||||
>>> dotproduct([1, 2, 3], [1000, 100, 10])
|
||||
1230
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return sum([x * y for x, y in zip(X, Y)])
|
||||
|
||||
def vector_add(a, b):
|
||||
"""Component-wise addition of two vectors.
|
||||
>>> vector_add((0, 1), (8, 9))
|
||||
(8, 10)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return tuple(map(operator.add, a, b))
|
||||
|
||||
def probability(p):
|
||||
"Return true with probability p."
|
||||
return p > random.uniform(0.0, 1.0)
|
||||
|
||||
def weighted_sample_with_replacement(seq, weights, n):
|
||||
"""Pick n samples from seq at random, with replacement, with the
|
||||
probability of each element in proportion to its corresponding
|
||||
weight."""
|
||||
sample = weighted_sampler(seq, weights)
|
||||
return [sample() for s in range(n)]
|
||||
|
||||
def weighted_sampler(seq, weights):
|
||||
"Return a random-sample function that picks from seq weighted by weights."
|
||||
totals = []
|
||||
for w in weights:
|
||||
totals.append(w + totals[-1] if totals else w)
|
||||
return lambda: seq[bisect.bisect(totals, random.uniform(0, totals[-1]))]
|
||||
|
||||
def num_or_str(x):
|
||||
"""The argument is a string; convert to a number if possible, or strip it.
|
||||
>>> num_or_str('42')
|
||||
42
|
||||
>>> num_or_str(' 42x ')
|
||||
'42x'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isnumber(x): return x
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return int(x)
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return float(x)
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
return str(x).strip()
|
||||
|
||||
def normalize(numbers):
|
||||
"""Multiply each number by a constant such that the sum is 1.0
|
||||
>>> normalize([1,2,1])
|
||||
[0.25, 0.5, 0.25]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
total = float(sum(numbers))
|
||||
return [n / total for n in numbers]
|
||||
|
||||
def clip(x, lowest, highest):
|
||||
"""Return x clipped to the range [lowest..highest].
|
||||
>>> [clip(x, 0, 1) for x in [-1, 0.5, 10]]
|
||||
[0, 0.5, 1]
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return max(lowest, min(x, highest))
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
## OK, the following are not as widely useful utilities as some of the other
|
||||
## functions here, but they do show up wherever we have 2D grids: Wumpus and
|
||||
## Vacuum worlds, TicTacToe and Checkers, and markov decision Processes.
|
||||
|
||||
orientations = [(1, 0), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (0, -1)]
|
||||
|
||||
def turn_heading(heading, inc, headings=orientations):
|
||||
return headings[(headings.index(heading) + inc) % len(headings)]
|
||||
|
||||
def turn_right(heading):
|
||||
return turn_heading(heading, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
def turn_left(heading):
|
||||
return turn_heading(heading, +1)
|
||||
|
||||
def distance(a, b):
|
||||
"The distance between two (x, y) points."
|
||||
(ax, ay) = a
|
||||
(bx, by) = b
|
||||
return math.hypot((ax - bx), (ay - by))
|
||||
|
||||
def distance2(a, b):
|
||||
"The square of the distance between two (x, y) points."
|
||||
(ax, ay) = a
|
||||
(bx, by) = b
|
||||
return (ax - bx)**2 + (ay - by)**2
|
||||
|
||||
def vector_clip(vector, lowest, highest):
|
||||
"""Return vector, except if any element is less than the corresponding
|
||||
value of lowest or more than the corresponding value of highest, clip to
|
||||
those values.
|
||||
>>> vector_clip((-1, 10), (0, 0), (9, 9))
|
||||
(0, 9)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return type(vector)(map(clip, vector, lowest, highest))
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Misc Functions
|
||||
|
||||
def printf(format, *args):
|
||||
"""Format args with the first argument as format string, and write.
|
||||
Return the last arg, or format itself if there are no args."""
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(str(format) % args)
|
||||
return if_(args, lambda: args[-1], lambda: format)
|
||||
|
||||
def caller(n=1):
|
||||
"""Return the name of the calling function n levels up in the frame stack.
|
||||
>>> caller(0)
|
||||
'caller'
|
||||
>>> def f():
|
||||
... return caller()
|
||||
>>> f()
|
||||
'f'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
return inspect.getouterframes(inspect.currentframe())[n][3]
|
||||
|
||||
def memoize(fn, slot=None):
|
||||
"""Memoize fn: make it remember the computed value for any argument list.
|
||||
If slot is specified, store result in that slot of first argument.
|
||||
If slot is false, store results in a dictionary."""
|
||||
if slot:
|
||||
def memoized_fn(obj, *args):
|
||||
if hasattr(obj, slot):
|
||||
return getattr(obj, slot)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
val = fn(obj, *args)
|
||||
setattr(obj, slot, val)
|
||||
return val
|
||||
else:
|
||||
def memoized_fn(*args):
|
||||
if not memoized_fn.cache.has_key(args):
|
||||
memoized_fn.cache[args] = fn(*args)
|
||||
return memoized_fn.cache[args]
|
||||
memoized_fn.cache = {}
|
||||
return memoized_fn
|
||||
|
||||
def if_(test, result, alternative):
|
||||
"""Like C++ and Java's (test ? result : alternative), except
|
||||
both result and alternative are always evaluated. However, if
|
||||
either evaluates to a function, it is applied to the empty arglist,
|
||||
so you can delay execution by putting it in a lambda.
|
||||
>>> if_(2 + 2 == 4, 'ok', lambda: expensive_computation())
|
||||
'ok'
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if test:
|
||||
if callable(result): return result()
|
||||
return result
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if callable(alternative): return alternative()
|
||||
return alternative
|
||||
|
||||
def name(object):
|
||||
"Try to find some reasonable name for the object."
|
||||
return (getattr(object, 'name', 0) or getattr(object, '__name__', 0)
|
||||
or getattr(getattr(object, '__class__', 0), '__name__', 0)
|
||||
or str(object))
|
||||
|
||||
def isnumber(x):
|
||||
"Is x a number? We say it is if it has a __int__ method."
|
||||
return hasattr(x, '__int__')
|
||||
|
||||
def issequence(x):
|
||||
"Is x a sequence? We say it is if it has a __getitem__ method."
|
||||
return hasattr(x, '__getitem__')
|
||||
|
||||
def print_table(table, header=None, sep=' ', numfmt='%g'):
|
||||
"""Print a list of lists as a table, so that columns line up nicely.
|
||||
header, if specified, will be printed as the first row.
|
||||
numfmt is the format for all numbers; you might want e.g. '%6.2f'.
|
||||
(If you want different formats in different columns, don't use print_table.)
|
||||
sep is the separator between columns."""
|
||||
justs = [if_(isnumber(x), 'rjust', 'ljust') for x in table[0]]
|
||||
if header:
|
||||
table = [header] + table
|
||||
table = [[if_(isnumber(x), lambda: numfmt % x, lambda: x) for x in row]
|
||||
for row in table]
|
||||
maxlen = lambda seq: max(map(len, seq))
|
||||
sizes = map(maxlen, zip(*[map(str, row) for row in table]))
|
||||
for row in table:
|
||||
print(sep.join(getattr(str(x), j)(size)
|
||||
for (j, size, x) in zip(justs, sizes, row)))
|
||||
|
||||
def AIMAFile(components, mode='r'):
|
||||
"Open a file based at the AIMA root directory."
|
||||
import logic_utils
|
||||
dir = os.path.dirname(logic_utils.__file__)
|
||||
return open(apply(os.path.join, [dir] + components), mode)
|
||||
|
||||
def DataFile(name, mode='r'):
|
||||
"Return a file in the AIMA /data directory."
|
||||
return AIMAFile(['..', 'data', name], mode)
|
||||
|
||||
def unimplemented():
|
||||
"Use this as a stub for not-yet-implemented functions."
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError()
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Queues: Stack, FIFOQueue, PriorityQueue
|
||||
|
||||
class Queue:
|
||||
"""Queue is an abstract class/interface. There are three types:
|
||||
Stack(): A Last In First Out Queue.
|
||||
FIFOQueue(): A First In First Out Queue.
|
||||
PriorityQueue(order, f): Queue in sorted order (default min-first).
|
||||
Each type supports the following methods and functions:
|
||||
q.append(item) -- add an item to the queue
|
||||
q.extend(items) -- equivalent to: for item in items: q.append(item)
|
||||
q.pop() -- return the top item from the queue
|
||||
len(q) -- number of items in q (also q.__len())
|
||||
item in q -- does q contain item?
|
||||
Note that isinstance(Stack(), Queue) is false, because we implement stacks
|
||||
as lists. If Python ever gets interfaces, Queue will be an interface."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
abstract
|
||||
|
||||
def extend(self, items):
|
||||
for item in items: self.append(item)
|
||||
|
||||
def Stack():
|
||||
"""Return an empty list, suitable as a Last-In-First-Out Queue."""
|
||||
return []
|
||||
|
||||
class FIFOQueue(Queue):
|
||||
"""A First-In-First-Out Queue."""
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.A = []; self.start = 0
|
||||
def append(self, item):
|
||||
self.A.append(item)
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return len(self.A) - self.start
|
||||
def extend(self, items):
|
||||
self.A.extend(items)
|
||||
def pop(self):
|
||||
e = self.A[self.start]
|
||||
self.start += 1
|
||||
if self.start > 5 and self.start > len(self.A)/2:
|
||||
self.A = self.A[self.start:]
|
||||
self.start = 0
|
||||
return e
|
||||
def __contains__(self, item):
|
||||
return item in self.A[self.start:]
|
||||
|
||||
class PriorityQueue(Queue):
|
||||
"""A queue in which the minimum (or maximum) element (as determined by f and
|
||||
order) is returned first. If order is min, the item with minimum f(x) is
|
||||
returned first; if order is max, then it is the item with maximum f(x).
|
||||
Also supports dict-like lookup."""
|
||||
def __init__(self, order=min, f=lambda x: x):
|
||||
update(self, A=[], order=order, f=f)
|
||||
def append(self, item):
|
||||
bisect.insort(self.A, (self.f(item), item))
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return len(self.A)
|
||||
def pop(self):
|
||||
if self.order == min:
|
||||
return self.A.pop(0)[1]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return self.A.pop()[1]
|
||||
def __contains__(self, item):
|
||||
return some(lambda _, x: x == item, self.A)
|
||||
def __getitem__(self, key):
|
||||
for _, item in self.A:
|
||||
if item == key:
|
||||
return item
|
||||
def __delitem__(self, key):
|
||||
for i, (value, item) in enumerate(self.A):
|
||||
if item == key:
|
||||
self.A.pop(i)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
## Fig: The idea is we can define things like Fig[3,10] later.
|
||||
## Alas, it is Fig[3,10] not Fig[3.10], because that would be the same
|
||||
## as Fig[3.1]
|
||||
Fig = {}
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
# Support for doctest
|
||||
|
||||
def ignore(x): None
|
||||
|
||||
def random_tests(text):
|
||||
"""Some functions are stochastic. We want to be able to write a test
|
||||
with random output. We do that by ignoring the output."""
|
||||
def fixup(test):
|
||||
if " = " in test:
|
||||
return ">>> " + test
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return ">>> ignore(" + test + ")"
|
||||
tests = re.findall(">>> (.*)", text)
|
||||
return '\n'.join(map(fixup, tests))
|
||||
|
||||
#______________________________________________________________________________
|
||||
|
||||
__doc__ += """
|
||||
>>> d = DefaultDict(0)
|
||||
>>> d['x'] += 1
|
||||
>>> d['x']
|
||||
1
|
||||
|
||||
>>> d = DefaultDict([])
|
||||
>>> d['x'] += [1]
|
||||
>>> d['y'] += [2]
|
||||
>>> d['x']
|
||||
[1]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> s = Struct(a=1, b=2)
|
||||
>>> s.a
|
||||
1
|
||||
>>> s.a = 3
|
||||
>>> s
|
||||
Struct(a=3, b=2)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def is_even(x):
|
||||
... return x % 2 == 0
|
||||
>>> sorted([1, 2, -3])
|
||||
[-3, 1, 2]
|
||||
>>> sorted(range(10), key=is_even)
|
||||
[1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
|
||||
>>> sorted(range(10), lambda x,y: y-x)
|
||||
[9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> removeall(4, [])
|
||||
[]
|
||||
>>> removeall('s', 'This is a test. Was a test.')
|
||||
'Thi i a tet. Wa a tet.'
|
||||
>>> removeall('s', 'Something')
|
||||
'Something'
|
||||
>>> removeall('s', '')
|
||||
''
|
||||
|
||||
>>> list(reversed([]))
|
||||
[]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> count_if(is_even, [1, 2, 3, 4])
|
||||
2
|
||||
>>> count_if(is_even, [])
|
||||
0
|
||||
|
||||
>>> argmax([1], lambda x: x*x)
|
||||
1
|
||||
>>> argmin([1], lambda x: x*x)
|
||||
1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Test of memoize with slots in structures
|
||||
>>> countries = [Struct(name='united states'), Struct(name='canada')]
|
||||
|
||||
# Pretend that 'gnp' was some big hairy operation:
|
||||
>>> def gnp(country):
|
||||
... print('calculating gnp ...')
|
||||
... return len(country.name) * 1e10
|
||||
|
||||
>>> gnp = memoize(gnp, '_gnp')
|
||||
>>> list(map(gnp, countries))
|
||||
calculating gnp ...
|
||||
calculating gnp ...
|
||||
[130000000000.0, 60000000000.0]
|
||||
>>> countries
|
||||
[Struct(_gnp=130000000000.0, name='united states'), Struct(_gnp=60000000000.0, name='canada')]
|
||||
|
||||
# This time we avoid re-doing the calculation
|
||||
>>> list(map(gnp, countries))
|
||||
[130000000000.0, 60000000000.0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Test Queues:
|
||||
>>> nums = [1, 8, 2, 7, 5, 6, -99, 99, 4, 3, 0]
|
||||
>>> def qtest(q):
|
||||
... q.extend(nums)
|
||||
... for num in nums: assert num in q
|
||||
... assert 42 not in q
|
||||
... return [q.pop() for i in range(len(q))]
|
||||
>>> qtest(Stack())
|
||||
[0, 3, 4, 99, -99, 6, 5, 7, 2, 8, 1]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> qtest(FIFOQueue())
|
||||
[1, 8, 2, 7, 5, 6, -99, 99, 4, 3, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> qtest(PriorityQueue(min))
|
||||
[-99, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 99]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> qtest(PriorityQueue(max))
|
||||
[99, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, -99]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> qtest(PriorityQueue(min, abs))
|
||||
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, -99, 99]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> qtest(PriorityQueue(max, abs))
|
||||
[99, -99, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vals = [100, 110, 160, 200, 160, 110, 200, 200, 220]
|
||||
>>> histogram(vals)
|
||||
[(100, 1), (110, 2), (160, 2), (200, 3), (220, 1)]
|
||||
>>> histogram(vals, 1)
|
||||
[(200, 3), (160, 2), (110, 2), (220, 1), (100, 1)]
|
||||
>>> histogram(vals, 1, lambda v: round(v, -2))
|
||||
[(200.0, 6), (100.0, 3)]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> log2(1.0)
|
||||
0.0
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def fib(n):
|
||||
... return (n<=1 and 1) or (fib(n-1) + fib(n-2))
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fib(9)
|
||||
55
|
||||
|
||||
# Now we make it faster:
|
||||
>>> fib = memoize(fib)
|
||||
>>> fib(9)
|
||||
55
|
||||
|
||||
>>> q = Stack()
|
||||
>>> q.append(1)
|
||||
>>> q.append(2)
|
||||
>>> q.pop(), q.pop()
|
||||
(2, 1)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> q = FIFOQueue()
|
||||
>>> q.append(1)
|
||||
>>> q.append(2)
|
||||
>>> q.pop(), q.pop()
|
||||
(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> abc = set('abc')
|
||||
>>> bcd = set('bcd')
|
||||
>>> 'a' in abc
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> 'a' in bcd
|
||||
False
|
||||
>>> list(abc.intersection(bcd))
|
||||
['c', 'b']
|
||||
>>> list(abc.union(bcd))
|
||||
['a', 'c', 'b', 'd']
|
||||
|
||||
## From "What's new in Python 2.4", but I added calls to sl
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def sl(x):
|
||||
... return sorted(list(x))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> a = set('abracadabra') # form a set from a string
|
||||
>>> 'z' in a # fast membership testing
|
||||
False
|
||||
>>> sl(a) # unique letters in a
|
||||
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'r']
|
||||
|
||||
>>> b = set('alacazam') # form a second set
|
||||
>>> sl(a - b) # letters in a but not in b
|
||||
['b', 'd', 'r']
|
||||
>>> sl(a | b) # letters in either a or b
|
||||
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'l', 'm', 'r', 'z']
|
||||
>>> sl(a & b) # letters in both a and b
|
||||
['a', 'c']
|
||||
>>> sl(a ^ b) # letters in a or b but not both
|
||||
['b', 'd', 'l', 'm', 'r', 'z']
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> a.add('z') # add a new element
|
||||
>>> a.update('wxy') # add multiple new elements
|
||||
>>> sl(a)
|
||||
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'r', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
|
||||
>>> a.remove('x') # take one element out
|
||||
>>> sl(a)
|
||||
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'r', 'w', 'y', 'z']
|
||||
|
||||
>>> weighted_sample_with_replacement([], [], 0)
|
||||
[]
|
||||
>>> weighted_sample_with_replacement('a', [3], 2)
|
||||
['a', 'a']
|
||||
>>> weighted_sample_with_replacement('ab', [0, 3], 3)
|
||||
['b', 'b', 'b']
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
__doc__ += random_tests("""
|
||||
>>> weighted_sample_with_replacement(range(10), [x*x for x in range(10)], 3)
|
||||
[8, 9, 6]
|
||||
""")
|
||||
745
logic/pacman.py
Normal file
745
logic/pacman.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,745 @@
|
||||
# pacman.py
|
||||
# ---------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Pacman.py holds the logic for the classic pacman game along with the main
|
||||
code to run a game. This file is divided into three sections:
|
||||
|
||||
(i) Your interface to the pacman world:
|
||||
Pacman is a complex environment. You probably don't want to
|
||||
read through all of the code we wrote to make the game runs
|
||||
correctly. This section contains the parts of the code
|
||||
that you will need to understand in order to complete the
|
||||
project. There is also some code in game.py that you should
|
||||
understand.
|
||||
|
||||
(ii) The hidden secrets of pacman:
|
||||
This section contains all of the logic code that the pacman
|
||||
environment uses to decide who can move where, who dies when
|
||||
things collide, etc. You shouldn't need to read this section
|
||||
of code, but you can if you want.
|
||||
|
||||
(iii) Framework to start a game:
|
||||
The final section contains the code for reading the command
|
||||
you use to set up the game, then starting up a new game, along with
|
||||
linking in all the external parts (agent functions, graphics).
|
||||
Check this section out to see all the options available to you.
|
||||
|
||||
To play your first game, type 'python pacman.py' from the command line.
|
||||
The keys are 'a', 's', 'd', and 'w' to move (or arrow keys). Have fun!
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from game import GameStateData
|
||||
from game import Game
|
||||
from game import Directions
|
||||
from game import Actions
|
||||
from util import nearestPoint
|
||||
from util import manhattanDistance
|
||||
import util
|
||||
import layout
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import types
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
###################################################
|
||||
# YOUR INTERFACE TO THE PACMAN WORLD: A GameState #
|
||||
###################################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GameState:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A GameState specifies the full game state, including the food, capsules,
|
||||
agent configurations and score changes.
|
||||
|
||||
GameStates are used by the Game object to capture the actual state of the game and
|
||||
can be used by agents to reason about the game.
|
||||
|
||||
Much of the information in a GameState is stored in a GameStateData object. We
|
||||
strongly suggest that you access that data via the accessor methods below rather
|
||||
than referring to the GameStateData object directly.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that in classic Pacman, Pacman is always agent 0.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
####################################################
|
||||
# Accessor methods: use these to access state data #
|
||||
####################################################
|
||||
|
||||
# static variable keeps track of which states have had getLegalActions called
|
||||
explored = set()
|
||||
|
||||
def getAndResetExplored():
|
||||
tmp = GameState.explored.copy()
|
||||
GameState.explored = set()
|
||||
return tmp
|
||||
getAndResetExplored = staticmethod(getAndResetExplored)
|
||||
|
||||
def getLegalActions(self, agentIndex=0):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the legal actions for the agent specified.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# GameState.explored.add(self)
|
||||
if self.isWin() or self.isLose():
|
||||
return []
|
||||
|
||||
if agentIndex == 0: # Pacman is moving
|
||||
return PacmanRules.getLegalActions(self)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return GhostRules.getLegalActions(self, agentIndex)
|
||||
|
||||
def generateSuccessor(self, agentIndex, action):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the successor state after the specified agent takes the action.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Check that successors exist
|
||||
if self.isWin() or self.isLose():
|
||||
raise Exception('Can\'t generate a successor of a terminal state.')
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy current state
|
||||
state = GameState(self)
|
||||
|
||||
# Let agent's logic deal with its action's effects on the board
|
||||
if agentIndex == 0: # Pacman is moving
|
||||
state.data._eaten = [False for i in range(state.getNumAgents())]
|
||||
PacmanRules.applyAction(state, action)
|
||||
else: # A ghost is moving
|
||||
GhostRules.applyAction(state, action, agentIndex)
|
||||
|
||||
# Time passes
|
||||
if agentIndex == 0:
|
||||
state.data.scoreChange += -TIME_PENALTY # Penalty for waiting around
|
||||
else:
|
||||
GhostRules.decrementTimer(state.data.agentStates[agentIndex])
|
||||
|
||||
# Resolve multi-agent effects
|
||||
GhostRules.checkDeath(state, agentIndex)
|
||||
|
||||
# Book keeping
|
||||
state.data._agentMoved = agentIndex
|
||||
state.data.score += state.data.scoreChange
|
||||
GameState.explored.add(self)
|
||||
GameState.explored.add(state)
|
||||
return state
|
||||
|
||||
def getLegalPacmanActions(self):
|
||||
return self.getLegalActions(0)
|
||||
|
||||
def generatePacmanSuccessor(self, action):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generates the successor state after the specified pacman move
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.generateSuccessor(0, action)
|
||||
|
||||
def getPacmanState(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns an AgentState object for pacman (in game.py)
|
||||
|
||||
state.pos gives the current position
|
||||
state.direction gives the travel vector
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.data.agentStates[0].copy()
|
||||
|
||||
def getPacmanPosition(self):
|
||||
return self.data.agentStates[0].getPosition()
|
||||
|
||||
def getGhostStates(self):
|
||||
return self.data.agentStates[1:]
|
||||
|
||||
def getGhostState(self, agentIndex):
|
||||
if agentIndex == 0 or agentIndex >= self.getNumAgents():
|
||||
raise Exception("Invalid index passed to getGhostState")
|
||||
return self.data.agentStates[agentIndex]
|
||||
|
||||
def getGhostPosition(self, agentIndex):
|
||||
if agentIndex == 0:
|
||||
raise Exception("Pacman's index passed to getGhostPosition")
|
||||
return self.data.agentStates[agentIndex].getPosition()
|
||||
|
||||
def getGhostPositions(self):
|
||||
return [s.getPosition() for s in self.getGhostStates()]
|
||||
|
||||
def getNumAgents(self):
|
||||
return len(self.data.agentStates)
|
||||
|
||||
def getScore(self):
|
||||
return float(self.data.score)
|
||||
|
||||
def getCapsules(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a list of positions (x,y) of the remaining capsules.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.data.capsules
|
||||
|
||||
def getNumFood(self):
|
||||
return self.data.food.count()
|
||||
|
||||
def getFood(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a Grid of boolean food indicator variables.
|
||||
|
||||
Grids can be accessed via list notation, so to check
|
||||
if there is food at (x,y), just call
|
||||
|
||||
currentFood = state.getFood()
|
||||
if currentFood[x][y] == True: ...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.data.food
|
||||
|
||||
def getWalls(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a Grid of boolean wall indicator variables.
|
||||
|
||||
Grids can be accessed via list notation, so to check
|
||||
if there is a wall at (x,y), just call
|
||||
|
||||
walls = state.getWalls()
|
||||
if walls[x][y] == True: ...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.data.layout.walls
|
||||
|
||||
def getCoordsWithoutWalls(self):
|
||||
wall_grid = self.getWalls()
|
||||
nonwall_coords_list = []
|
||||
for y in range(wall_grid.height):
|
||||
for x in range(wall_grid.width):
|
||||
if not wall_grid[x][y]:
|
||||
nonwall_coords_list.append((x,y))
|
||||
return nonwall_coords_list
|
||||
|
||||
def hasFood(self, x, y):
|
||||
return self.data.food[x][y]
|
||||
|
||||
def hasWall(self, x, y):
|
||||
return self.data.layout.walls[x][y]
|
||||
|
||||
def isLose(self):
|
||||
return self.data._lose
|
||||
|
||||
def isWin(self):
|
||||
return self.data._win
|
||||
|
||||
#############################################
|
||||
# Helper methods: #
|
||||
# You shouldn't need to call these directly #
|
||||
#############################################
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, prevState=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generates a new state by copying information from its predecessor.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if prevState != None: # Initial state
|
||||
self.data = GameStateData(prevState.data)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.data = GameStateData()
|
||||
|
||||
def deepCopy(self):
|
||||
state = GameState(self)
|
||||
state.data = self.data.deepCopy()
|
||||
return state
|
||||
|
||||
def __eq__(self, other):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Allows two states to be compared.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return hasattr(other, 'data') and self.data == other.data
|
||||
|
||||
def __hash__(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Allows states to be keys of dictionaries.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return hash(self.data)
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
|
||||
return str(self.data)
|
||||
|
||||
def initialize(self, layout, numGhostAgents=1000):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Creates an initial game state from a layout array (see layout.py).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.data.initialize(layout, numGhostAgents)
|
||||
|
||||
############################################################################
|
||||
# THE HIDDEN SECRETS OF PACMAN #
|
||||
# #
|
||||
# You shouldn't need to look through the code in this section of the file. #
|
||||
############################################################################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
SCARED_TIME = 40 # Moves ghosts are scared
|
||||
COLLISION_TOLERANCE = 0.7 # How close ghosts must be to Pacman to kill
|
||||
TIME_PENALTY = 1 # Number of points lost each round
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ClassicGameRules:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
These game rules manage the control flow of a game, deciding when
|
||||
and how the game starts and ends.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, timeout=30):
|
||||
self.timeout = timeout
|
||||
|
||||
def newGame(self, layout, pacmanAgent, ghostAgents, display, quiet=False, catchExceptions=False):
|
||||
agents = [pacmanAgent] + ghostAgents[:layout.getNumGhosts()]
|
||||
initState = GameState()
|
||||
initState.initialize(layout, len(ghostAgents))
|
||||
game = Game(agents, display, self, catchExceptions=catchExceptions)
|
||||
game.state = initState
|
||||
self.initialState = initState.deepCopy()
|
||||
self.quiet = quiet
|
||||
return game
|
||||
|
||||
def process(self, state, game):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks to see whether it is time to end the game.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if state.isWin():
|
||||
self.win(state, game)
|
||||
if state.isLose():
|
||||
self.lose(state, game)
|
||||
|
||||
def win(self, state, game):
|
||||
if not self.quiet:
|
||||
print("Pacman emerges victorious! Score: %d" % state.data.score)
|
||||
game.gameOver = True
|
||||
|
||||
def lose(self, state, game):
|
||||
if not self.quiet:
|
||||
print("Pacman died! Score: %d" % state.data.score)
|
||||
game.gameOver = True
|
||||
|
||||
def getProgress(self, game):
|
||||
return float(game.state.getNumFood()) / self.initialState.getNumFood()
|
||||
|
||||
def agentCrash(self, game, agentIndex):
|
||||
if agentIndex == 0:
|
||||
print("Pacman crashed")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("A ghost crashed")
|
||||
|
||||
def getMaxTotalTime(self, agentIndex):
|
||||
return self.timeout
|
||||
|
||||
def getMaxStartupTime(self, agentIndex):
|
||||
return self.timeout
|
||||
|
||||
def getMoveWarningTime(self, agentIndex):
|
||||
return self.timeout
|
||||
|
||||
def getMoveTimeout(self, agentIndex):
|
||||
return self.timeout
|
||||
|
||||
def getMaxTimeWarnings(self, agentIndex):
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PacmanRules:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
These functions govern how pacman interacts with his environment under
|
||||
the classic game rules.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
PACMAN_SPEED = 1
|
||||
|
||||
def getLegalActions(state):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns a list of possible actions.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return Actions.getPossibleActions(state.getPacmanState().configuration, state.data.layout.walls)
|
||||
getLegalActions = staticmethod(getLegalActions)
|
||||
|
||||
def applyAction(state, action):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Edits the state to reflect the results of the action.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
legal = PacmanRules.getLegalActions(state)
|
||||
if action not in legal:
|
||||
raise Exception("Illegal action " + str(action))
|
||||
|
||||
pacmanState = state.data.agentStates[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Update Configuration
|
||||
vector = Actions.directionToVector(action, PacmanRules.PACMAN_SPEED)
|
||||
pacmanState.configuration = pacmanState.configuration.generateSuccessor(vector)
|
||||
|
||||
# Eat
|
||||
next = pacmanState.configuration.getPosition()
|
||||
nearest = nearestPoint(next)
|
||||
if manhattanDistance(nearest, next) <= 0.5:
|
||||
# Remove food
|
||||
PacmanRules.consume(nearest, state)
|
||||
applyAction = staticmethod(applyAction)
|
||||
|
||||
def consume(position, state):
|
||||
x, y = position
|
||||
# Eat food
|
||||
if state.data.food[x][y]:
|
||||
state.data.scoreChange += 10
|
||||
state.data.food = state.data.food.copy()
|
||||
state.data.food[x][y] = False
|
||||
state.data._foodEaten = position
|
||||
# TODO: cache numFood?
|
||||
numFood = state.getNumFood()
|
||||
if numFood == 0 and not state.data._lose:
|
||||
state.data.scoreChange += 500
|
||||
state.data._win = True
|
||||
# Eat capsule
|
||||
if(position in state.getCapsules()):
|
||||
state.data.capsules.remove(position)
|
||||
state.data._capsuleEaten = position
|
||||
# Reset all ghosts' scared timers
|
||||
for index in range(1, len(state.data.agentStates)):
|
||||
state.data.agentStates[index].scaredTimer = SCARED_TIME
|
||||
consume = staticmethod(consume)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GhostRules:
|
||||
# PMV
|
||||
ghostCanStop = True
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
These functions dictate how ghosts interact with their environment.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
GHOST_SPEED = 1.0
|
||||
|
||||
def getLegalActions(state, ghostIndex):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Ghosts cannot stop, and cannot turn around unless they
|
||||
reach a dead end, but can turn 90 degrees at intersections.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
conf = state.getGhostState(ghostIndex).configuration
|
||||
possibleActions = Actions.getPossibleActions(conf, state.data.layout.walls)
|
||||
reverse = Actions.reverseDirection(conf.direction)
|
||||
|
||||
# PMV
|
||||
if not GhostRules.ghostCanStop and Directions.STOP in possibleActions:
|
||||
possibleActions.remove(Directions.STOP)
|
||||
if reverse in possibleActions and len(possibleActions) > 1 and reverse != Directions.STOP:
|
||||
possibleActions.remove(reverse)
|
||||
return possibleActions
|
||||
getLegalActions = staticmethod(getLegalActions)
|
||||
|
||||
def applyAction(state, action, ghostIndex):
|
||||
|
||||
legal = GhostRules.getLegalActions(state, ghostIndex)
|
||||
if action not in legal:
|
||||
raise Exception("Illegal ghost action " + str(action))
|
||||
|
||||
ghostState = state.data.agentStates[ghostIndex]
|
||||
speed = GhostRules.GHOST_SPEED
|
||||
if ghostState.scaredTimer > 0:
|
||||
speed /= 2.0
|
||||
vector = Actions.directionToVector(action, speed)
|
||||
ghostState.configuration = ghostState.configuration.generateSuccessor(vector)
|
||||
applyAction = staticmethod(applyAction)
|
||||
|
||||
def decrementTimer(ghostState):
|
||||
timer = ghostState.scaredTimer
|
||||
if timer == 1:
|
||||
ghostState.configuration.pos = nearestPoint(ghostState.configuration.pos)
|
||||
ghostState.scaredTimer = max(0, timer - 1)
|
||||
decrementTimer = staticmethod(decrementTimer)
|
||||
|
||||
def checkDeath(state, agentIndex):
|
||||
pacmanPosition = state.getPacmanPosition()
|
||||
if agentIndex == 0: # Pacman just moved; Anyone can kill him
|
||||
for index in range(1, len(state.data.agentStates)):
|
||||
ghostState = state.data.agentStates[index]
|
||||
ghostPosition = ghostState.configuration.getPosition()
|
||||
if GhostRules.canKill(pacmanPosition, ghostPosition):
|
||||
GhostRules.collide(state, ghostState, index)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ghostState = state.data.agentStates[agentIndex]
|
||||
ghostPosition = ghostState.configuration.getPosition()
|
||||
if GhostRules.canKill(pacmanPosition, ghostPosition):
|
||||
GhostRules.collide(state, ghostState, agentIndex)
|
||||
checkDeath = staticmethod(checkDeath)
|
||||
|
||||
def collide(state, ghostState, agentIndex):
|
||||
if ghostState.scaredTimer > 0:
|
||||
state.data.scoreChange += 200
|
||||
GhostRules.placeGhost(state, ghostState)
|
||||
ghostState.scaredTimer = 0
|
||||
# Added for first-person
|
||||
state.data._eaten[agentIndex] = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if not state.data._win:
|
||||
state.data.scoreChange -= 500
|
||||
state.data._lose = True
|
||||
collide = staticmethod(collide)
|
||||
|
||||
def canKill(pacmanPosition, ghostPosition):
|
||||
return manhattanDistance(ghostPosition, pacmanPosition) <= COLLISION_TOLERANCE
|
||||
canKill = staticmethod(canKill)
|
||||
|
||||
def placeGhost(state, ghostState):
|
||||
ghostState.configuration = ghostState.start
|
||||
placeGhost = staticmethod(placeGhost)
|
||||
|
||||
#############################
|
||||
# FRAMEWORK TO START A GAME #
|
||||
#############################
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def default(str):
|
||||
return str + ' [Default: %default]'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parseAgentArgs(str):
|
||||
if str == None:
|
||||
return {}
|
||||
pieces = str.split(',')
|
||||
opts = {}
|
||||
for p in pieces:
|
||||
if '=' in p:
|
||||
key, val = p.split('=')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
key, val = p, 1
|
||||
opts[key] = val
|
||||
return opts
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def readCommand(argv):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Processes the command used to run pacman from the command line.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from optparse import OptionParser
|
||||
usageStr = """
|
||||
USAGE: python pacman.py <options>
|
||||
EXAMPLES: (1) python pacman.py
|
||||
- starts an interactive game
|
||||
(2) python pacman.py --layout smallClassic --zoom 2
|
||||
OR python pacman.py -l smallClassic -z 2
|
||||
- starts an interactive game on a smaller board, zoomed in
|
||||
"""
|
||||
parser = OptionParser(usageStr)
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_option('-n', '--numGames', dest='numGames', type='int',
|
||||
help=default('the number of GAMES to play'), metavar='GAMES', default=1)
|
||||
parser.add_option('-l', '--layout', dest='layout',
|
||||
help=default('the LAYOUT_FILE from which to load the map layout'),
|
||||
metavar='LAYOUT_FILE', default='mediumClassic')
|
||||
parser.add_option('-p', '--pacman', dest='pacman',
|
||||
help=default('the agent TYPE in the pacmanAgents module to use'),
|
||||
metavar='TYPE', default='KeyboardAgent')
|
||||
parser.add_option('-t', '--textGraphics', action='store_true', dest='textGraphics',
|
||||
help='Display output as text only', default=False)
|
||||
parser.add_option('-q', '--quietTextGraphics', action='store_true', dest='quietGraphics',
|
||||
help='Generate minimal output and no graphics', default=False)
|
||||
parser.add_option('-g', '--ghosts', dest='ghost',
|
||||
help=default('the ghost agent TYPE in the ghostAgents module to use'),
|
||||
metavar='TYPE', default='RandomGhost')
|
||||
parser.add_option('-k', '--numghosts', type='int', dest='numGhosts',
|
||||
help=default('The maximum number of ghosts to use'), default=4)
|
||||
parser.add_option('-z', '--zoom', type='float', dest='zoom',
|
||||
help=default('Zoom the size of the graphics window'), default=1.0)
|
||||
parser.add_option('-f', '--fixRandomSeed', action='store_true', dest='fixRandomSeed',
|
||||
help='Fixes the random seed to always play the same game', default=False)
|
||||
parser.add_option('-r', '--recordActions', action='store_true', dest='record',
|
||||
help='Writes game histories to a file (named by the time they were played)', default=False)
|
||||
parser.add_option('--replay', dest='gameToReplay',
|
||||
help='A recorded game file (pickle) to replay', default=None)
|
||||
parser.add_option('-a', '--agentArgs', dest='agentArgs',
|
||||
help='Comma separated values sent to agent. e.g. "opt1=val1,opt2,opt3=val3"')
|
||||
parser.add_option('-x', '--numTraining', dest='numTraining', type='int',
|
||||
help=default('How many episodes are training (suppresses output)'), default=0)
|
||||
parser.add_option('--frameTime', dest='frameTime', type='float',
|
||||
help=default('Time to delay between frames; <0 means keyboard'), default=0.1)
|
||||
parser.add_option('-c', '--catchExceptions', action='store_true', dest='catchExceptions',
|
||||
help='Turns on exception handling and timeouts during games', default=False)
|
||||
parser.add_option('--timeout', dest='timeout', type='int',
|
||||
help=default('Maximum length of time an agent can spend computing in a single game'), default=30)
|
||||
|
||||
options, otherjunk = parser.parse_args(argv)
|
||||
if len(otherjunk) != 0:
|
||||
raise Exception('Command line input not understood: ' + str(otherjunk))
|
||||
args = dict()
|
||||
|
||||
# Fix the random seed
|
||||
if options.fixRandomSeed:
|
||||
random.seed('cs188')
|
||||
|
||||
# Choose a layout
|
||||
args['layout'] = layout.getLayout(options.layout)
|
||||
if args['layout'] == None:
|
||||
raise Exception("The layout " + options.layout + " cannot be found")
|
||||
|
||||
# Choose a Pacman agent
|
||||
noKeyboard = options.gameToReplay == None and (options.textGraphics or options.quietGraphics)
|
||||
pacmanType = loadAgent(options.pacman, noKeyboard)
|
||||
agentOpts = parseAgentArgs(options.agentArgs)
|
||||
if options.numTraining > 0:
|
||||
args['numTraining'] = options.numTraining
|
||||
if 'numTraining' not in agentOpts:
|
||||
agentOpts['numTraining'] = options.numTraining
|
||||
pacman = pacmanType(**agentOpts) # Instantiate Pacman with agentArgs
|
||||
args['pacman'] = pacman
|
||||
|
||||
# Don't display training games
|
||||
if 'numTrain' in agentOpts:
|
||||
options.numQuiet = int(agentOpts['numTrain'])
|
||||
options.numIgnore = int(agentOpts['numTrain'])
|
||||
|
||||
# Choose a ghost agent
|
||||
ghostType = loadAgent(options.ghost, noKeyboard)
|
||||
args['ghosts'] = [ghostType(i+1) for i in range(options.numGhosts)]
|
||||
|
||||
# Choose a display format
|
||||
if options.quietGraphics:
|
||||
import textDisplay
|
||||
args['display'] = textDisplay.NullGraphics()
|
||||
elif options.textGraphics:
|
||||
import textDisplay
|
||||
textDisplay.SLEEP_TIME = options.frameTime
|
||||
args['display'] = textDisplay.PacmanGraphics()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import graphicsDisplay
|
||||
if "fn" in agentOpts:
|
||||
is_mapping_problem = agentOpts['fn'] in ["mp", 'slam']
|
||||
else:
|
||||
is_mapping_problem = False
|
||||
args['display'] = graphicsDisplay.PacmanGraphics(
|
||||
options.zoom, frameTime=options.frameTime, render_walls_beforehand=(not is_mapping_problem))
|
||||
args['numGames'] = options.numGames
|
||||
args['record'] = options.record
|
||||
args['catchExceptions'] = options.catchExceptions
|
||||
args['timeout'] = options.timeout
|
||||
|
||||
# Special case: recorded games don't use the runGames method or args structure
|
||||
if options.gameToReplay != None:
|
||||
print('Replaying recorded game %s.' % options.gameToReplay)
|
||||
import pickle
|
||||
f = open(options.gameToReplay, 'rb')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
recorded = pickle.load(f)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
f.close()
|
||||
recorded['display'] = args['display']
|
||||
replayGame(**recorded)
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
|
||||
return args
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def loadAgent(pacman, nographics):
|
||||
# Looks through all pythonPath Directories for the right module,
|
||||
pythonPathStr = os.path.expandvars("$PYTHONPATH")
|
||||
if pythonPathStr.find(';') == -1:
|
||||
pythonPathDirs = pythonPathStr.split(':')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pythonPathDirs = pythonPathStr.split(';')
|
||||
pythonPathDirs.append('.')
|
||||
|
||||
for moduleDir in pythonPathDirs:
|
||||
if not os.path.isdir(moduleDir):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
moduleNames = [f for f in os.listdir(moduleDir) if f.endswith('gents.py')]
|
||||
for modulename in moduleNames:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
module = __import__(modulename[:-3])
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if pacman in dir(module):
|
||||
if nographics and modulename == 'keyboardAgents.py':
|
||||
raise Exception('Using the keyboard requires graphics (not text display)')
|
||||
return getattr(module, pacman)
|
||||
raise Exception('The agent ' + pacman + ' is not specified in any *Agents.py.')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def replayGame(layout, actions, display):
|
||||
import pacmanAgents
|
||||
import ghostAgents
|
||||
rules = ClassicGameRules()
|
||||
agents = [pacmanAgents.GreedyAgent()] + [ghostAgents.RandomGhost(i+1) for i in range(layout.getNumGhosts())]
|
||||
game = rules.newGame(layout, agents[0], agents[1:], display)
|
||||
state = game.state
|
||||
display.initialize(state.data)
|
||||
|
||||
for action in actions:
|
||||
# Execute the action
|
||||
state = state.generateSuccessor(*action)
|
||||
# Change the display
|
||||
display.update(state.data)
|
||||
# Allow for game specific conditions (winning, losing, etc.)
|
||||
rules.process(state, game)
|
||||
|
||||
display.finish()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def runGames(layout, pacman, ghosts, display, numGames, record, numTraining=0, catchExceptions=False, timeout=30, steps=1000):
|
||||
import __main__
|
||||
__main__.__dict__['_display'] = display
|
||||
|
||||
rules = ClassicGameRules(timeout)
|
||||
games = []
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(numGames):
|
||||
beQuiet = i < numTraining
|
||||
if beQuiet:
|
||||
# Suppress output and graphics
|
||||
import textDisplay
|
||||
gameDisplay = textDisplay.NullGraphics()
|
||||
rules.quiet = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
gameDisplay = display
|
||||
rules.quiet = False
|
||||
game = rules.newGame(layout, pacman, ghosts, gameDisplay, beQuiet, catchExceptions)
|
||||
if pacman.live_checking:
|
||||
yield from game.run()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for _ in game.run():
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
if not beQuiet:
|
||||
games.append(game)
|
||||
|
||||
if record:
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import pickle
|
||||
fname = ('recorded-game-%d' % (i + 1)) + '-'.join([str(t) for t in time.localtime()[1:6]])
|
||||
f = open(fname, 'wb')
|
||||
components = {'layout': layout, 'actions': game.moveHistory}
|
||||
pickle.dump(components, f)
|
||||
f.close()
|
||||
|
||||
if (numGames-numTraining) > 0:
|
||||
scores = [game.state.getScore() for game in games]
|
||||
wins = [game.state.isWin() for game in games]
|
||||
winRate = wins.count(True) / float(len(wins))
|
||||
print('Average Score:', sum(scores) / float(len(scores)))
|
||||
print('Scores: ', ', '.join([str(score) for score in scores]))
|
||||
print('Win Rate: %d/%d (%.2f)' % (wins.count(True), len(wins), winRate))
|
||||
print('Record: ', ', '.join([['Loss', 'Win'][int(w)] for w in wins]))
|
||||
|
||||
yield games
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
"""
|
||||
The main function called when pacman.py is run
|
||||
from the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
> python pacman.py
|
||||
|
||||
See the usage string for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
> python pacman.py --help
|
||||
"""
|
||||
args = readCommand(sys.argv[1:]) # Get game components based on input
|
||||
next(runGames(**args))
|
||||
|
||||
# import cProfile
|
||||
# cProfile.run("runGames( **args )")
|
||||
pass
|
||||
63
logic/pacmanAgents.py
Normal file
63
logic/pacmanAgents.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
# pacmanAgents.py
|
||||
# ---------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from pacman import Directions
|
||||
from game import Agent
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import game
|
||||
import util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LeftTurnAgent(game.Agent):
|
||||
"An agent that turns left at every opportunity"
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
legal = state.getLegalPacmanActions()
|
||||
current = state.getPacmanState().configuration.direction
|
||||
if current == Directions.STOP:
|
||||
current = Directions.NORTH
|
||||
left = Directions.LEFT[current]
|
||||
if left in legal:
|
||||
return left
|
||||
if current in legal:
|
||||
return current
|
||||
if Directions.RIGHT[current] in legal:
|
||||
return Directions.RIGHT[current]
|
||||
if Directions.LEFT[left] in legal:
|
||||
return Directions.LEFT[left]
|
||||
return Directions.STOP
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GreedyAgent(Agent):
|
||||
def __init__(self, evalFn="scoreEvaluation"):
|
||||
self.evaluationFunction = util.lookup(evalFn, globals())
|
||||
assert self.evaluationFunction != None
|
||||
|
||||
def getAction(self, state):
|
||||
# Generate candidate actions
|
||||
legal = state.getLegalPacmanActions()
|
||||
if Directions.STOP in legal:
|
||||
legal.remove(Directions.STOP)
|
||||
|
||||
successors = [(state.generateSuccessor(0, action), action)
|
||||
for action in legal]
|
||||
scored = [(self.evaluationFunction(state), action)
|
||||
for state, action in successors]
|
||||
bestScore = max(scored)[0]
|
||||
bestActions = [pair[1] for pair in scored if pair[0] == bestScore]
|
||||
return random.choice(bestActions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def scoreEvaluation(state):
|
||||
return state.getScore()
|
||||
18
logic/projectParams.py
Normal file
18
logic/projectParams.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
# projectParams.py
|
||||
# ----------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
STUDENT_CODE_DEFAULT = 'logicPlan.py'
|
||||
PROJECT_TEST_CLASSES = 'logic_planTestClasses.py'
|
||||
PROJECT_NAME = 'Project 3: Logic'
|
||||
BONUS_PIC = False
|
||||
20
logic/pycosat_test.py
Normal file
20
logic/pycosat_test.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
# pycosat_test.py
|
||||
# ---------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import pycosat
|
||||
|
||||
cnf = [[1, -5, 4], [-1, 5, 3, 4], [-3, -4]]
|
||||
|
||||
print(pycosat.solve(cnf))
|
||||
|
||||
251
logic/testClasses.py
Normal file
251
logic/testClasses.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
||||
# testClasses.py
|
||||
# --------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# import modules from python standard library
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import math
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def invertLayout(layout_text):
|
||||
# Keep lower left fix as this is hardcoded in PositionSearchProblem (gah)
|
||||
# as the goal.
|
||||
lines = [l.strip() for l in layout_text.split('\n')]
|
||||
h = len(lines)
|
||||
w = len(lines[0])
|
||||
tiles = {}
|
||||
for y, line in enumerate(lines):
|
||||
for x, tile in enumerate(line):
|
||||
# (x,y)
|
||||
# (0,0) -> (h,w)
|
||||
# (0,h) -> (0,w)
|
||||
tiles[h-1-y, w-1-x] = tile
|
||||
|
||||
new_lines = []
|
||||
for y in range(w):
|
||||
new_lines.append("")
|
||||
for x in range(h):
|
||||
new_lines[-1] += tiles[x,y]
|
||||
#return layout_text
|
||||
return "\n".join(new_lines)
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
# Class which models a question in a project. Note that questions have a
|
||||
# maximum number of points they are worth, and are composed of a series of
|
||||
# test cases
|
||||
class Question(object):
|
||||
|
||||
def raiseNotDefined(self):
|
||||
print('Method not implemented: %s' % inspect.stack()[1][3])
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, questionDict, display):
|
||||
self.maxPoints = int(questionDict['max_points'])
|
||||
self.testCases = []
|
||||
self.display = display
|
||||
|
||||
def getDisplay(self):
|
||||
return self.display
|
||||
|
||||
def getMaxPoints(self):
|
||||
return self.maxPoints
|
||||
|
||||
# Note that 'thunk' must be a function which accepts a single argument,
|
||||
# namely a 'grading' object
|
||||
def addTestCase(self, testCase, thunk):
|
||||
self.testCases.append((testCase, thunk))
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades):
|
||||
self.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Question in which all test cases must be passed in order to receive credit
|
||||
class PassAllTestsQuestion(Question):
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades):
|
||||
# TODO: is this the right way to use grades? The autograder doesn't seem to use it.
|
||||
testsFailed = False
|
||||
grades.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
for _, f in self.testCases:
|
||||
if not f(grades):
|
||||
testsFailed = True
|
||||
if testsFailed:
|
||||
grades.fail("Tests failed.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
grades.assignFullCredit()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ExtraCreditPassAllTestsQuestion(Question):
|
||||
def __init__(self, questionDict, display):
|
||||
Question.__init__(self, questionDict, display)
|
||||
self.extraPoints = int(questionDict['extra_points'])
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades):
|
||||
# TODO: is this the right way to use grades? The autograder doesn't seem to use it.
|
||||
testsFailed = False
|
||||
grades.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
for _, f in self.testCases:
|
||||
if not f(grades):
|
||||
testsFailed = True
|
||||
if testsFailed:
|
||||
grades.fail("Tests failed.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
grades.assignFullCredit()
|
||||
grades.addPoints(self.extraPoints)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Question in which predict credit is given for test cases with a ``points'' property.
|
||||
# All other tests are mandatory and must be passed.
|
||||
class HackedPartialCreditQuestion(Question):
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades):
|
||||
# TODO: is this the right way to use grades? The autograder doesn't seem to use it.
|
||||
grades.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
|
||||
points = 0
|
||||
passed = True
|
||||
for testCase, f in self.testCases:
|
||||
testResult = f(grades)
|
||||
if "points" in testCase.testDict:
|
||||
if testResult:
|
||||
points += float(testCase.testDict["points"])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
passed = passed and testResult
|
||||
|
||||
# FIXME: Below terrible hack to match q3's logic
|
||||
if int(points) == self.maxPoints and not passed:
|
||||
grades.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
grades.addPoints(int(points))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Q6PartialCreditQuestion(Question):
|
||||
"""Fails any test which returns False, otherwise doesn't effect the grades object.
|
||||
Partial credit tests will add the required points."""
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades):
|
||||
grades.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
|
||||
results = []
|
||||
for _, f in self.testCases:
|
||||
results.append(f(grades))
|
||||
if False in results:
|
||||
grades.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PartialCreditQuestion(Question):
|
||||
"""Fails any test which returns False, otherwise doesn't effect the grades object.
|
||||
Partial credit tests will add the required points."""
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades):
|
||||
grades.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
|
||||
for _, f in self.testCases:
|
||||
if not f(grades):
|
||||
grades.assignZeroCredit()
|
||||
grades.fail("Tests failed.")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class NumberPassedQuestion(Question):
|
||||
"""Grade is the number of test cases passed."""
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades):
|
||||
grades.addPoints([f(grades) for _, f in self.testCases].count(True))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PercentPassedQuestion(Question):
|
||||
"""Grade is the number of test cases passed."""
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades):
|
||||
count = [f(grades) for _, f in self.testCases].count(True)
|
||||
grades.addPoints(math.floor(self.maxPoints*(count/len(self.testCases))))
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
from testParser import emitTestDict
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
|
||||
# Template modeling a generic test case
|
||||
class TestCase(object):
|
||||
|
||||
def raiseNotDefined(self):
|
||||
print('Method not implemented: %s' % inspect.stack()[1][3])
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def getPath(self):
|
||||
return self.path
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, question, testDict):
|
||||
self.question = question
|
||||
self.testDict = testDict
|
||||
self.path = testDict['path']
|
||||
self.messages = []
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
self.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
def execute(self, grades, moduleDict, solutionDict):
|
||||
self.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
def writeSolution(self, moduleDict, filePath):
|
||||
self.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
# Tests should call the following messages for grading
|
||||
# to ensure a uniform format for test output.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# TODO: this is hairy, but we need to fix grading.py's interface
|
||||
# to get a nice hierarchical project - question - test structure,
|
||||
# then these should be moved into Question proper.
|
||||
def testPass(self, grades):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('PASS: %s' % (self.path,))
|
||||
for line in self.messages:
|
||||
grades.addMessage(' %s' % (line,))
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def testFail(self, grades):
|
||||
grades.addMessage('FAIL: %s' % (self.path,))
|
||||
for line in self.messages:
|
||||
grades.addMessage(' %s' % (line,))
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
# This should really be question level?
|
||||
def testPartial(self, grades, points, maxPoints):
|
||||
grades.addPoints(points)
|
||||
extraCredit = max(0, points - maxPoints)
|
||||
regularCredit = points - extraCredit
|
||||
|
||||
grades.addMessage('%s: %s (%s of %s points)' % (
|
||||
"PASS" if points >= maxPoints else "FAIL", self.path, regularCredit, maxPoints))
|
||||
if extraCredit > 0:
|
||||
grades.addMessage('EXTRA CREDIT: %s points' % (extraCredit,))
|
||||
|
||||
for line in self.messages:
|
||||
grades.addMessage(' %s' % (line,))
|
||||
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def addMessage(self, message):
|
||||
self.messages.extend(message.split('\n'))
|
||||
|
||||
# BEGIN SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
def createPublicVersion(self):
|
||||
self.raiseNotDefined()
|
||||
|
||||
def emitPublicVersion(self, filePath):
|
||||
with open(filePath, 'w') as handle:
|
||||
emitTestDict(self.testDict, handle)
|
||||
# END SOLUTION NO PROMPT
|
||||
87
logic/testParser.py
Normal file
87
logic/testParser.py
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
# testParser.py
|
||||
# -------------
|
||||
# Licensing Information: You are free to use or extend these projects for
|
||||
# educational purposes provided that (1) you do not distribute or publish
|
||||
# solutions, (2) you retain this notice, and (3) you provide clear
|
||||
# attribution to UC Berkeley, including a link to http://ai.berkeley.edu.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Attribution Information: The Pacman AI projects were developed at UC Berkeley.
|
||||
# The core projects and autograders were primarily created by John DeNero
|
||||
# (denero@cs.berkeley.edu) and Dan Klein (klein@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
# Student side autograding was added by Brad Miller, Nick Hay, and
|
||||
# Pieter Abbeel (pabbeel@cs.berkeley.edu).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestParser(object):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, path):
|
||||
# save the path to the test file
|
||||
self.path = path
|
||||
|
||||
def removeComments(self, rawlines):
|
||||
# remove any portion of a line following a '#' symbol
|
||||
fixed_lines = []
|
||||
for l in rawlines:
|
||||
idx = l.find('#')
|
||||
if idx == -1:
|
||||
fixed_lines.append(l)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
fixed_lines.append(l[0:idx])
|
||||
return '\n'.join(fixed_lines)
|
||||
|
||||
def parse(self):
|
||||
# read in the test case and remove comments
|
||||
test = {}
|
||||
with open(self.path) as handle:
|
||||
raw_lines = handle.read().split('\n')
|
||||
|
||||
test_text = self.removeComments(raw_lines)
|
||||
test['__raw_lines__'] = raw_lines
|
||||
test['path'] = self.path
|
||||
test['__emit__'] = []
|
||||
lines = test_text.split('\n')
|
||||
i = 0
|
||||
# read a property in each loop cycle
|
||||
while (i < len(lines)):
|
||||
# skip blank lines
|
||||
if re.match(r'\A\s*\Z', lines[i]):
|
||||
test['__emit__'].append(("raw", raw_lines[i]))
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
continue
|
||||
m = re.match(r'\A([^"]*?):\s*"([^"]*)"\s*\Z', lines[i])
|
||||
if m:
|
||||
test[m.group(1)] = m.group(2)
|
||||
test['__emit__'].append(("oneline", m.group(1)))
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
continue
|
||||
m = re.match(r'\A([^"]*?):\s*"""\s*\Z', lines[i])
|
||||
if m:
|
||||
msg = []
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
while (not re.match(r'\A\s*"""\s*\Z', lines[i])):
|
||||
msg.append(raw_lines[i])
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
test[m.group(1)] = '\n'.join(msg)
|
||||
test['__emit__'].append(("multiline", m.group(1)))
|
||||
i += 1
|
||||
continue
|
||||
print('error parsing test file: {}'.format(self.path))
|
||||
sys.exit(1)
|
||||
return test
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def emitTestDict(testDict, handle):
|
||||
for kind, data in testDict['__emit__']:
|
||||
if kind == "raw":
|
||||
handle.write(data + "\n")
|
||||
elif kind == "oneline":
|
||||
handle.write('%s: "%s"\n' % (data, testDict[data]))
|
||||
elif kind == "multiline":
|
||||
handle.write('%s: """\n%s\n"""\n' % (data, testDict[data]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise Exception("Bad __emit__")
|
||||
1
logic/test_cases/CONFIG
Normal file
1
logic/test_cases/CONFIG
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
order: "q1 q2 q3 q4 q5 q6 q7 q8"
|
||||
2
logic/test_cases/q1/CONFIG
Normal file
2
logic/test_cases/q1/CONFIG
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
class: "PassAllTestsQuestion"
|
||||
max_points: "2"
|
||||
3
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence1.solution
Normal file
3
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence1.solution
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
# This is the solution file for test_cases/q1/correctSentence1.test.
|
||||
# The result of evaluating the test must equal the below when cast to a string.
|
||||
result: "((A | B) & (~A <=> (~B | C)) & (~A | ~B | C))"
|
||||
9
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence1.test
Normal file
9
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence1.test
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
class: "EvalTest"
|
||||
success: "PASS"
|
||||
failure: "NO PASS"
|
||||
|
||||
# A python expression to be evaluated. This expression must return the
|
||||
# same result for the student and instructor's code.
|
||||
|
||||
test: "logicPlan.sentence1()"
|
||||
|
||||
3
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence2.solution
Normal file
3
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence2.solution
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
# This is the solution file for test_cases/q1/correctSentence2.test.
|
||||
# The result of evaluating the test must equal the below when cast to a string.
|
||||
result: "((C <=> (B | D)) & (A >> (~B & ~D)) & (~(B & ~C) >> A) & (~D >> C))"
|
||||
9
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence2.test
Normal file
9
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence2.test
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
class: "EvalTest"
|
||||
success: "PASS"
|
||||
failure: "NO PASS"
|
||||
|
||||
# A python expression to be evaluated. This expression must return the
|
||||
# same result for the student and instructor's code.
|
||||
|
||||
test: "logicPlan.sentence2()"
|
||||
|
||||
3
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence3.solution
Normal file
3
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence3.solution
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
# This is the solution file for test_cases/q1/correctSentence3.test.
|
||||
# The result of evaluating the test must equal the below when cast to a string.
|
||||
result: "((PacmanAlive_1 <=> ((PacmanAlive_0 & ~PacmanKilled_0) | (~PacmanAlive_0 & PacmanBorn_0))) & ~(PacmanAlive_0 & PacmanBorn_0) & PacmanBorn_0)"
|
||||
9
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence3.test
Normal file
9
logic/test_cases/q1/correctSentence3.test
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
class: "EvalTest"
|
||||
success: "PASS"
|
||||
failure: "NO PASS"
|
||||
|
||||
# A python expression to be evaluated. This expression must return the
|
||||
# same result for the student and instructor's code.
|
||||
|
||||
test: "logicPlan.sentence3()"
|
||||
|
||||
3
logic/test_cases/q1/entails.solution
Normal file
3
logic/test_cases/q1/entails.solution
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
# This is the solution file for test_cases/q1/entails.test.
|
||||
# The result of evaluating the test must equal the below when cast to a string.
|
||||
result: "True True False True True False"
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user